问答
发起
提问
文章
攻防
活动
Toggle navigation
首页
(current)
问答
商城
实战攻防技术
活动
摸鱼办
搜索
登录
注册
浅谈Spring Security身份验证绕过漏洞(CVE-2023-34034)
漏洞分析
Spring官方发布了CVE-2023-34034,当Spring Security使用**作为匹配模式时,在SpringSecurity与SpringWebFlux之间会发生模式不匹配,最终可能导致身份认证绕过。
0x00 前言 ======= 前段时间,Spring官方发布了Spring Framework 身份认证绕过漏洞(CVE-2023-20860),当Spring Security使用mvcRequestMatcher配置并将`**`作为匹配模式时,在Spring Security 和 Spring MVC 之间会发生模式不匹配,最终可能导致身份认证绕过。 漏洞原理也比较简单,主要是mvcRequestMatcher的问题。主要是其在在比对用户配置的权限pattern与请求path是否一致时,与Spring MVC的方式存在差异(mvcRequestMatcher在调用PathPattern的match方法之前没有判断pattern是否以`/`开头,如果不是的话进行补全),导致了某些场景下存在权限绕过。 具体分析可见https://forum.butian.net/share/2199 0x01 漏洞描述 ========= 主要是SpringSecurity与SpringWebFlux之间的差异导致的绕过问题:  1.1 影响版本 -------- Spring Security: - 6.1.0 to 6.1.1 - 6.0.0 to 6.0.4 - 5.8.0 to 5.8.4 - 5.7.0 to 5.7.9 - 5.6.0 to 5.6.11 0x02 原理分析 ========= 漏洞的产生主要在在Spring WebFlux 和 Spring MVC 之间模式不匹配。对比两者的解析过程: 2.1 SpringSecurity对Spring WebFlux的支持 ------------------------------------ 首先看看SpringSecurity是怎么支持Spring WebFlux的。 SpringSecurity对WebFlux的支持主要依赖于 `WebFilter`。 具体可以参考https://springdoc.cn/spring-security/reactive/configuration/webflux.html 首先创建一个配置类来定义安全规则。使用`@EnableWebFluxSecurity`注解启用WebFlux安全配置,并通过实现`SecurityFilterChain`来定义安全规则链。然后使用`ServerHttpSecurity`配置类来定义授权规则。通过`authorizeExchange()`方法来为不同的请求路径和HTTP方法定义授权要求。例如下面的例子: ```Java @EnableWebFluxSecurity public class SecurityConfig { @Bean public SecurityWebFilterChain securityWebFilterChain(ServerHttpSecurity http) { return http .authorizeExchange() .pathMatchers("/public/**").permitAll() .pathMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("ADMIN") .anyExchange().authenticated() .and() .build(); } } ``` 使用`pathMatchers`来定义不同的请求路径模式,并使用相应的权限规则。例如,`/public/`路径模式允许所有用户访问,`/admin/`路径模式要求用户具有"ADMIN"角色,而对于其他任意请求路径,则要求用户进行身份验证。 2.2 Spring WebFlux解析过程 ---------------------- 在Spring WebFlux中,具体的解析过程可以参考https://forum.butian.net/share/2317 核心是调用org.springframework.web.reactive.result.condition.PatternsRequestCondition#getMatchingPatterns方法进行相关的匹配: 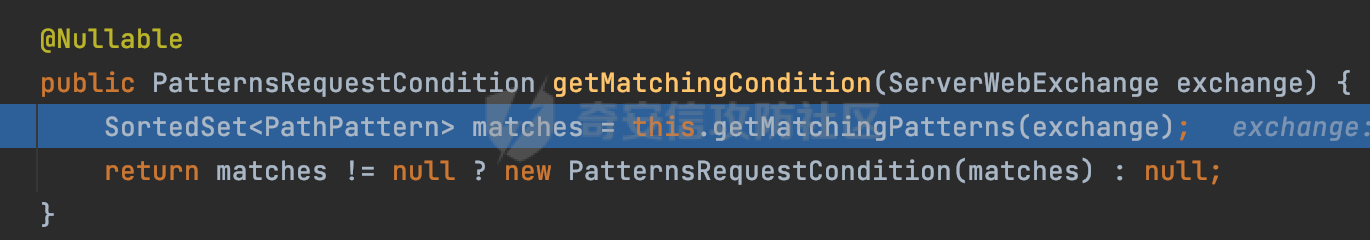 这里首先会从exchange对象中获取请求的路径信息并赋值给lookupPath,然后通过PathPattern的方式进行路径匹配: 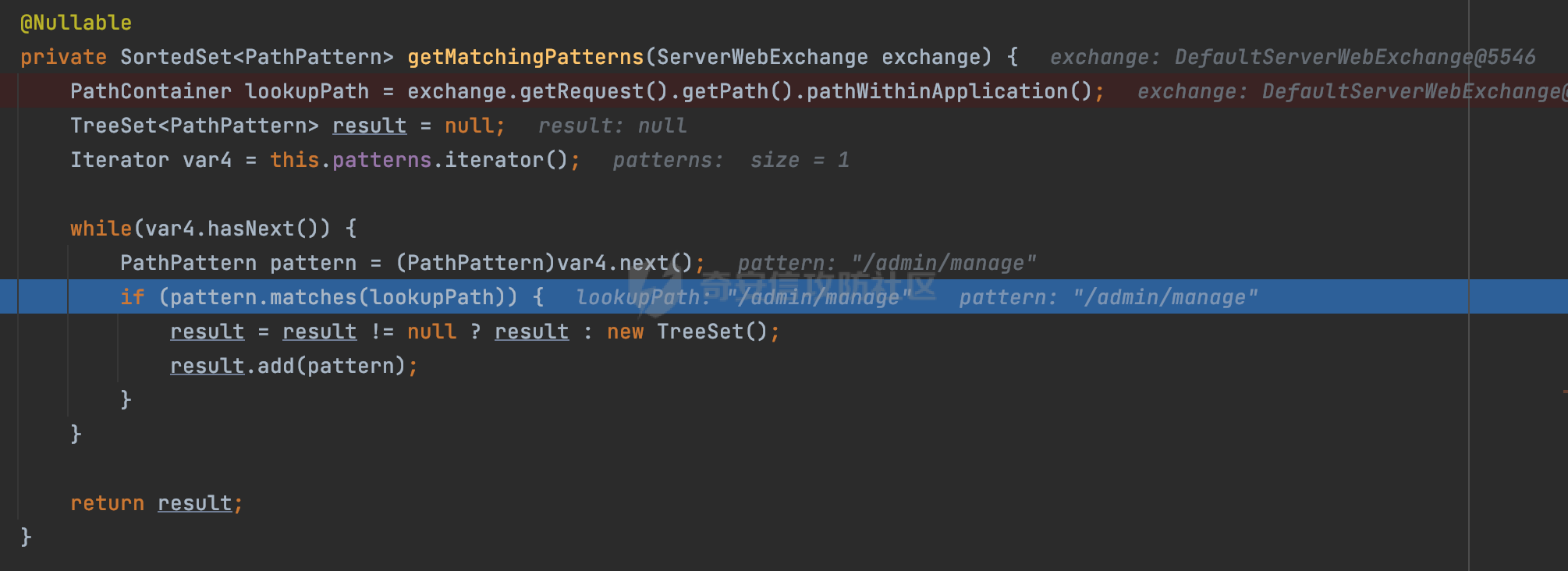 匹配的pattern是从`org.springframework.web.reactive.result.method.RequestMappingInfo`的patternsCondition属性获取的,所以需要看看RequestMappingInfo的实例化过程: 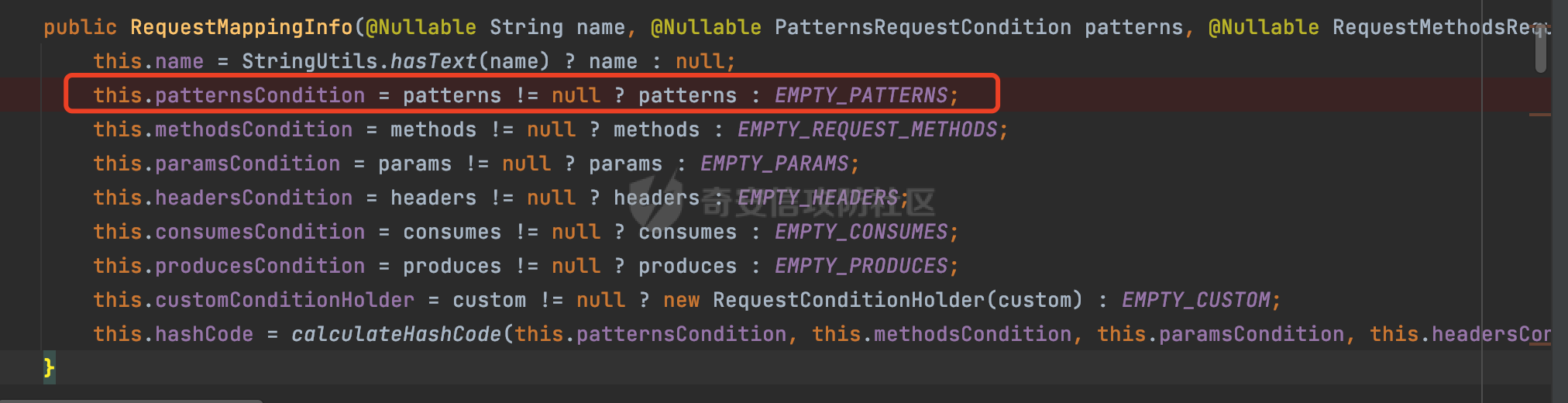 在Spring WebFlux中,`RequestMappingHandlerMapping`是一个用于映射请求到处理方法的处理器映射器。它负责确定给定请求的处理方法,并返回与该请求最匹配的映射信息。 而`getMappingForMethod`方法是`RequestMappingHandlerMapping`类中的一个方法,其作用是为给定的处理方法(`HandlerMethod`)获取与之匹配的请求映射(`RequestMappingInfo`): 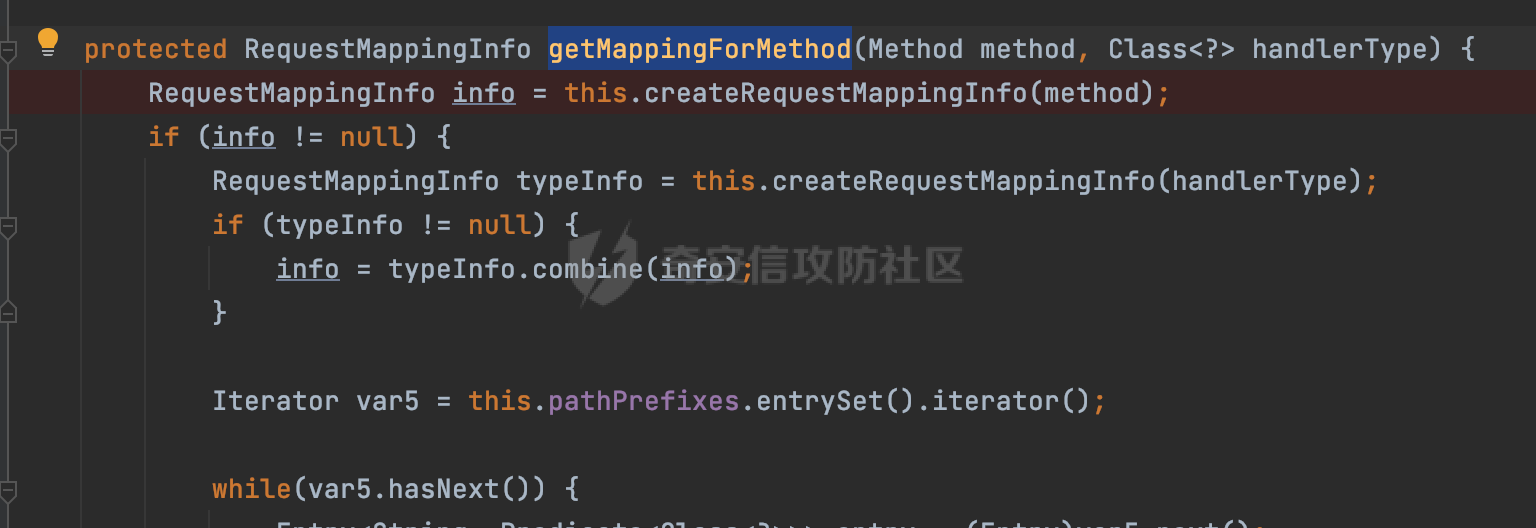 首先调用`AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation`方法获取`element`上的`RequestMapping`注解。这个注解可以用于定义请求路径、请求方法、请求参数等信息。最后根据获取到的`RequestMapping`注解和自定义条件,调用`createRequestMappingInfo`方法创建一个完整的请求映射信息(`RequestMappingInfo`)对象,并返回: 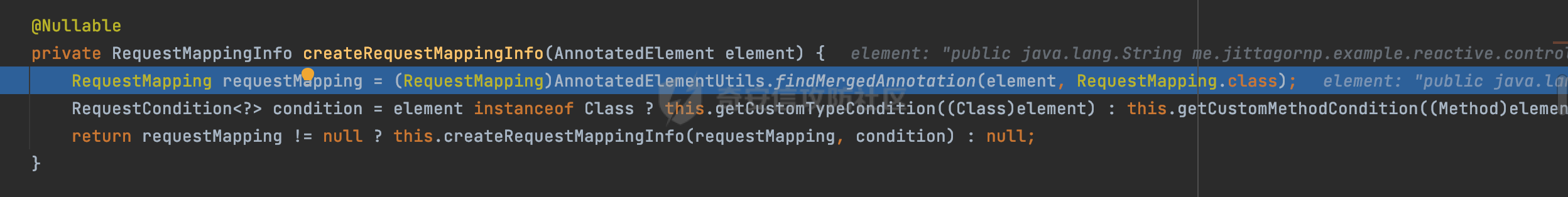 继续跟进具体的过程,调用`builder.options(this.config).build()`方法,使用提供的配置(`this.config`)构建并返回最终的请求映射信息(`RequestMappingInfo`)对象: 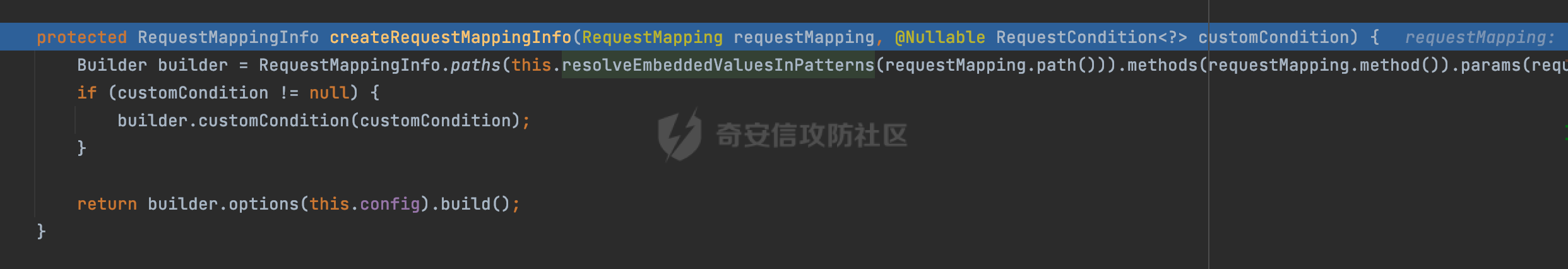 这里可以看到对RequestMappingInfo进行了实例化,通过包括了前面提到的PatternsRequestCondition的处理: 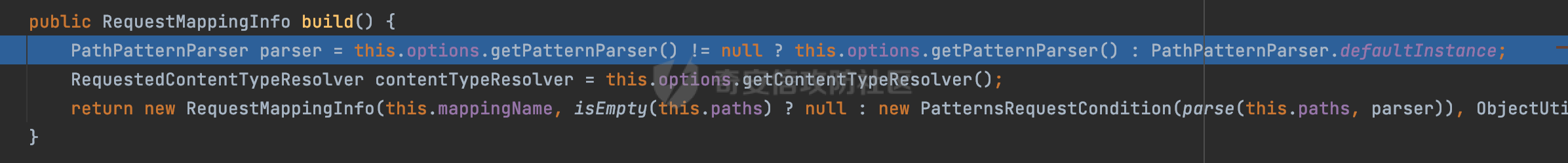 跟进parse方法,可以看到这里回到patterns进行处理,如果不是以`/`开头的话,会进行补全: 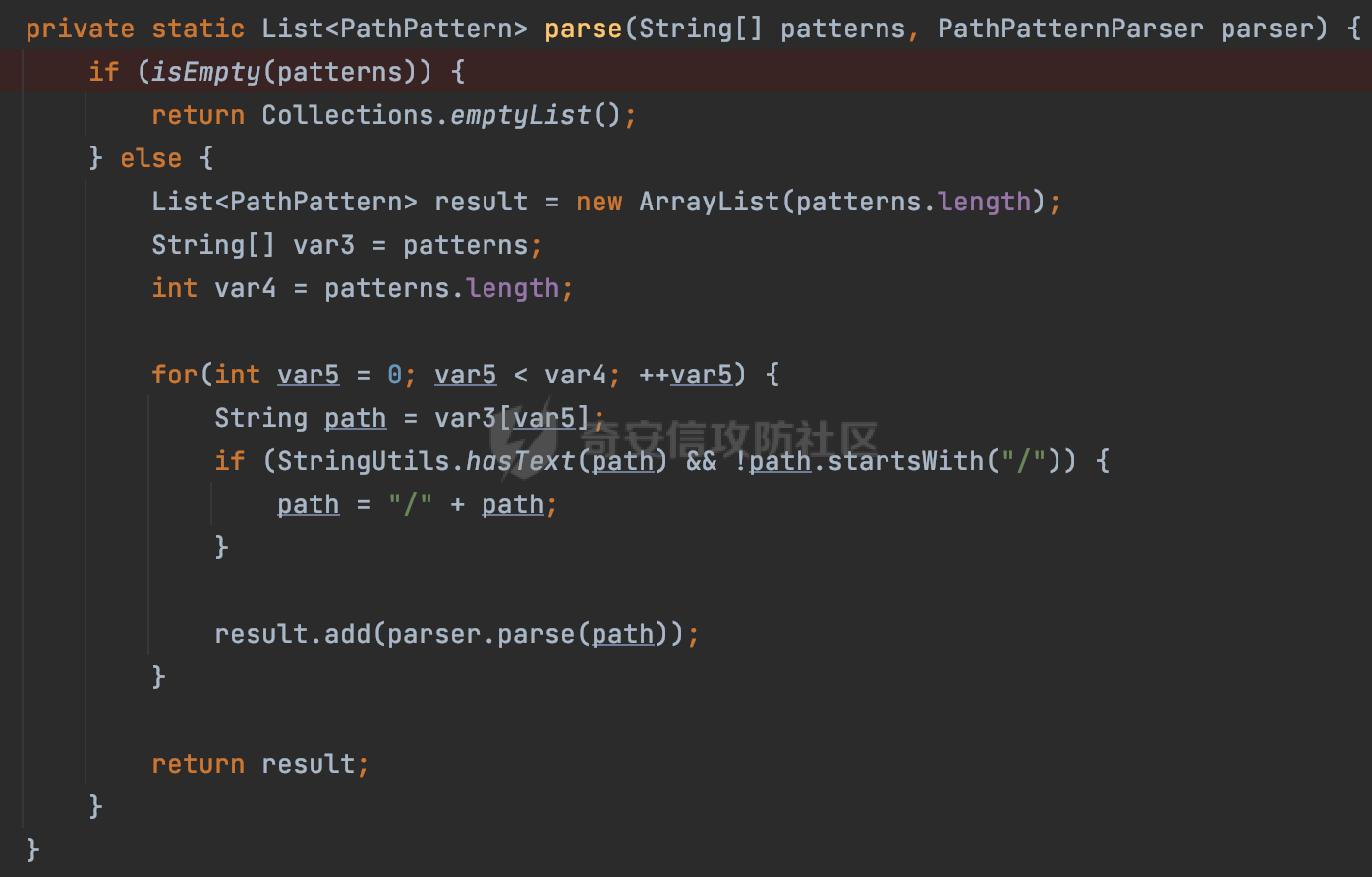 也就是说跟Spring MVC一样,对于类似如下的Controller,同样可以正常解析: ```Java @RequestMapping("admin") public class AdminController { @RequestMapping("/page") public String manage() { return "admin page"; } } ``` 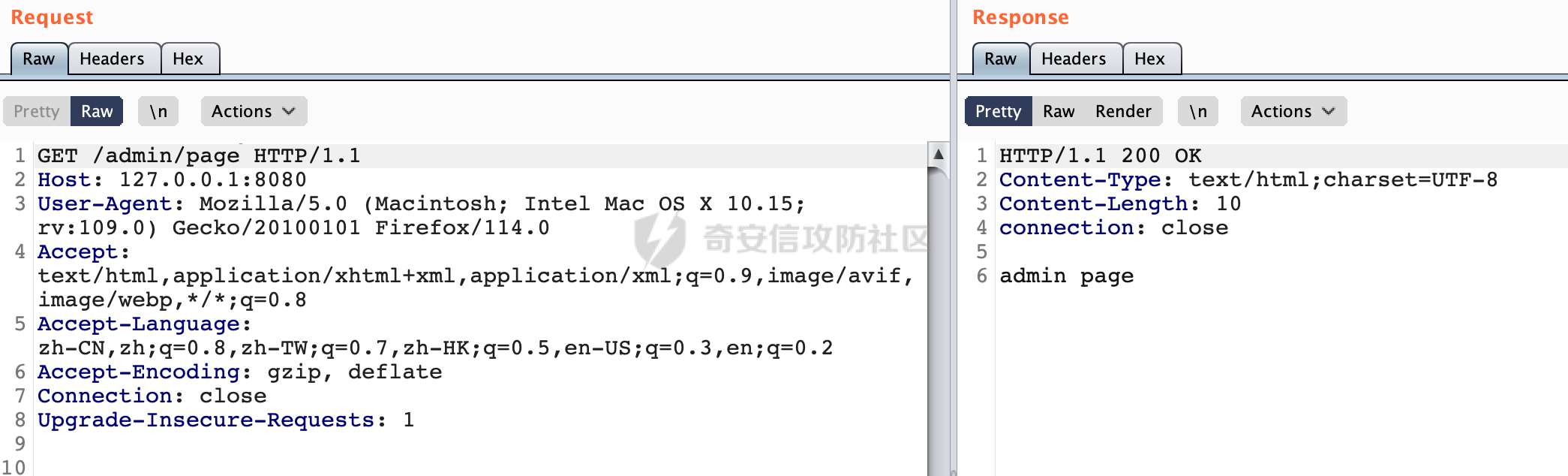 2.3 pathMatchers解析过程 -------------------- 以spring-security-web-5.7.8为例,查看具体的解析过程: 在SpringSecurity中,对于Spring WebFlux,可以使用`pathMatchers`来实现基于请求路径进行权限配置的功能。 查看pathMatchers的实现,可以看到这里跟PathPatternParserServerWebExchangeMatcher有关: 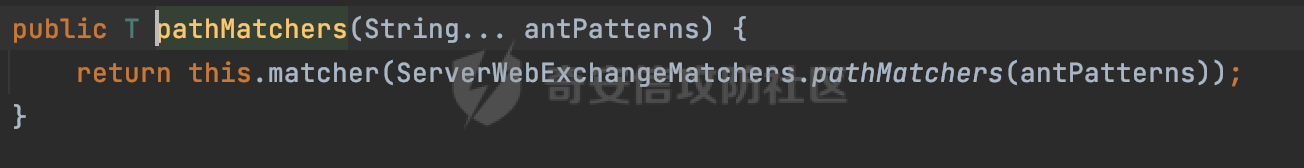 其会根据用户配置创建基于路径匹配的 `ServerWebExchangeMatcher` 对象。首先创建一个空的 `matchers` 列表,用于存储创建的 `PathPatternParserServerWebExchangeMatcher` 对象。匹配请求路径的功能是由 PathPatterParserServerWebExchangeMatcher 来实现的。其会拦截请求路径,并且提取请求路径的参数。遍历传入的 `patterns` 数组,并对于每个路径模式,创建一个 `PathPatternParserServerWebExchangeMatcher` 对象,并传入该模式和请求方法,然后添加到`matchers` 列表中:  查看`PathPatternParserServerWebExchangeMatcher`的实例化过程,其中传入的pattern属性会调用`DEFAULT_PATTERN_PARSER.parse`进行处理: 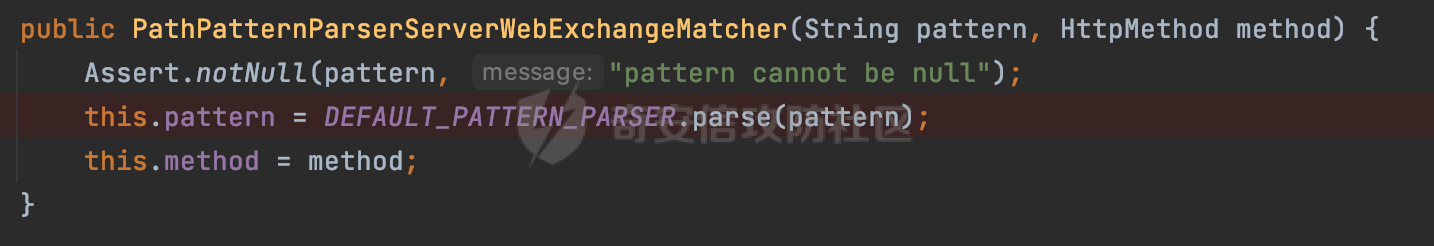 实际上会调用`org.springframework.web.util.pattern.InternalPathPatternParser#parser`进行处理:  查看具体的处理过程: 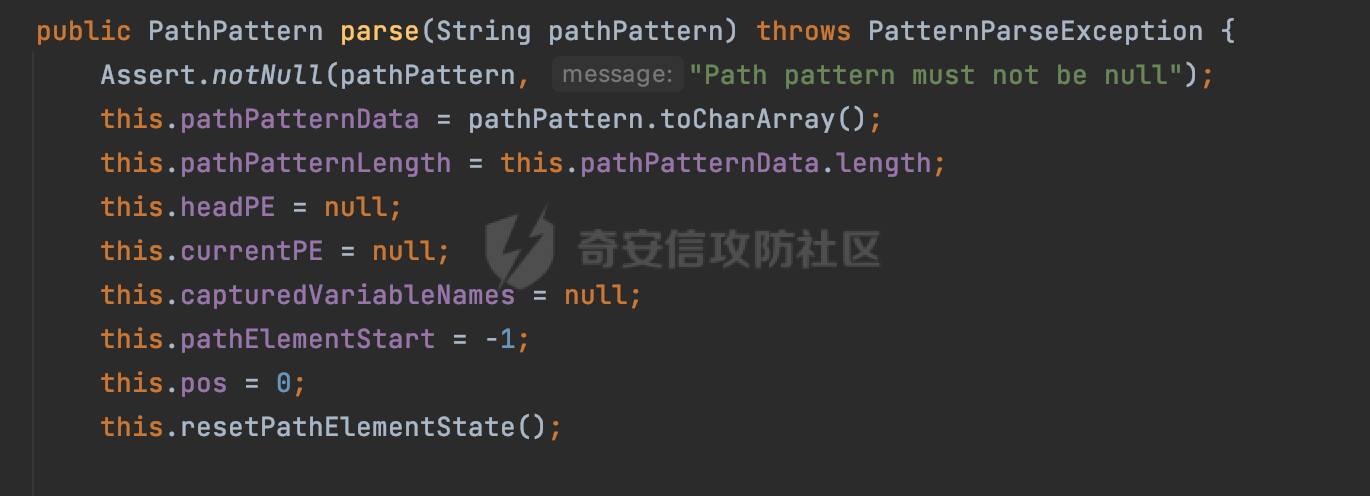 首先遍历路径模式字符串的每个字符,在遍历过程中,首先检查是否遇到路径分隔符(`separator`),如果是,则创建对应的 `SeparatorPathElement` 或 `WildcardTheRestPathElement` 并添加到解析结果中: 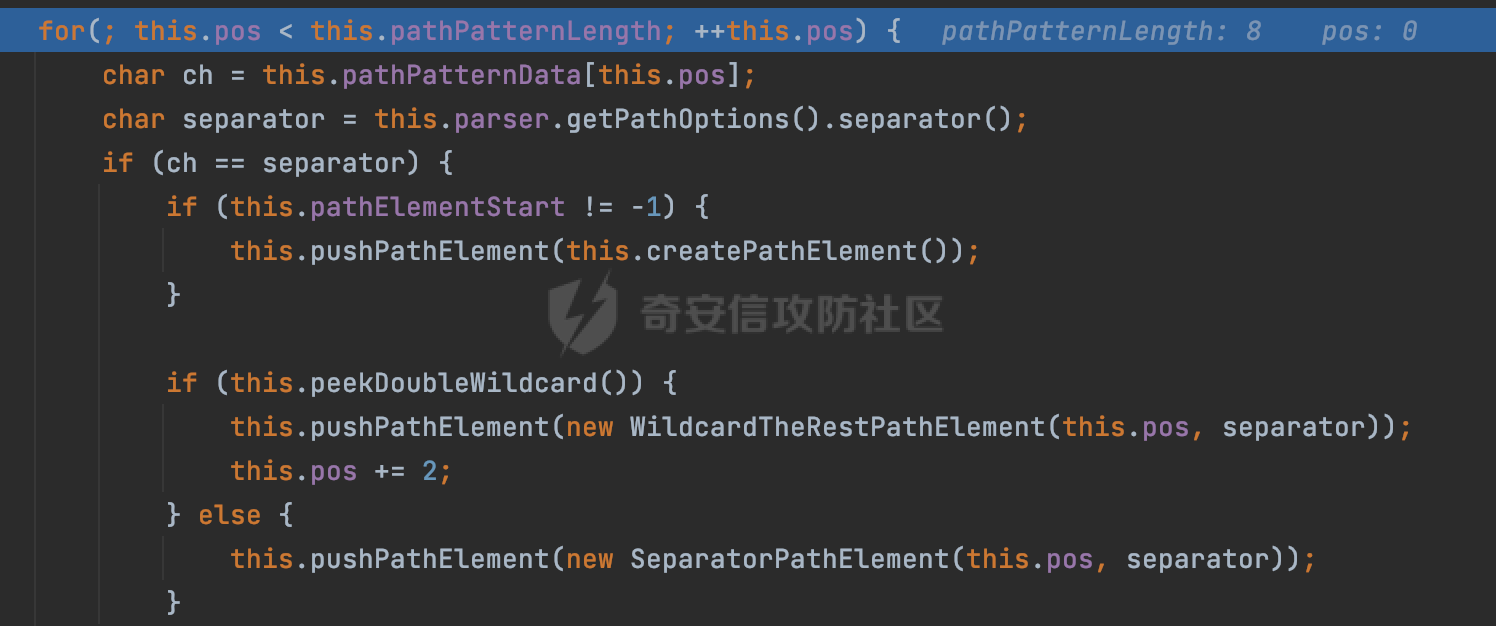 然后是对一些特殊字符的处理,主要包括`?{}:*`,以`:` 字符为例,其表示变量捕获的正则表达式结束,会进行相应的状态更新: 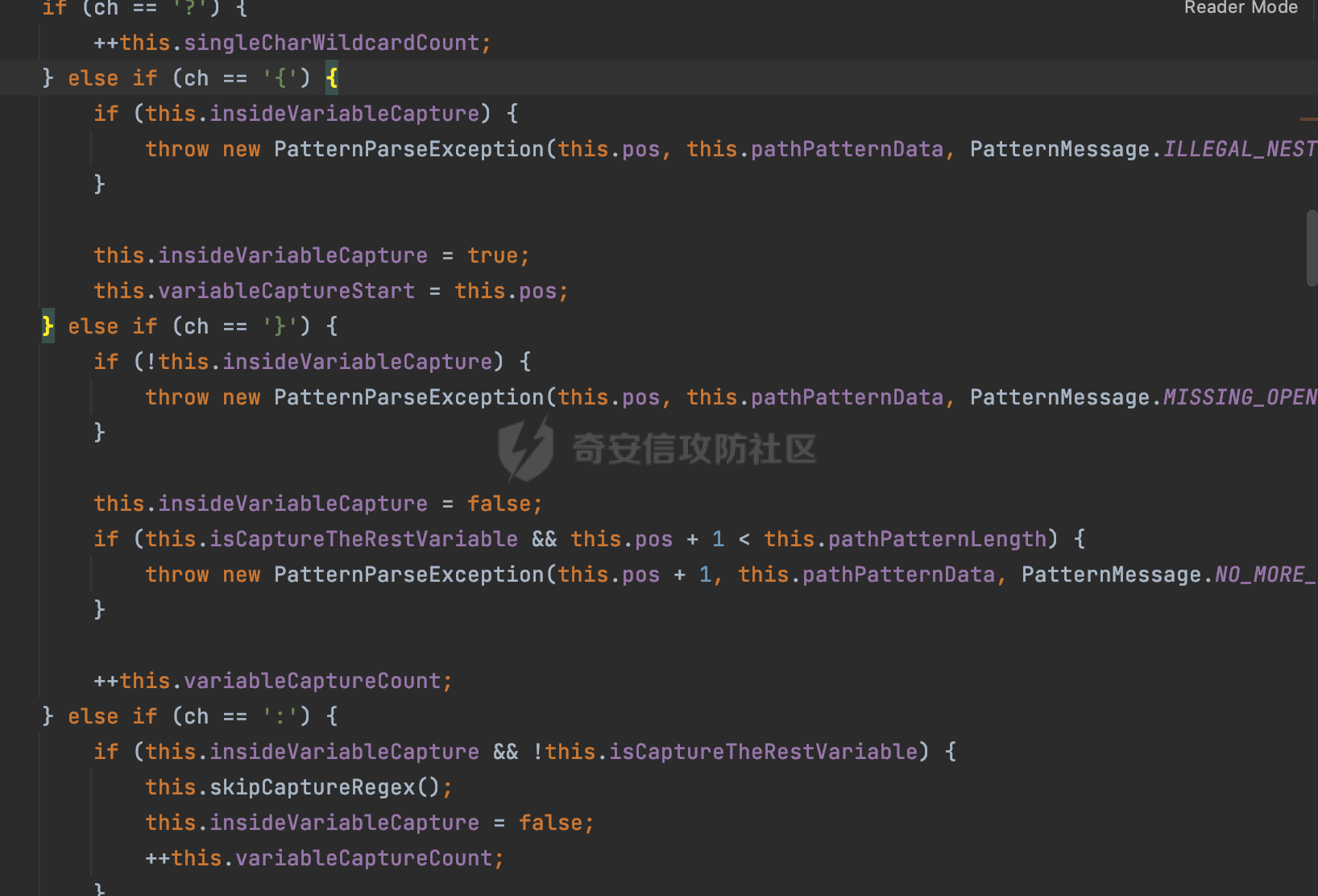 如果处于变量捕获状态,则根据规则检查字符的合法性,并抛出对应的异常:  遍历完成后,将最后一个路径元素添加到解析结果中。并使用解析得到的路径模式字符串、解析器和解析结果创建并返回 `PathPattern` 对象,用于后续的路径匹配和处理:  **整个过程中并没有判断pattern是否以`/`开头,如果不是的话进行补全**。所以这里可能会存在跟CVE-2023-20860类似的问题。 当请求对应的path时,Spring Security会遍历前面封装好的安全配置,进行匹配: 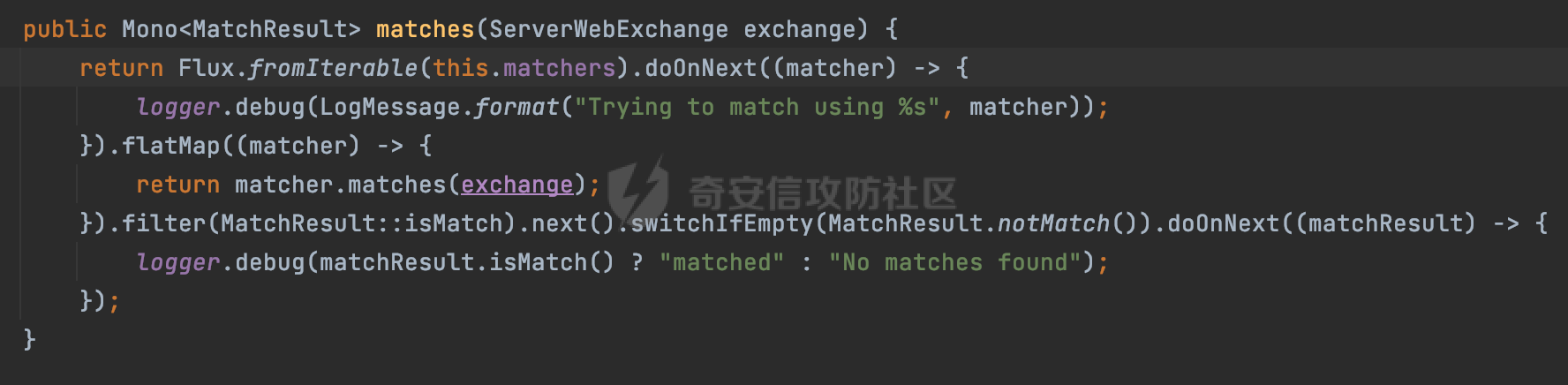 接下来查看PathPatternParserServerWebExchangeMatcher的matches方法,该方法用来用来判断请求是否匹配。这里实际上也是使用的PathPattern进行解析,也就是说SpringSecurity在解析时跟Spring WebFlux的路径解析模式是一致的。 首先通过exchange使用 `getRequest()` 方法获取 `ServerHttpRequest` 对象,然后再通过`getPath()` 方法获取请求路径,然后获取当前请求的方法,判断请求方法与当前规则是否一致: 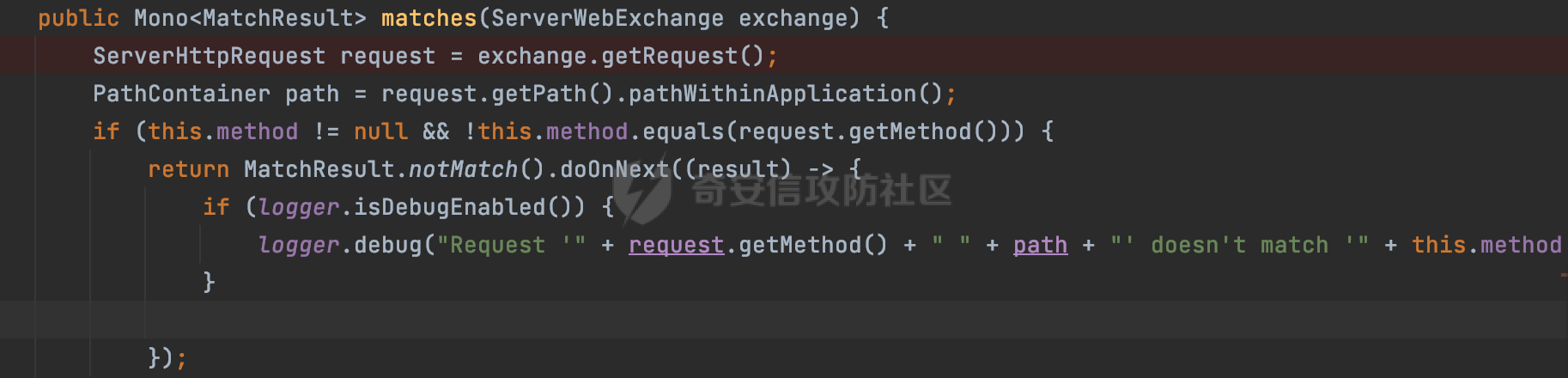 如果请求方法匹配或者没有指定请求方法,会调用 `PathPattern` 对象的 `matches` 方法,将当前请求的路径和请求方法传递给路径模式对象,进行路径匹配判断,如果匹配失败,则返回一个不匹配的结果,并在日志中记录对应的信息: 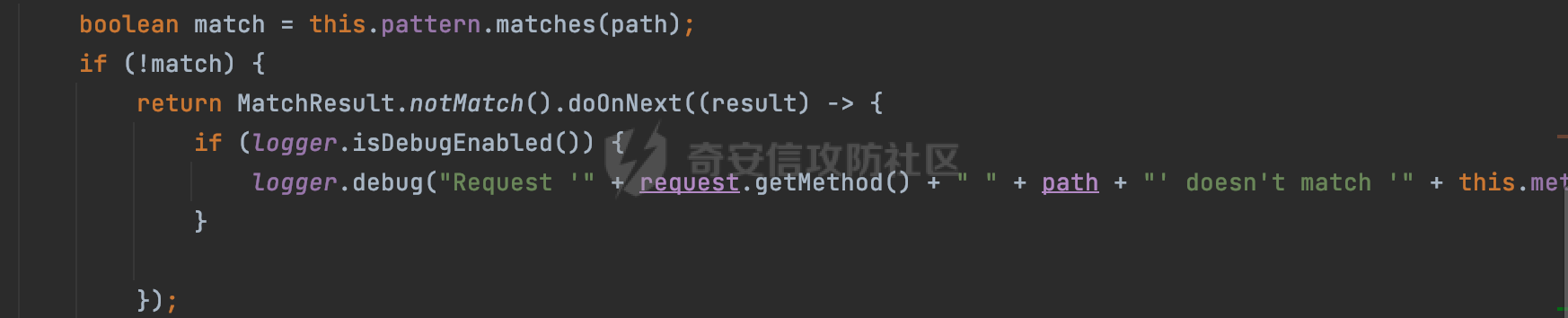 如果路径匹配成功,则使用当前的路径模式 (`pattern`) 提取路径变量,并将路径变量保存在 `pathVariables` 中: 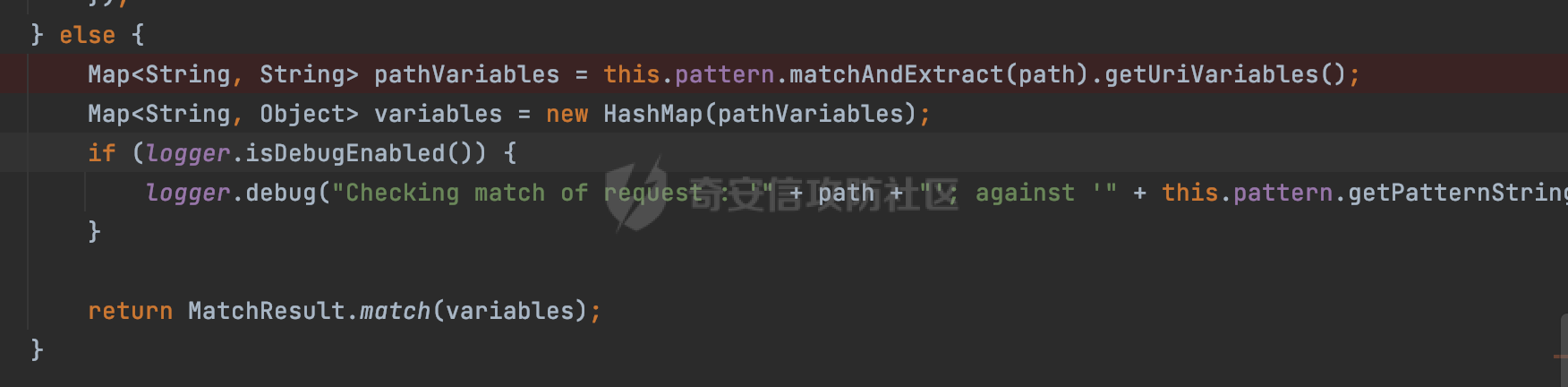 最终返回匹配的结果供后续权限校验使用。 0x03 漏洞复现 ========= 假设当前配置类的安全规则如下,对于admin路径下的资源要求用户具有"UPDATE\_USER"权限(只有admin用户登陆才会具有该权限),而对于其他任意请求路径,则要求用户进行身份验证。: ```Java @EnableWebFluxSecurity public class SecurityConfig { @Bean public SecurityWebFilterChain securityWebFilterChain(final ServerHttpSecurity http) { return http .csrf().disable() .authorizeExchange() .pathMatchers("/", "/login", "/logout").permitAll() .pathMatchers("admin/**").hasAuthority("UPDATE_USER") .anyExchange().authenticated() .and() .formLogin() .loginPage("/login") .and() .logout() .logoutUrl("/logout") .requiresLogout(ServerWebExchangeMatchers.pathMatchers(HttpMethod.GET, "/logout")) .and() .build(); } @Bean public ReactiveUserDetailsService reactiveUserDetailsService(final PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder) { return username -> { log.debug("login with username => {}", username); UserDetails user; switch (username) { case "admin": { user = User.withUsername(username) .password(passwordEncoder.encode("password")) .authorities( () -> "CREATE_USER", () -> "UPDATE_USER", () -> "DELETE_USER", () -> "RESET_USER_PASSWORD" ) .build(); break; } case "supervisor": { user = User.withUsername(username) .password(passwordEncoder.encode("password")) .authorities( () -> "RESET_USER_PASSWORD" ) .build(); break; } default: { user = User.withUsername(username) .password(passwordEncoder.encode("password")) .authorities(Collections.emptyList()) .build(); } } return Mono.just(user); }; } @Bean public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() { return new BCryptPasswordEncoder(); } } ``` 对应admin目录的Controller资源如下: ```Java @RestController @RequestMapping("/admin") public class AdminController { @GetMapping("/page") public String manage() { return "admin page"; } } ``` 根据前面的分析,当对应的配置没有以`/`开头时,会因为解析差异导致权限绕过的问题。 根据PathPattern的matches的调用,这里会根据PathPattern的链式节点中对应的PathElement的matches方法逐个进行匹配,当安全规则的pattern为`admin/*`时,此时第一个Element是admin,对应LiteralPathElement#matches解析: 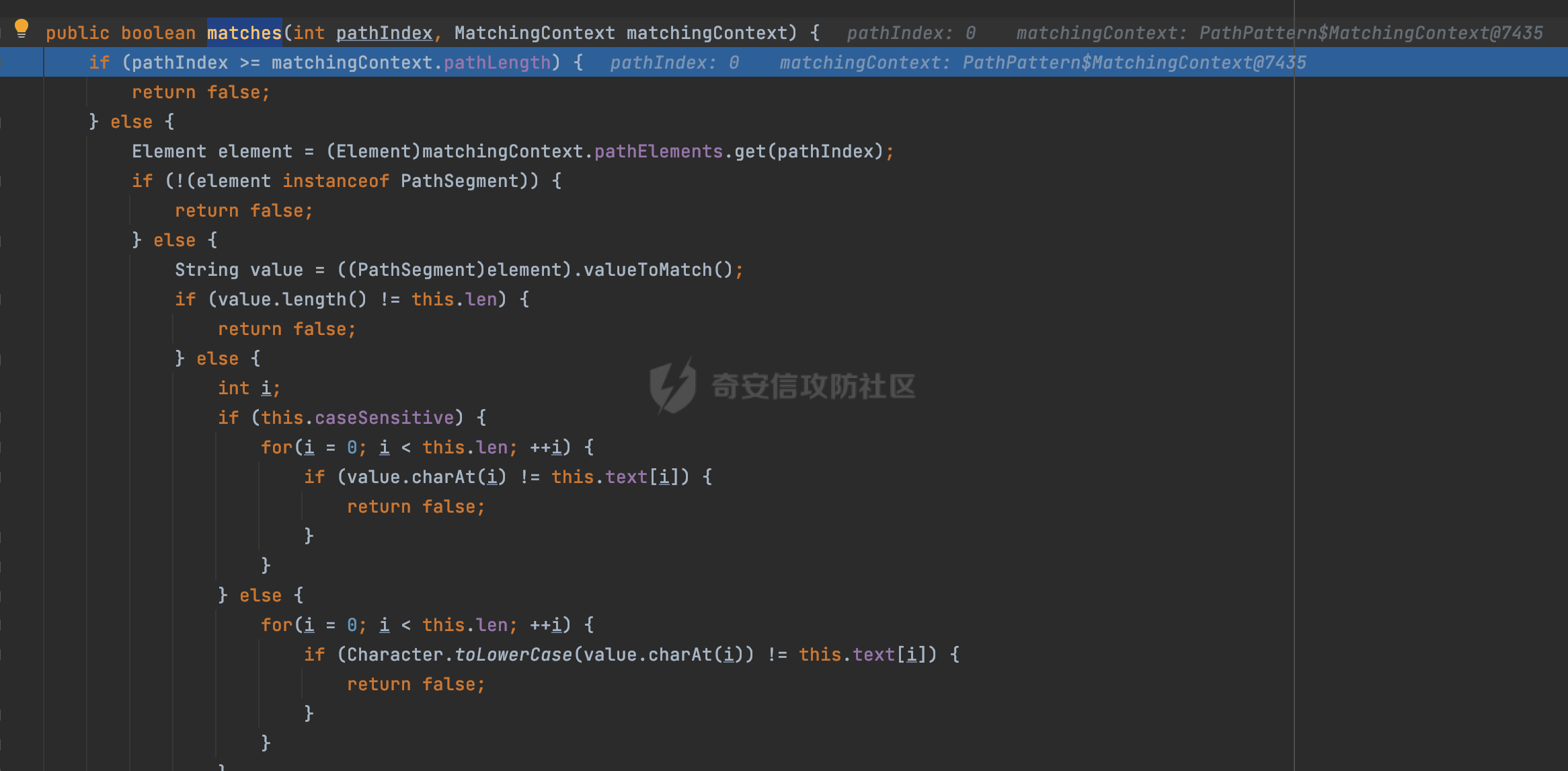 此时会获取path的第一个Element(如果访问的path是/admin/index,那么第一个Element是`/`): 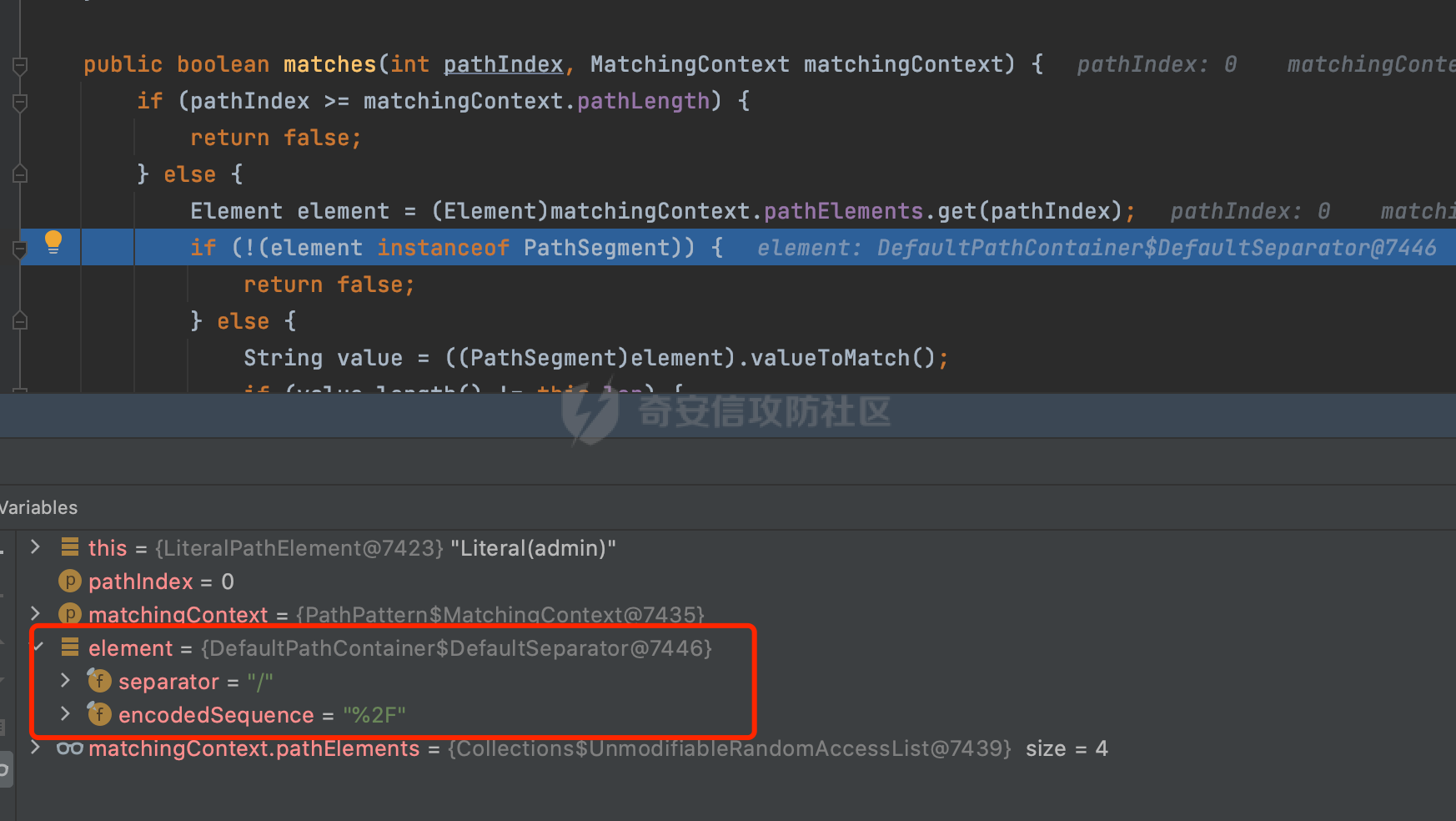 而`/`明显不是PathSegment的实例,此时匹配失败会返回false,但是Spring WebFlux却能正常解析,导致了绕过。 下面印证前面的猜想,首先以test用户登陆,其是不具有"UPDATE\_USER"权限的: 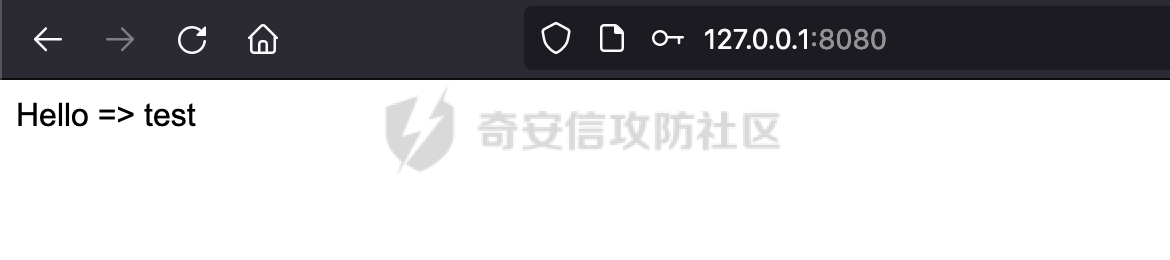 此时访问目标路由,可以看到成功绕过了配置的Spring security规则,以没有"UPDATE\_USER"权限的test用户身份访问了/admin/page: 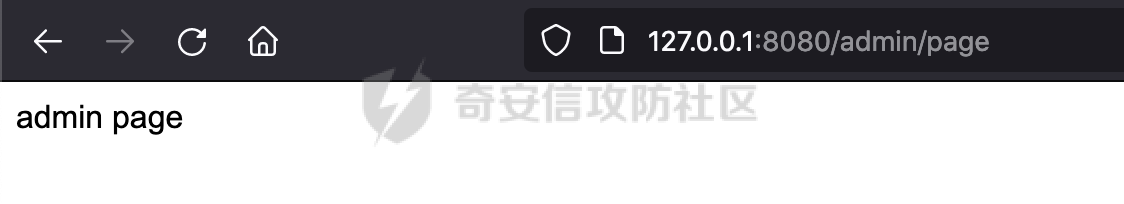 0x04 修复方式 ========= 首先在PathPatternParser中添加了一个新方法,会将传入的pattern初始化成完整 URL 路径匹配的模式。 以spring-web-5.3.29为例,查看具体的实现,可以看到这里主要是对不是以`/`开头的情况进行补全:  在SpringSecurity中,同样进行了类似的操作,以5.8.5版本为例,在`PathPatternParserServerWebExchangeMatcher`的实例化过程中,同样的会调用parse方法进行处理: 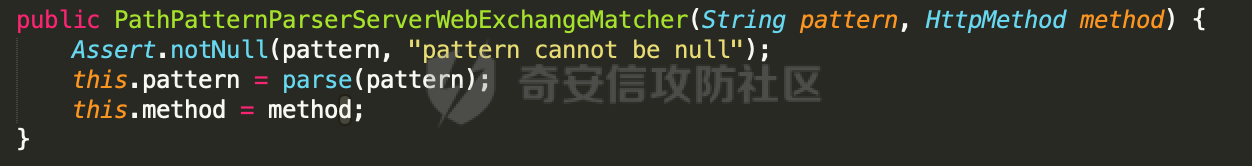 可以看到这里调用了`initFullPathPattern`对不是以`/`开头的pattern情况进行补全,保证两者的解析模式是一致的,避免绕过问题: 
发表于 2023-08-04 09:00:02
阅读 ( 11443 )
分类:
漏洞分析
0 推荐
收藏
0 条评论
请先
登录
后评论
tkswifty
66 篇文章
×
发送私信
请先
登录
后发送私信
×
举报此文章
垃圾广告信息:
广告、推广、测试等内容
违规内容:
色情、暴力、血腥、敏感信息等内容
不友善内容:
人身攻击、挑衅辱骂、恶意行为
其他原因:
请补充说明
举报原因:
×
如果觉得我的文章对您有用,请随意打赏。你的支持将鼓励我继续创作!