问答
发起
提问
文章
攻防
活动
Toggle navigation
首页
(current)
问答
商城
实战攻防技术
活动
摸鱼办
搜索
登录
注册
JOOQ框架常见SQL注入场景
渗透测试
JOOQ是一个ORM框架,利用其生成的Java代码和流畅的API,可以快速构建有类型约束的安全的SQL语句。本文主要介绍该框架常见的SQL注入场景。給代码安全审计提供一定的思路。
0x01 关于JOOQ =========== JOOQ是一个ORM框架,利用其生成的Java代码和流畅的API,可以快速构建有类型约束的安全的SQL语句。其使用与mybatis和Hibernate ORM不同的思路来实现对象关系映射ORM 。  1.1 核心接口 -------- 通过这两个接口可以执行对应的SQL语句: - org.jooq.impl.DSL是生成所有jOOQ对象的主要类。它作为一个静态的工厂去生成数据库表表达式,列表达式,条件表达式和其他查询部分。 - org.jooq.DSLContex可以理解为一个SQL执行器,通过静态方法 `DSL.using`,可以获取一个 `DSLContext` 实例,此实例抽象了所有对于SQL的操作API,可以通过其提供的API方便的进行SQL操作。 举例说明: ```java public JooqPojo selectByName(String name) { return dslContext.select() .from(jooq) .where(jooq.NAME.eq(name)).fetchAny(r -> r.into(JooqPojo.class)); } ``` 查看SQL执行日志,可以看到jooq已经对name参数进行了参数绑定,避免了SQL注入的问题:  1.2 常见参数绑定方式 ------------ - DSL.param() DSL.param()创建一个绑定变量,该绑定变量的生成方式?与SQL一样。例如如下例子,参数绑定Name: ```Java public JooqPojo selectByName(String name, String content) { return dslContext.select() .from(jooq).where(DSL.field("name").eq(DSL.param(jooq.NAME.getName(),name))).fetchAny(r -> r.into(JooqPojo.class)); } ``` 查看对应的的sql日志,对应的查询已经完成了绑定,避免了SQL注入的风险: 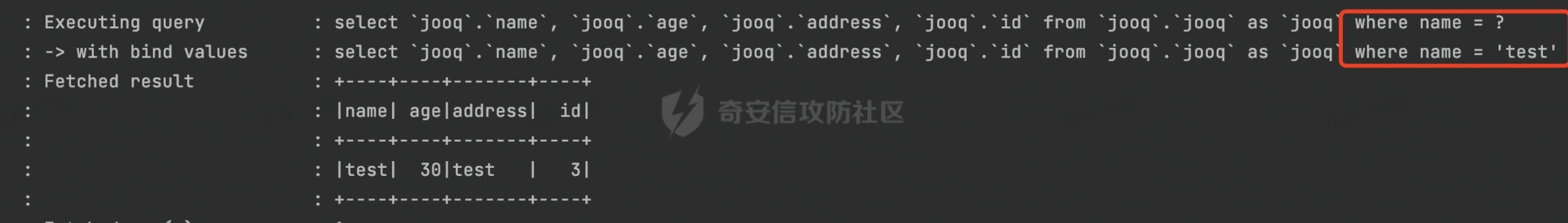 - Object... bindings参数 跟其他框架类似,均支持?和:param的方式进行参数绑定: ```Java dslContext.select().from(jooq).where("name=?",name).fetchAny(r -> r.into(JooqPojo.class)); dslContext.select().from(jooq).where("name=:name",name).fetchAny(r -> r.into(JooqPojo.class)); ``` 对应的SQL执行日志:  除此之外还支持{index}的方式: ```Java dslContext.select().from(jooq).where("name={0} and address={1}",name,content).fetchAny(r -> r.into(JooqPojo.class)) ``` 对应的SQL执行日志:  - 表达式自身处理 例如mybatis里常见的like查询,经常会出现SQL注入问题,jooq提供的表达式已经进行了相应的处理,使用也比较方便: ```Java result=result.and(jooq.NAME.like("%" + name + "%")); ``` 查看对应的日志已经进行了参数绑定:  0x02 常见SQL注入场景 ============== 2.1 Plain SQL API ----------------- 在一定的程度上,JOOQ确实解决了大部分场景的SQL注入问题。 但是jOOQ并不支持每个数据库中的所有SQL功能,JOOQ还存在很多字符串sql拼接的API,例如如下的`and(String s)`,可以看到JOOQ給对应的API标记了@PlainSQL注解,注释里也提醒了会存在SQL注入风险: ```Java /** * Combine the currently assembled conditions with another one using the * {@link Operator#AND} operator and proceed to the next step. * <p> * <b>NOTE</b>: When inserting plain SQL into jOOQ objects, you must * guarantee syntax integrity. You may also create the possibility of * malicious SQL injection. Be sure to properly use bind variables and/or * escape literals when concatenated into SQL clauses! * * @see DSL#condition(SQL) * @see SQL */ @Support @PlainSQL SelectConditionStep<R> and(SQL sql); ``` 举个例子,这里and()用户可控,且可以执行Plain SQL,那么直接在content参数写入恶意sql语句即可: ```Java public JooqPojo selectByName(String name,String content) { return dslContext.select() .from(jooq) .where(jooq.NAME.eq(name)).and(content).fetchAny(r -> r.into(JooqPojo.class)); } ``` 这里直接使用updatexml尝试报错注入,成功获取数据库用户名:  对于Plain SQL的情况,官方文档也进行了说明:  下面再列举一些常见的场景: ### 2.1.1 执行任意 SQL、函数和存储过程 在查询where 子句中经常需要包含执行任意 SQL、函数和存储过程的需求。通过condition可以满足该需求。 - org.jooq.Condition条件表达式 在Condition接口中提供了如下几个方法执行plain SQL: ```Java and(String) // Combine conditions with AND. Convenience for adding plain SQL to the right-hand side and(String, Object...) // Combine conditions with AND. Convenience for adding plain SQL to the right-hand side and(String, QueryPart...) // Combine conditions with AND. Convenience for adding plain SQL to the right-hand side or(String) // Combine conditions with OR. Convenience for adding plain SQL to the right-hand side or(String, Object...) // Combine conditions with OR. Convenience for adding plain SQL to the right-hand side or(String, QueryPart...) // Combine conditions with OR. Convenience for adding plain SQL to the right-hand side ``` 例如如下例子: ```Java public Condition condition(String name){ Condition result = DSL.noCondition(); result=result.and("name like '%"+name+"%'"); return result; } ``` 在service层进行对应的调用: ```Java return dslContext.select().from(jooq).where(condition(name)).fetchAny(r -> r.into(JooqPojo.class)); ``` 这里直接将name进行SQL拼接,存在SQL注入的风险(报错注入验证): 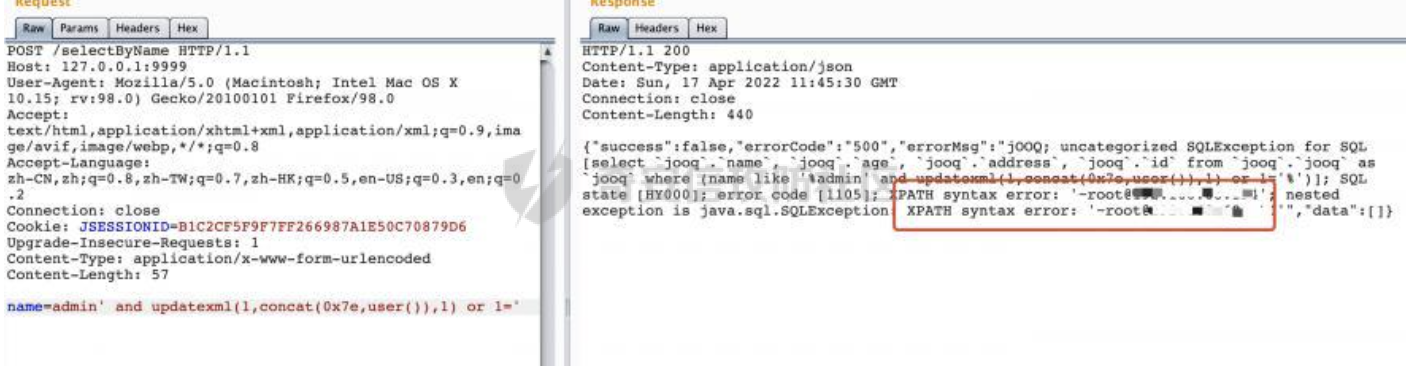 正确的做法应该是对对应的参数进行预编译处理: ```Java result=result.and("name like CONCAT('%',?,'%')",name); ``` ```Java result=result.and(jooq.NAME.like("%" + name + "%")); ``` - DSL.condition() 可以通过DSL创建condition,然后在where子句中执行。例如需要执行length()函数,搜索name小于对应长度的记录: ```Java return dslContext.select() .from(jooq).where(DSL.condition("length(name)<"+size)).fetchAny(r -> r.into(JooqPojo.class)); ``` 同样的这里也是直接调用的Plain SQL API: ```Java @Support @PlainSQL public static Condition condition(String sql) { return condition(sql); } ``` 如果size参数是string类型且用户可控的话会存在SQL注入风险(这里执行updatexml报错注入演示):  ### 2.1.2 动态表名 实际业务中往往有动态表名的需求,例如函数接受一个名为"entityType"的参数,并根据该参数查询表`entityType_other_stuff`。使用DSL.table()即可满足类似的需求。 DSL.table()也有很多重载的方法,部分方法是@PlainSQL标注的,使用不当会存在SQL注入风险: ```Java @Support @PlainSQL public static Table<Record> table(String sql) { return table(sql); } ``` Example: 这里直接传入tableName对对应的表进行查询: ```Java public JooqPojo selectByTableName(String tableName) { return dslContext.select() .from(DSL.table(name(tableName))) .limit(0,1).fetchAny(r -> r.into(JooqPojo.class)); } ``` 可以直接在tableName写入恶意SQL,达到SQL注入的效果: 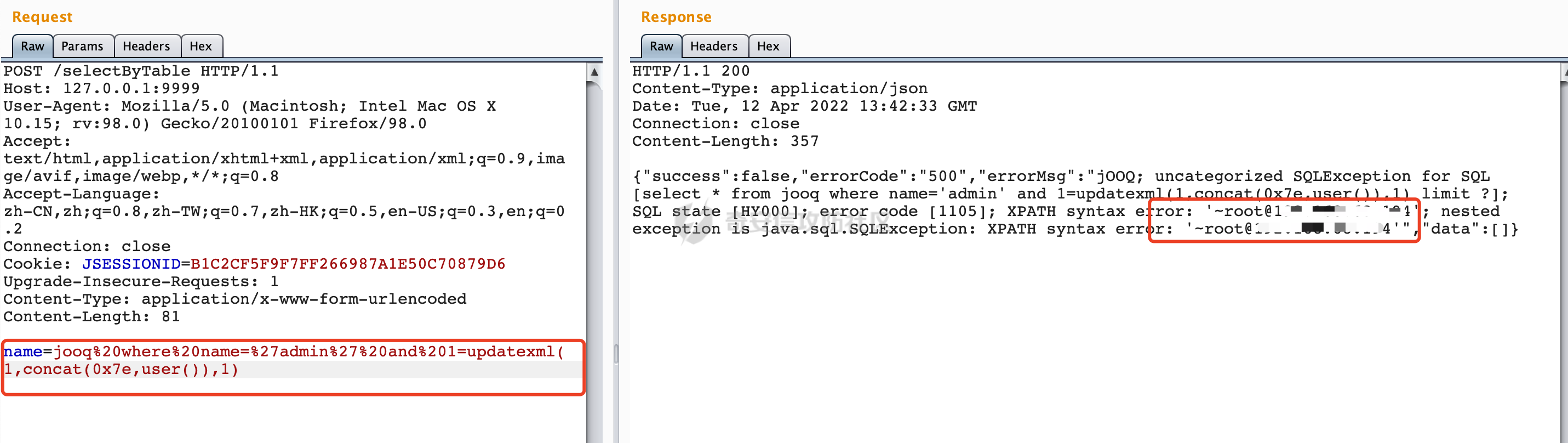 PS:参考官方文档里的https://www.jooq.org/doc/3.16/manual/sql-building/names/ 更为安全的用法是DSL.table(name(tableName)),使用org.jooq.impl.DSL.name进行处理。 同样是上面的例子,修改后具体的查询将tableName用``包裹,此时输入任意内容均会被认为是表名的一部分,从某种程度上避免了SQL注入的风险。 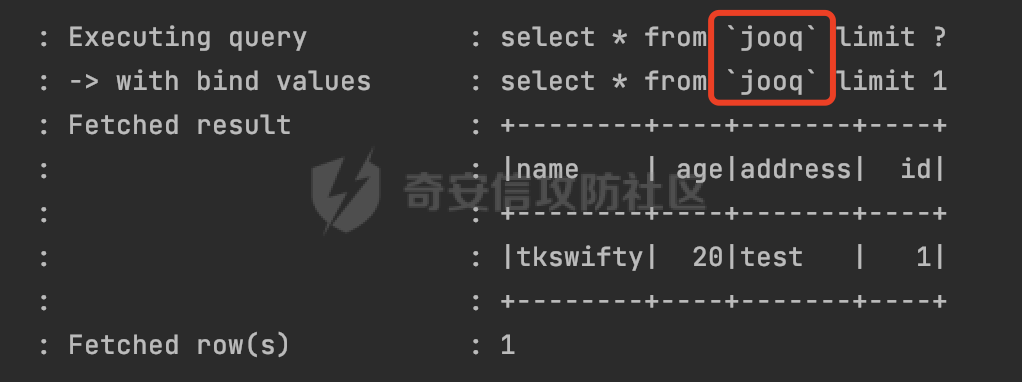 动态列名DSL.field()同理。 ### 2.1.3 直接执行SQL DSLContext/DSL包含了几个API用于执行plain SQL,如果使用不当直接使用了SQL拼接,可能会存在SQL注入的风险: - query - ResultQuery - execute - fetech(等价于resultQuery(...).fetch()) 根据官方文档提供的case可以看到,实际上是直接SQL执行,如果SQL内容用户可控的话,那么可能存在SQL注入风险: ```Java // Create a Query object and execute it: Query query = create.query("DELETE FROM BOOK"); query.execute(); // Create a ResultQuery object and execute it, fetching results: ResultQuery<Record> resultQuery = create.resultQuery("SELECT * FROM BOOK"); Result<Record> result = resultQuery.fetch(); ``` 同样的,可以通过参数绑定来避免对应的问题(类似orderby等动态场景可以考虑过滤输入或者白名单的方式来避免SQL注入): ```Java String sqlTemp="select * from jooq where name ={0}"; return dslContext.resultQuery(sqlTemp,name).fetchAny(r -> r.into(JooqPojo.class)); ``` 除了上面提到的3种场景以外,还有**很多由于使用不当导致SQL注入风险,本质上其实都是@PlainSQL方法的调用**。 0x03 其他 ======= 一般情况下,为了避免错误使用@PlainSQL注解标记的API导致SQL注入问题,可以引入jooq-checker来进行检查: ```XML <dependency> <groupId>org.jooq</groupId> <artifactId>jooq-checker</artifactId> <version>${version}</version> </dependency> ``` 引入依赖后,指定如下Maven编译器配置即可: ```XML <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.3</version> <configuration> <source>1.8</source> <target>1.8</target> <fork>true</fork> <annotationProcessors> <annotationProcessor>org.jooq.checker.PlainSQLChecker</annotationProcessor> </annotationProcessors> <compilerArgs> <arg>-Xbootclasspath/p:1.8</arg> </compilerArgs> </configuration> </plugin> ``` 其中org.jooq.checker.PlainSQLChecker将确保不会编译使用带有@PlainSQL注释的API,并抛出对应的错误: ```Plain java: [Plain SQL usage not allowed at current scope. Use @Allow.PlainSQL.] (Plain SQL usage not allowed at current scope. Use @Allow.PlainSQL.) ``` 如果确实需要使用jOOQ的@PlainSQL API,则可以通过@Allow.PlainSQL对该位置(scope)进行注释,此时即可通过编译: ```Java @Override @Allow.PlainSQL public JooqPojo selectByName(String name,String content) { return dslContext.select() .from(jooq) .where(jooq.NAME.eq(name)).and(content).fetchAny(r -> r.into(JooqPojo.class)); } ``` 也就是说,**在进行代码审计的时候,可以通过检索** **`@Allow.PlainSQ`** **关键字,来查看对应的方法使用是否合理,是否通过** **`?`** **占位符** **进行预编译处理/是否对用户的输入进行安全过滤等** 。 0x04 参考资料 ========= - <https://www.jooq.org/doc/>
发表于 2022-05-06 09:50:24
阅读 ( 10195 )
分类:
代码审计
2 推荐
收藏
0 条评论
请先
登录
后评论
tkswifty
66 篇文章
×
发送私信
请先
登录
后发送私信
×
举报此文章
垃圾广告信息:
广告、推广、测试等内容
违规内容:
色情、暴力、血腥、敏感信息等内容
不友善内容:
人身攻击、挑衅辱骂、恶意行为
其他原因:
请补充说明
举报原因:
×
如果觉得我的文章对您有用,请随意打赏。你的支持将鼓励我继续创作!