问答
发起
提问
文章
攻防
活动
Toggle navigation
首页
(current)
问答
商城
实战攻防技术
活动
摸鱼办
搜索
登录
注册
浅谈SpringWeb请求解析过程
渗透测试
在Java生态中,Spring全家桶是比较常见的。浅谈SpringWeb的请求解析过程。
0x00前言 ====== 在SpringMvc中,**DispatcherServlet**是前端控制器设计模式的实现,提供Spring Web MVC的集中访问点,而且负责职责的分派。主要职责如下: - 文件上传解析,如果请求类型是multipart将通过MultipartResolve进行文件上传解析; - 通过HandlerMapping,将请求映射到处理器(返回一个HandlerExecutionChain,它包括一个处理器,多个HandlerIntercept拦截器) - 通过HandlerAdapter支持多种类型的处理器(HandlerExecutionChain中的处理器); - 通过ViewReslver解析逻辑视图名到具体视图实现; - 本地化解析; - 渲染具体的视图等; - 执行过程中遇到异常将交给HandlerExecutionResolver来解析; 0x01 Spring Web解析过程 =================== 以spring-webmvc 5.3.9为例。当向Spring MVC发送一个请求时,看看具体的处理过程是怎么样的。 当Spring MVC接收到请求时,Servlet容器会调用DispatcherServlet的service方法(方法的实现在其父类FrameworkServlet中定义): 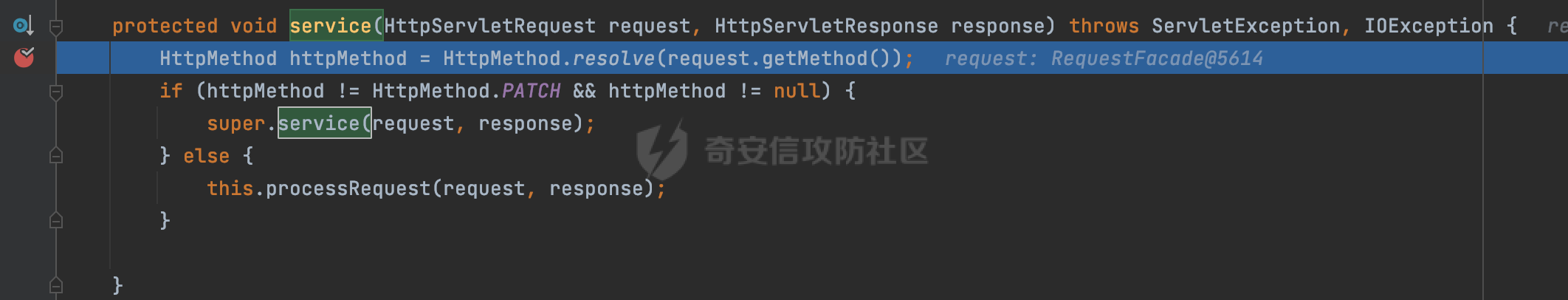 这里首先获取request请求的类型,除了PATCH方法以外都会通过HttpServlet的service方法进行处理: 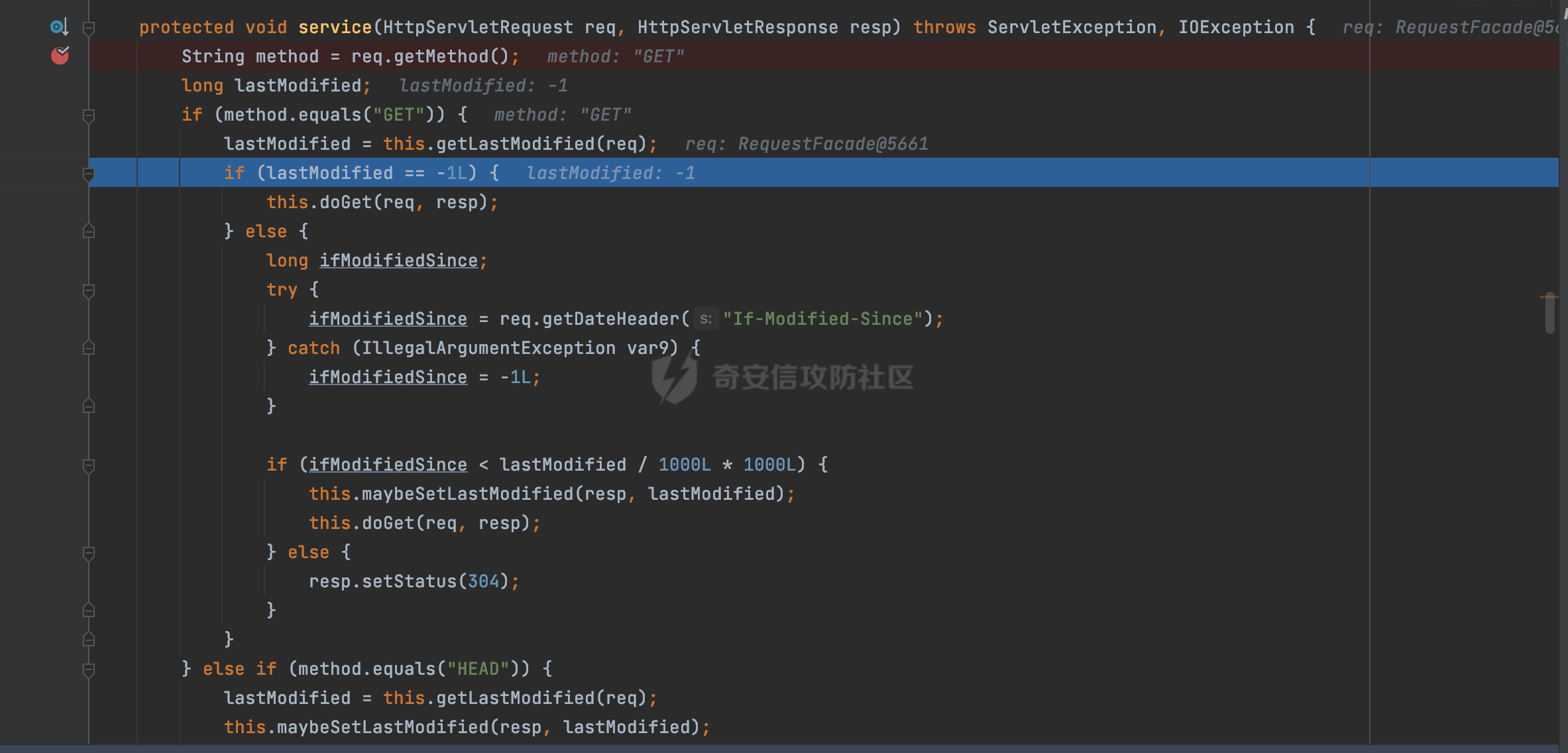 这里实际上是根据不同的请求方法,调用processRequest方法,例如GET请求会调用doGet方法:  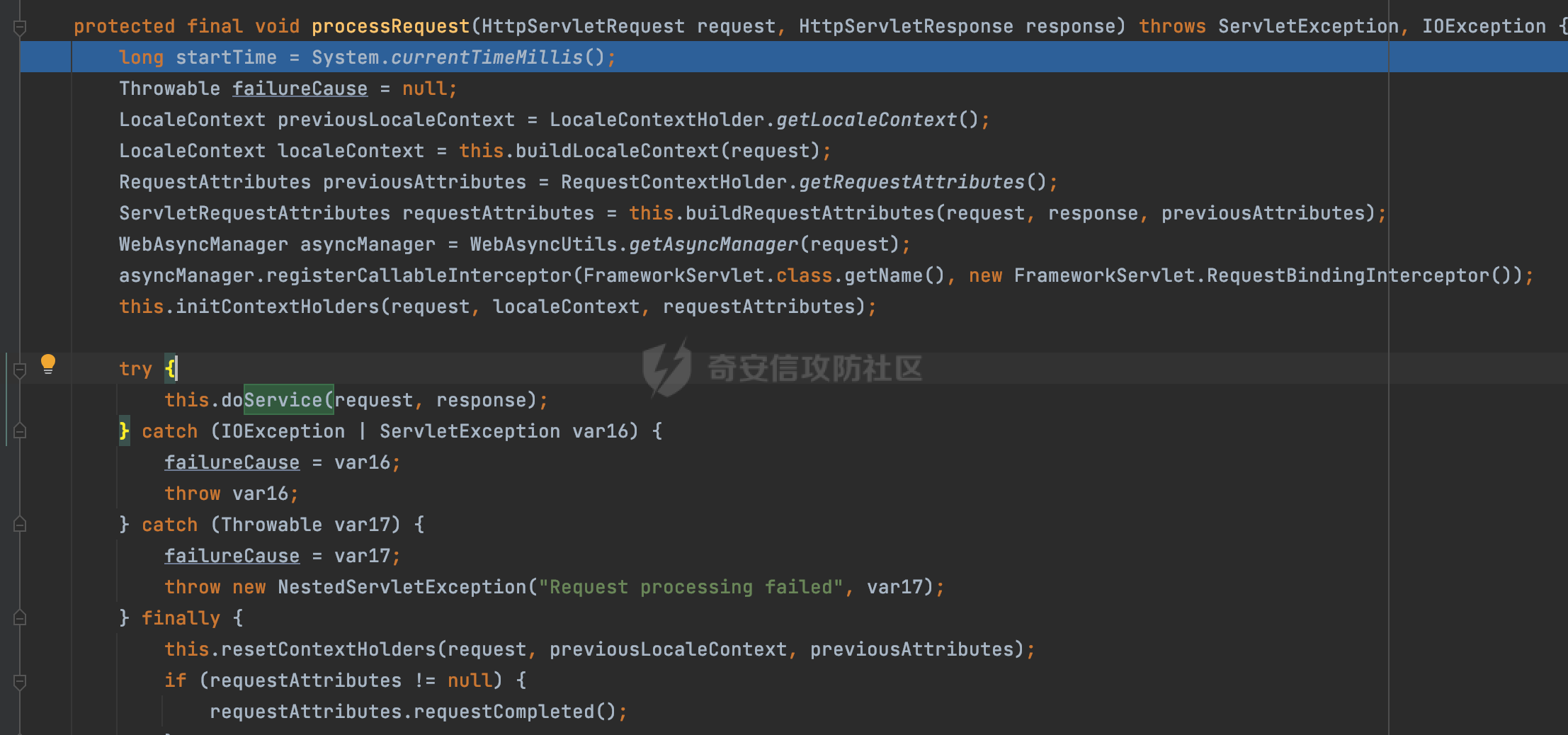 在执行doService方法后,继而调用doDispatch方法处理: 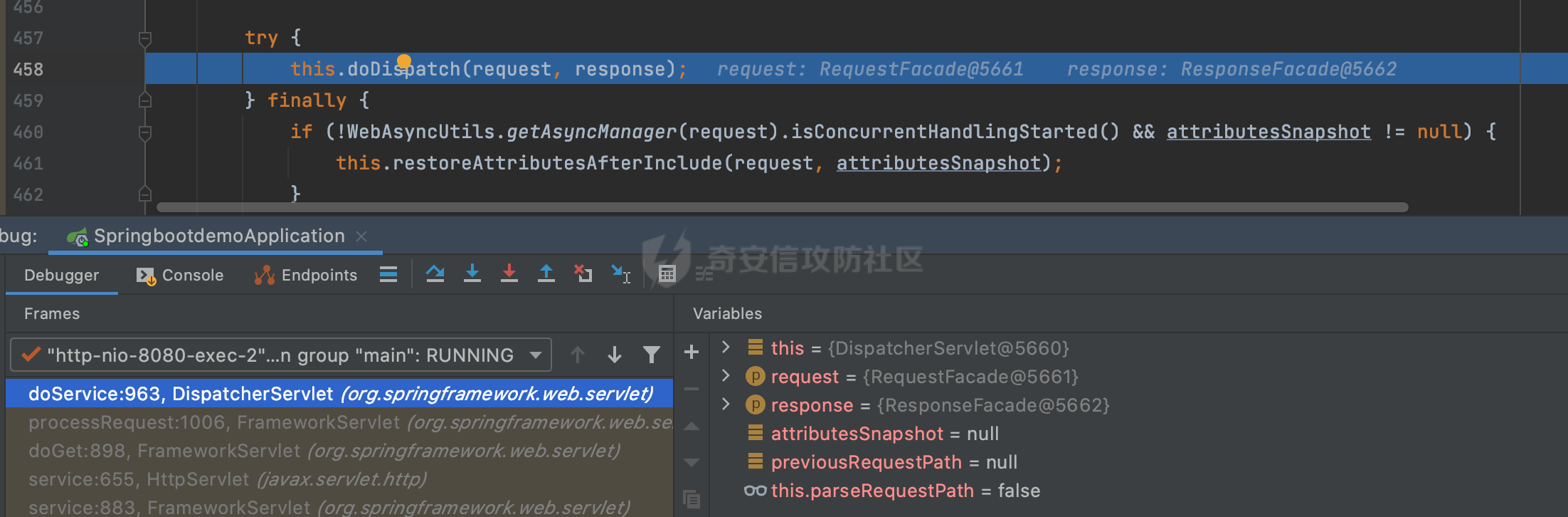 在doDispatch方法中,首先会对multipart请求进行处理,然后获取对应的mappedHandler: 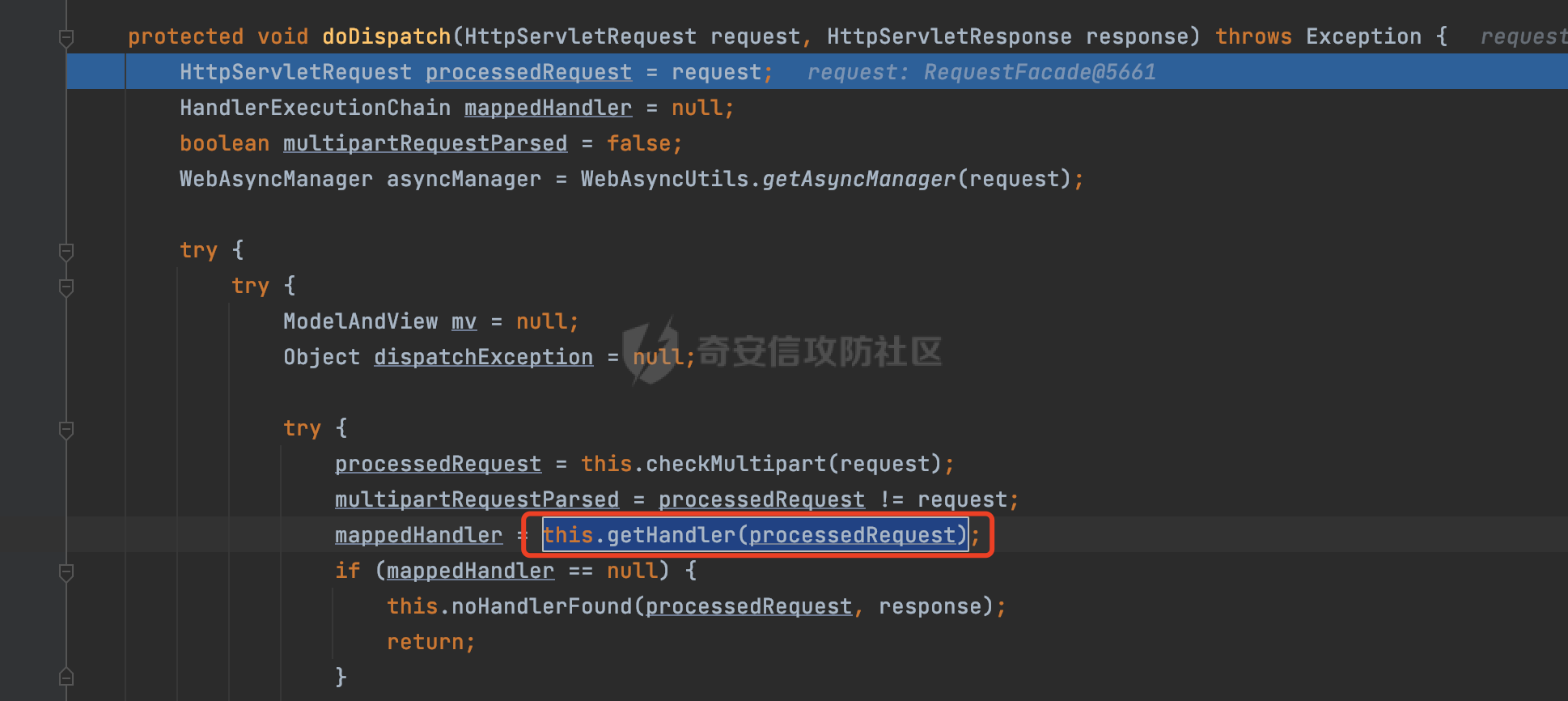 在getHandler方法中,按顺序循环调用HandlerMapping的getHandler方法: 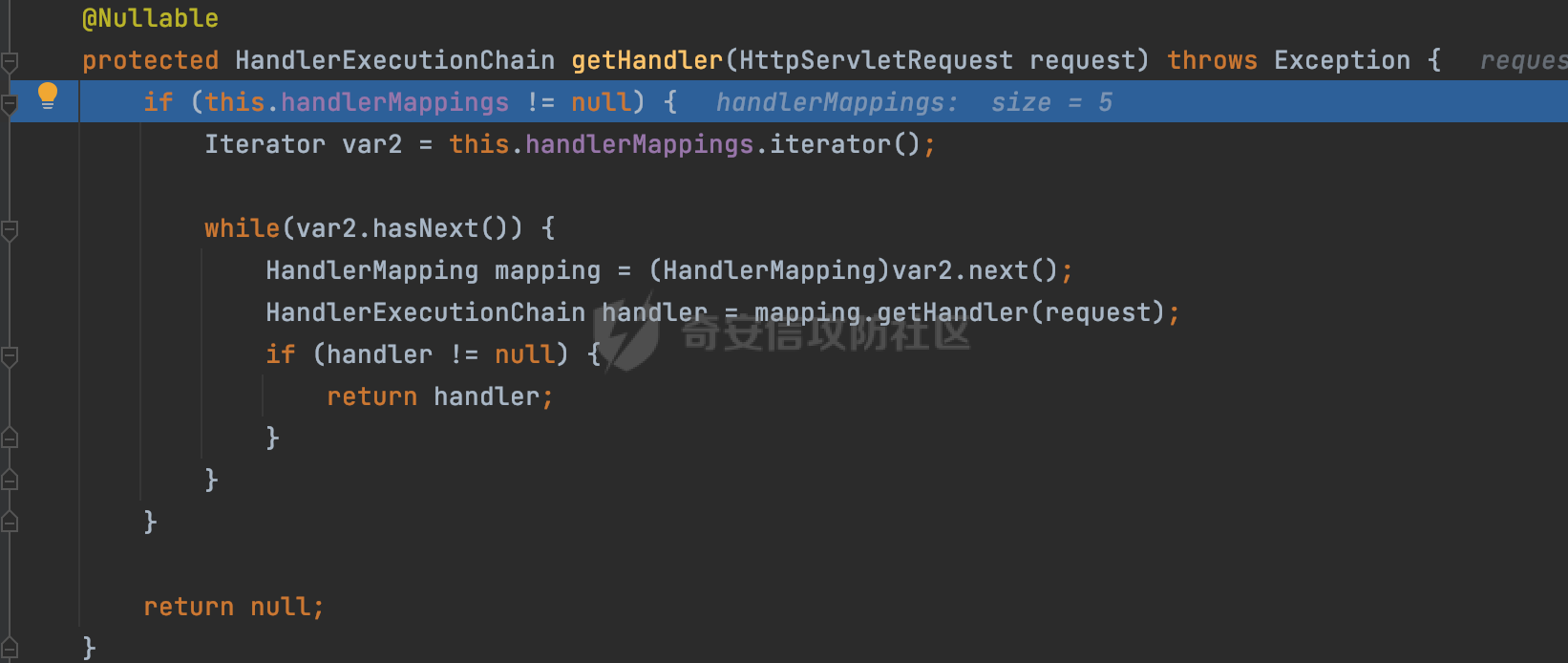 常见的HandlerMapping有如下几个,查阅JavaDoc文档可知注解中配置的路由是通过RequestMappingHandlerMapping处理: 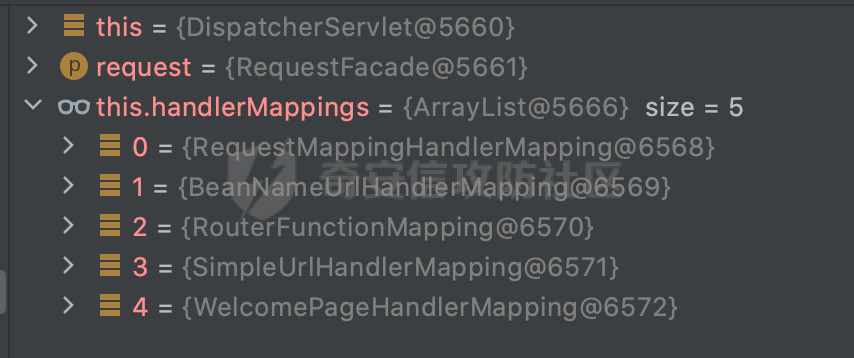 在getHandler方法中通过getHandlerInternal获取handler构建HandlerExecutionChain并返回: 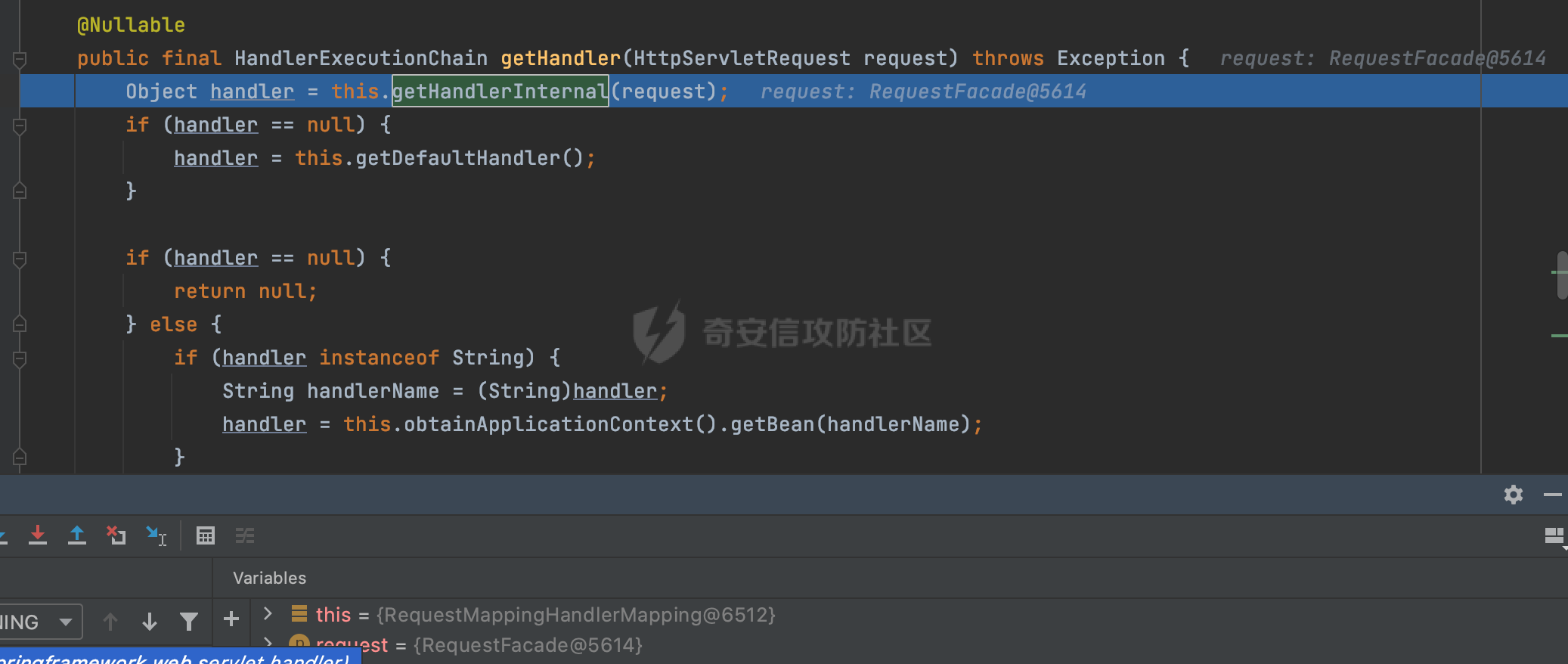 getHandlerInternal方法从request对象中获取请求的path并根据path找到handlerMethod: 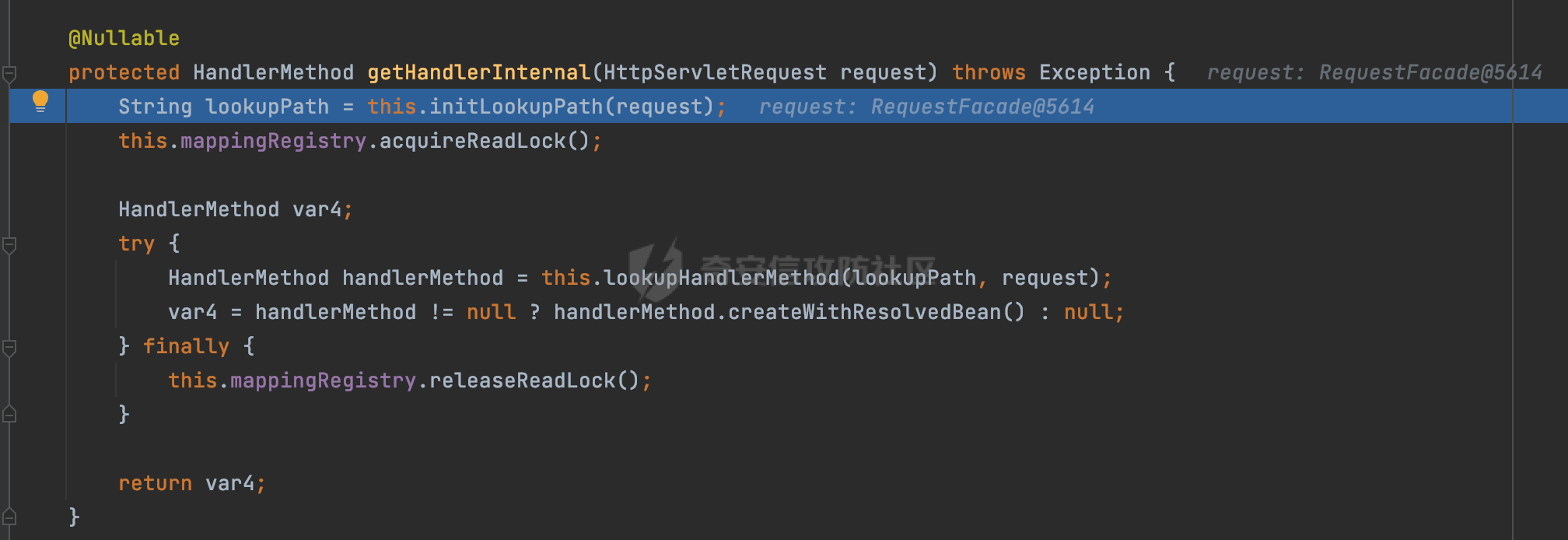 在initLookupPath方法中,主要用于初始化请求映射的路径: 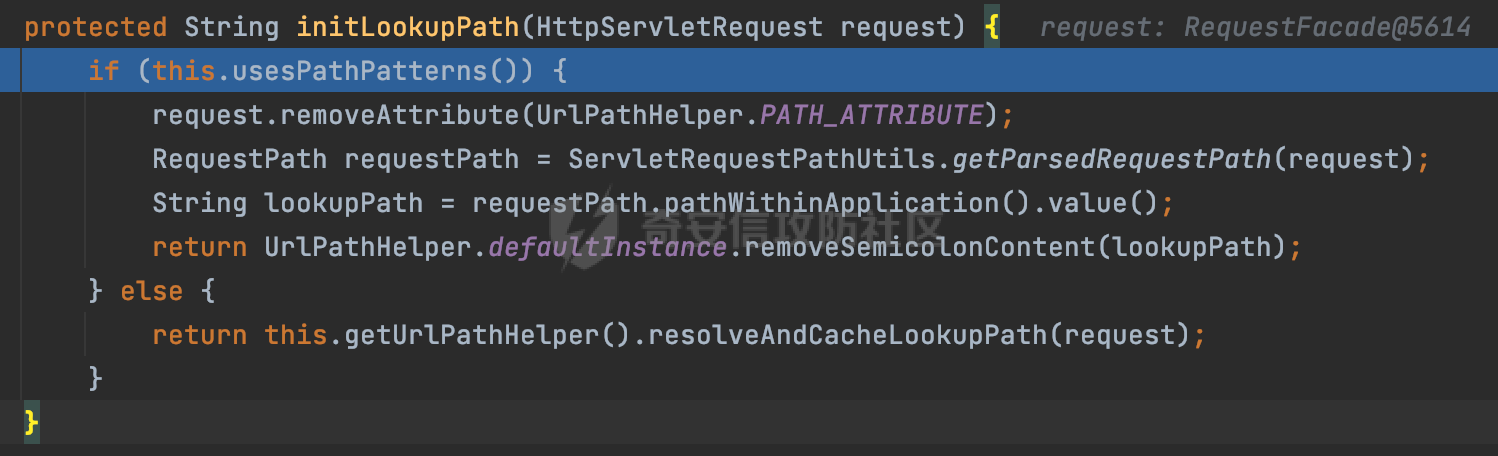 这里通过**UrlPathHelper**类进行路径的处理,UrlPathHelper是Spring中的一个帮助类,有很多与URL路径处理有关的方法。后续单独分析。 获取到路径后,调用lookupHandlerMethod方法,首先直接根据路径获取对应的Mapping,获取不到的话调用addMatchingMappings遍历所有的ReuqestMappingInfo对象并进行匹配: 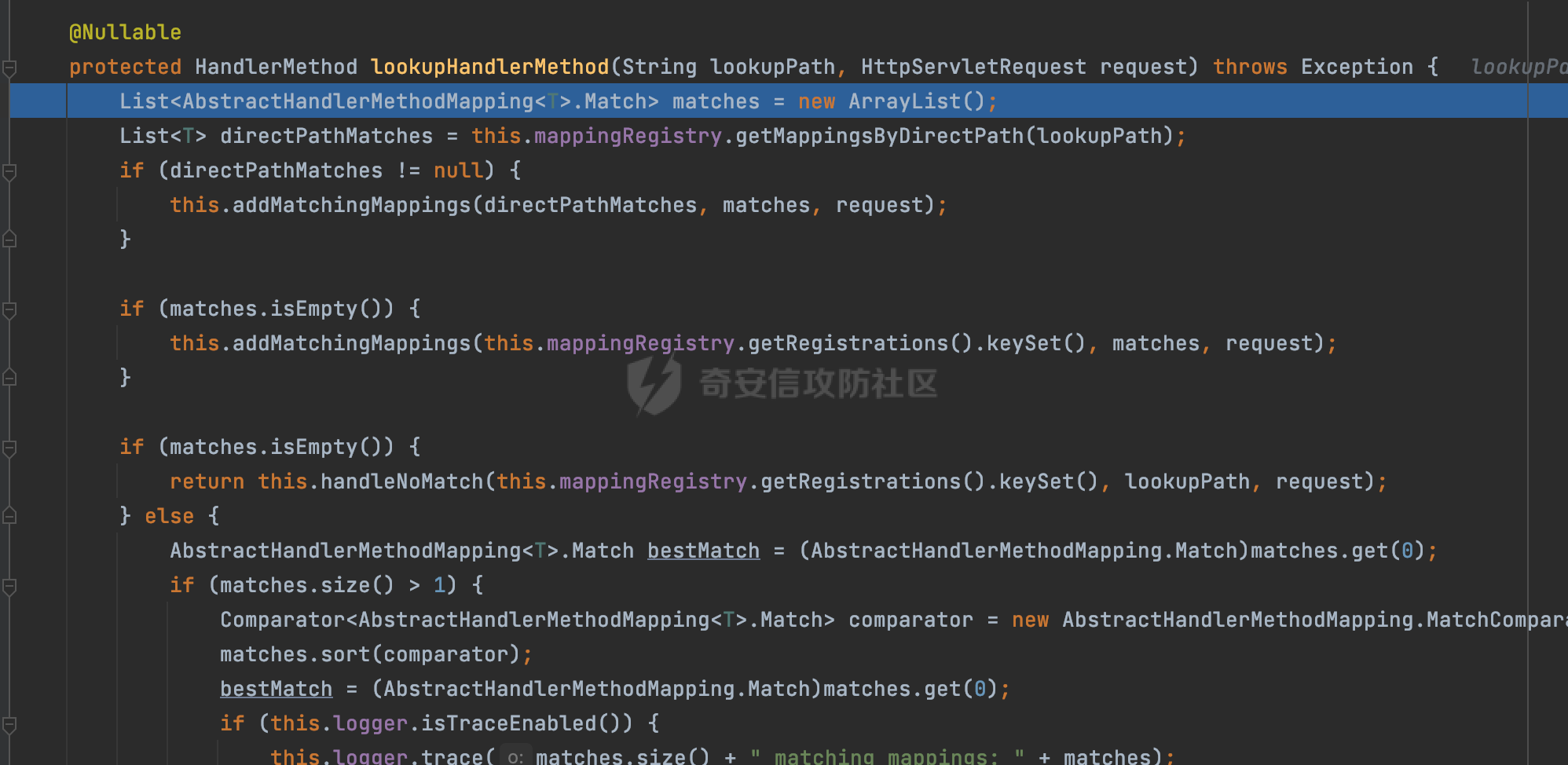 在addMatchingMappings方法中,遍历识别到的ReuqestMappingInfo对象并进行匹配: 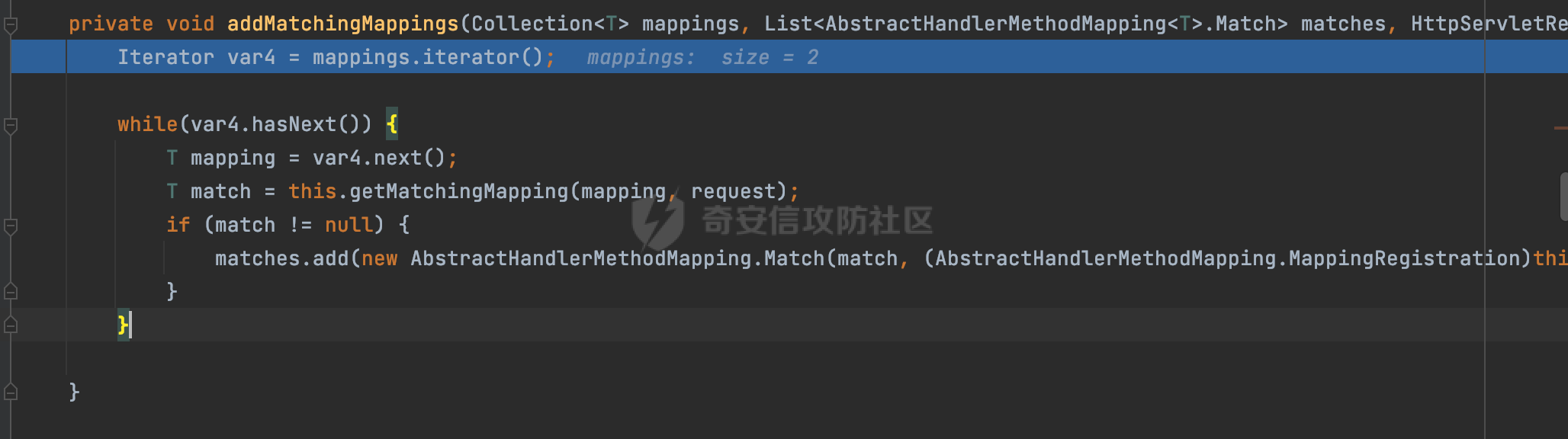 核心方法getMatchingMapping实际上调用的是org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping#getMatchingCondition方法:  getMatchingCondition不同版本的实现也是不一样的,高版本会使用PathPattern来进行URL匹配(**不同版本会有差异,在 2.6之前,默认使用的是AntPathMatcher**进行的字符串模式匹配): 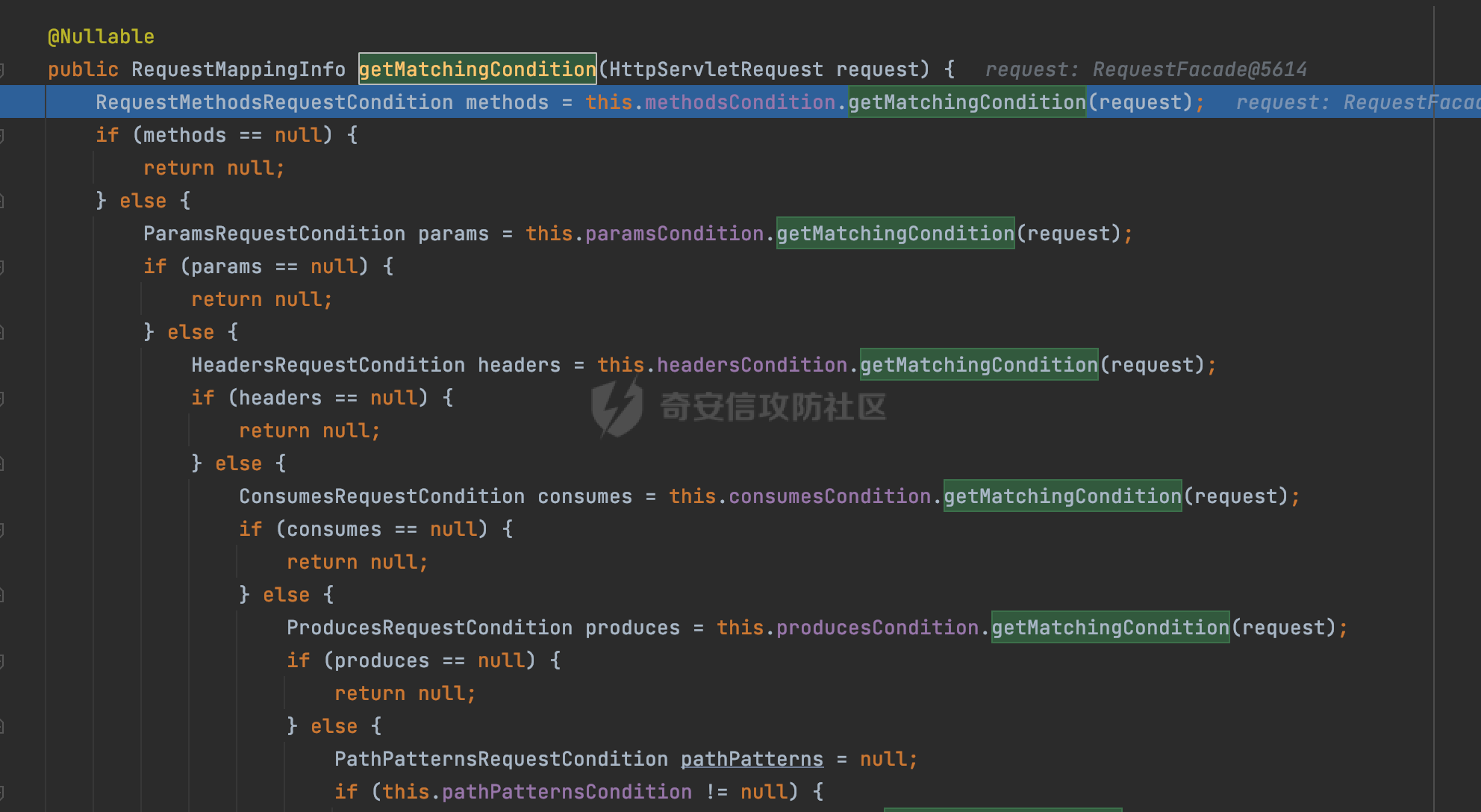 在getMatchingCondition中会检查各种条件是否匹配,例如请求方法methods、参数params、请求头headers还有出入参类型等等,其中patternsCondition.getMatchingCondition(request)是核心的路径匹配方法: 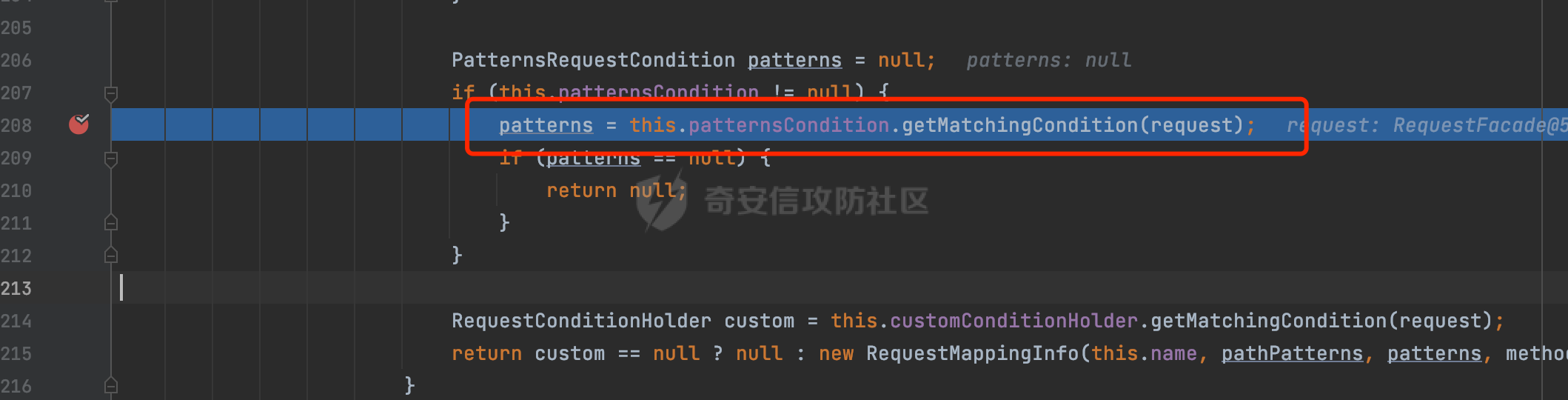 然后会调用PatternsRequestCondition#getMatchingPattern方法进行相关的匹配: 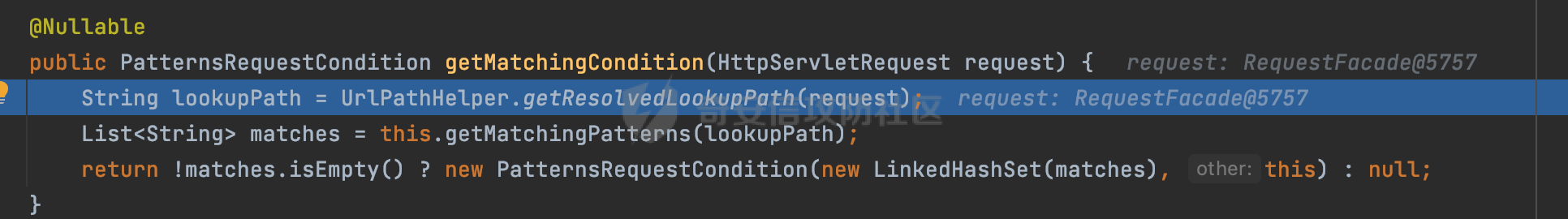 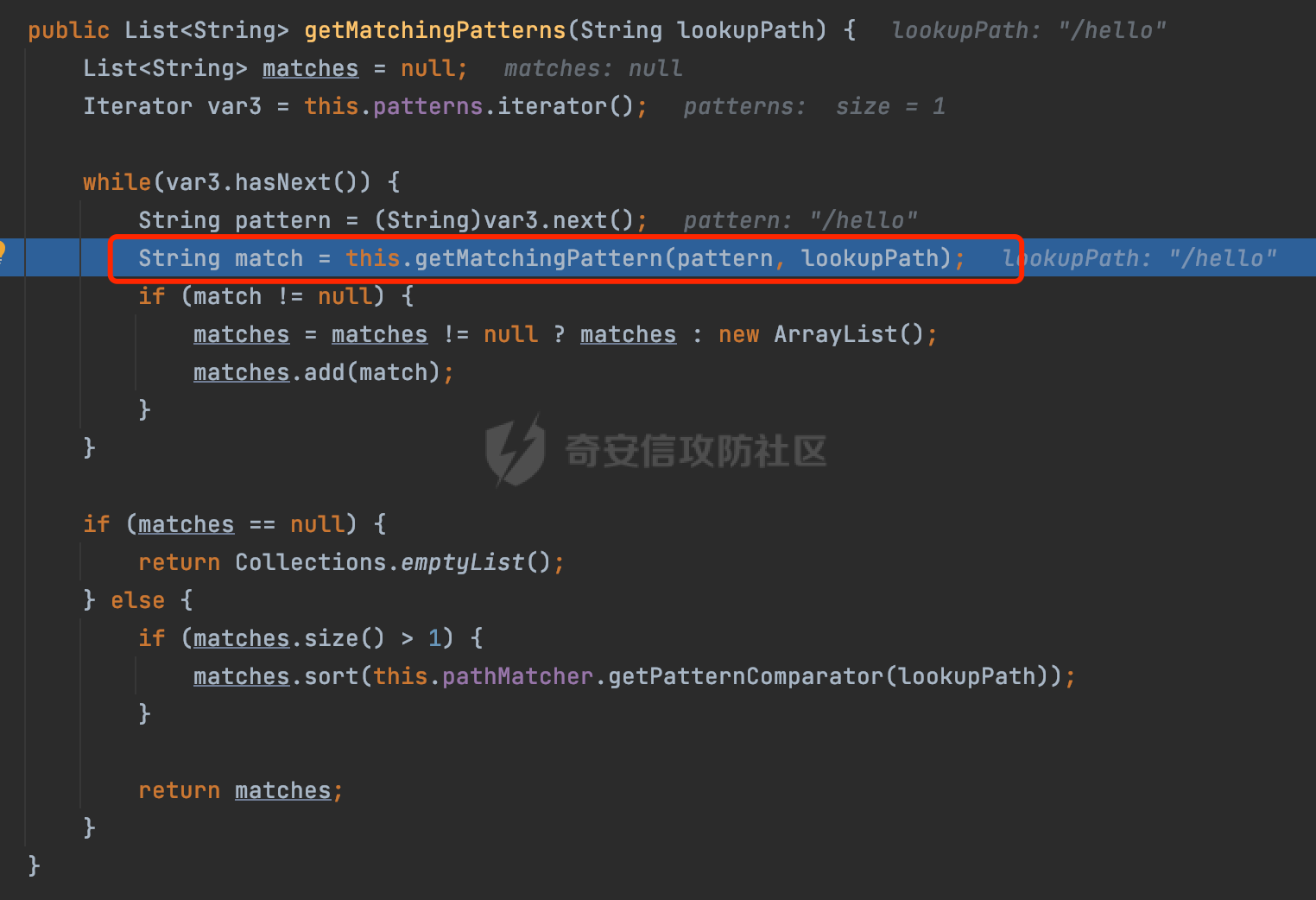 查看PatternRequestCondition#getMatchingPattern方法的具体实现,如果模式与路径相等,直接返回模式,否则进行后缀模式匹配,这里涉及到两个属性**SuffixPatternMatch&TrailingSlashMatch**,根据这两个属性的boolean值会调用pathMatcher#match方法进行进一步的匹配: 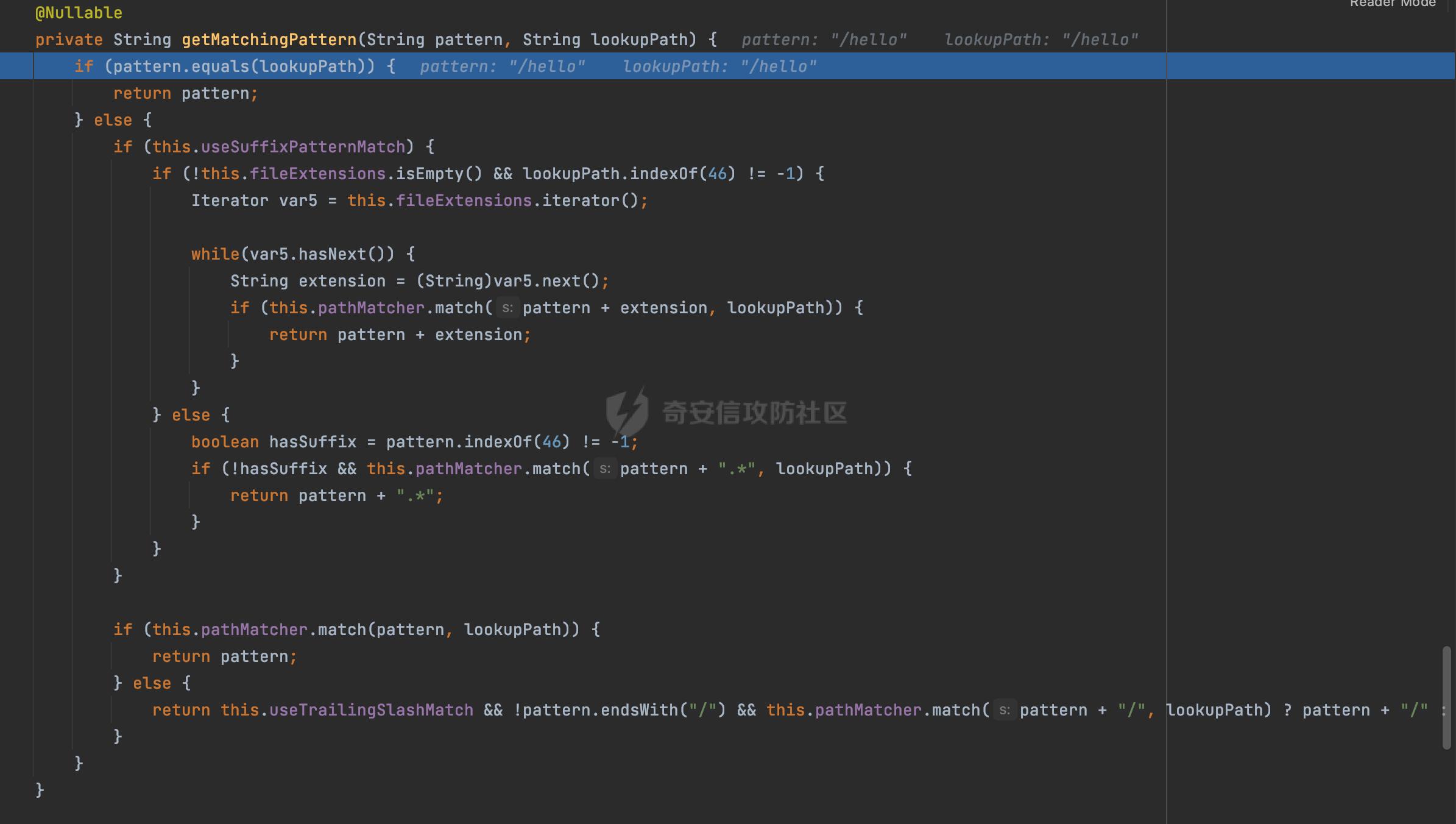 查后续获取到url 和 Handler 映射关系后,springMVC就可以根据请求的uri来找到对应的Controller和method,处理和响应请求: 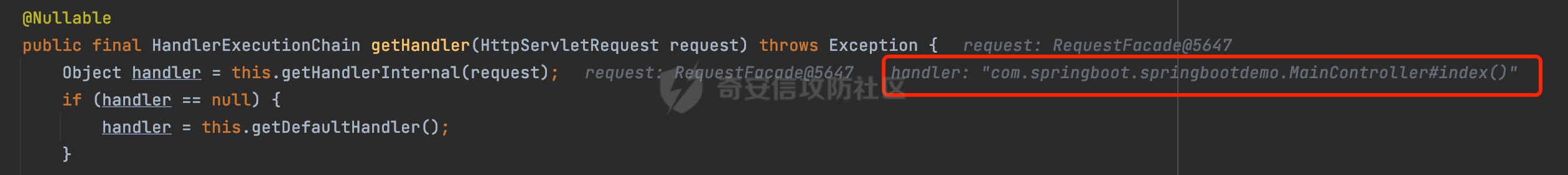 0x02 工具类 ======== 2.1 路径处理帮助类UrlPathHelper ------------------------ UrlPathHelper类是Spring的一个帮助类,主要根据相应的配置解析请求中的路径,里面实现了很多与URL路径处理有关的方法。 以spring-web-5.3.9为例,接前面SpringMvc请求解析过程的分析,当进入到UrlPathHelper时,首先调用resolveAndCacheLookupPath方法: 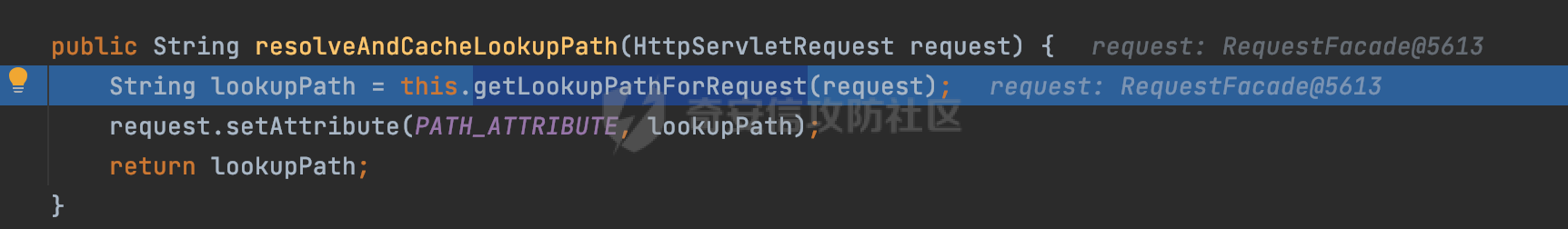 继续跟进,这里调用了getPathWithinApplication方法: 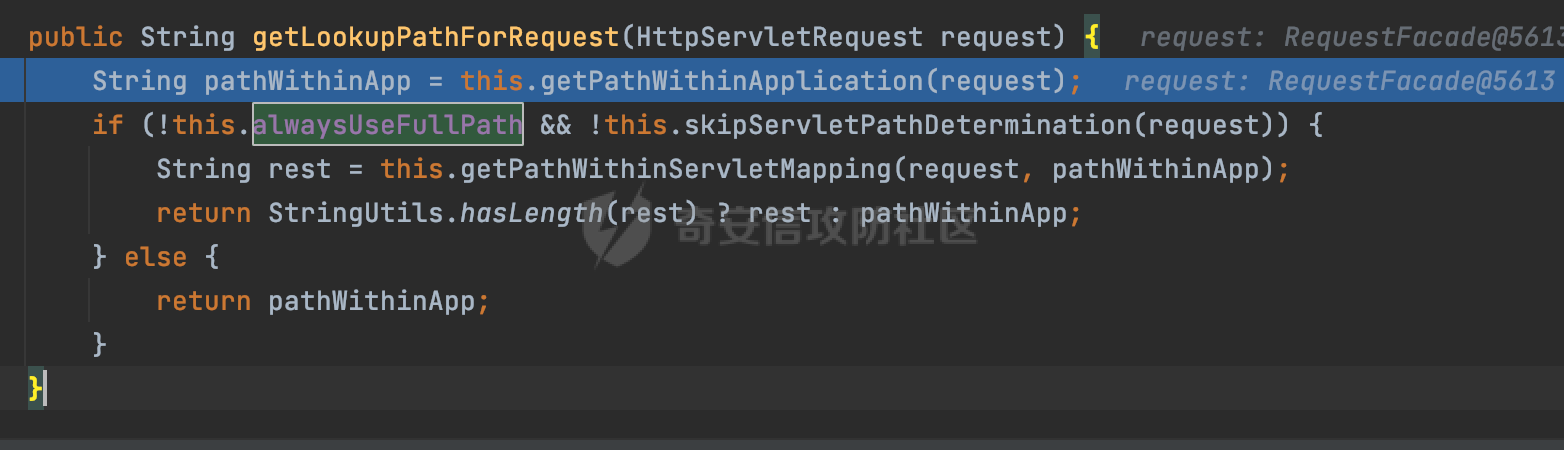 查看getPathWithinApplication的具体实现,这里分别获取了ContextPath和requestUri然后进行处理: 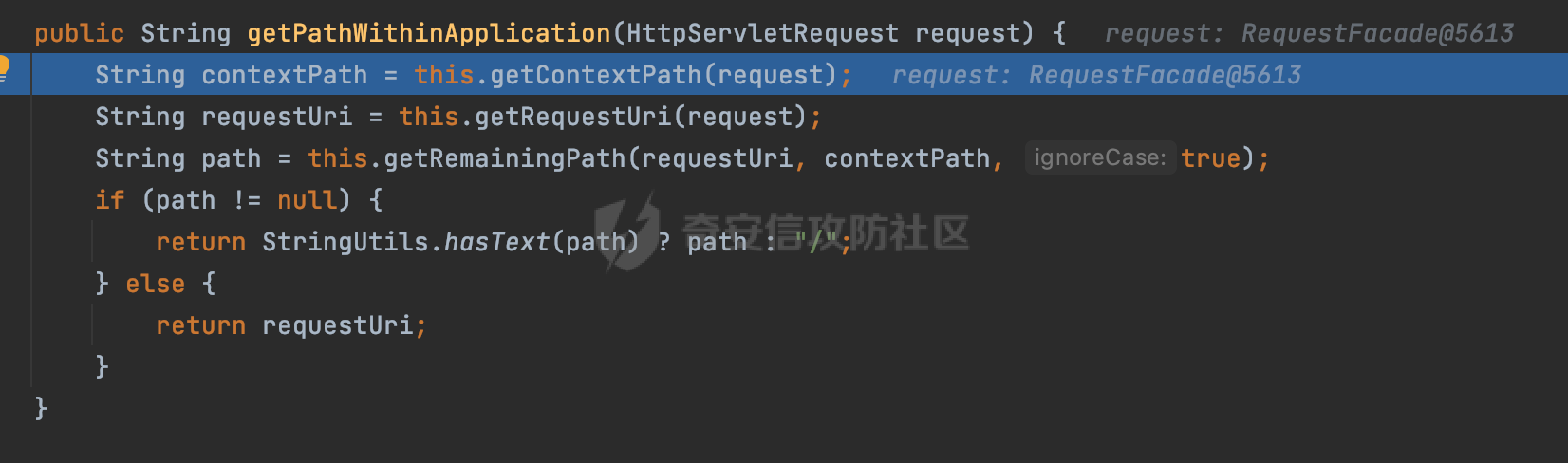 首先是ContextPath,这里会进行对应的解码操作,相关方法(decodeRequestString->decodeInternal,若设置了解码属性便进行对应的解码操作): 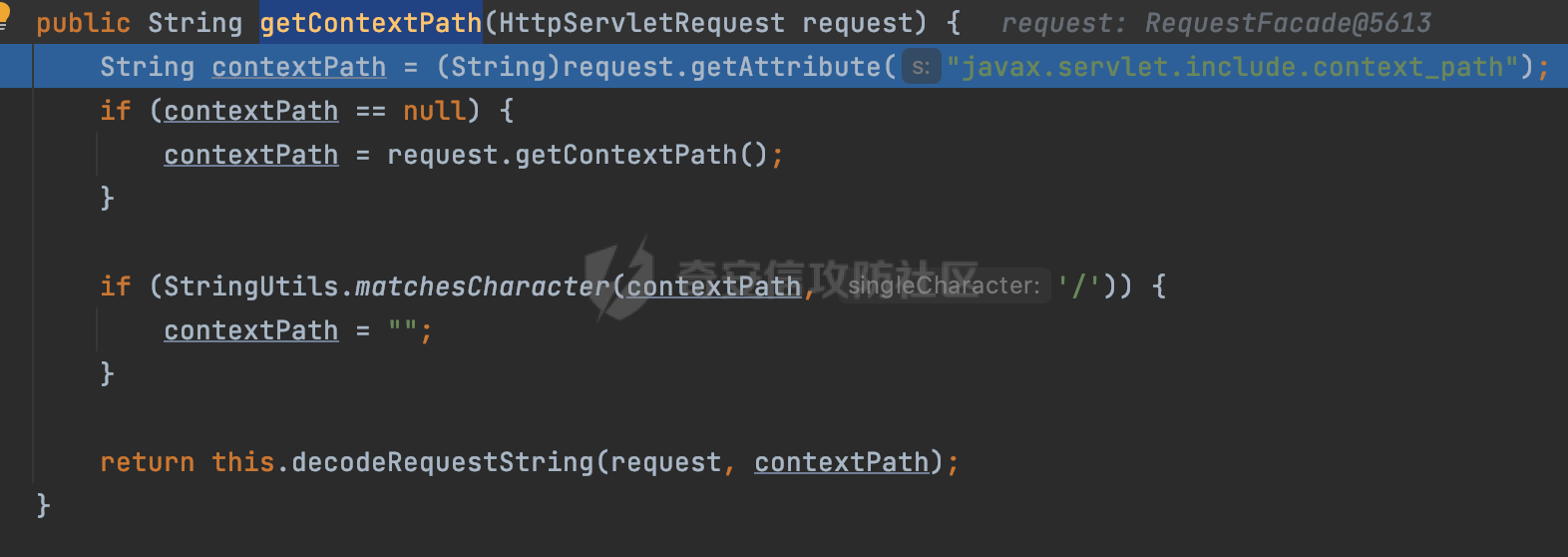 然后是requestUri,这里通过request.getRequestURI()方法获取当前request中的URI/URL,并不会对获取到的内容进行规范化处理,所以UrlPathHelper进行了URI解码、移除分号内容并清理斜线等进一步的处理: 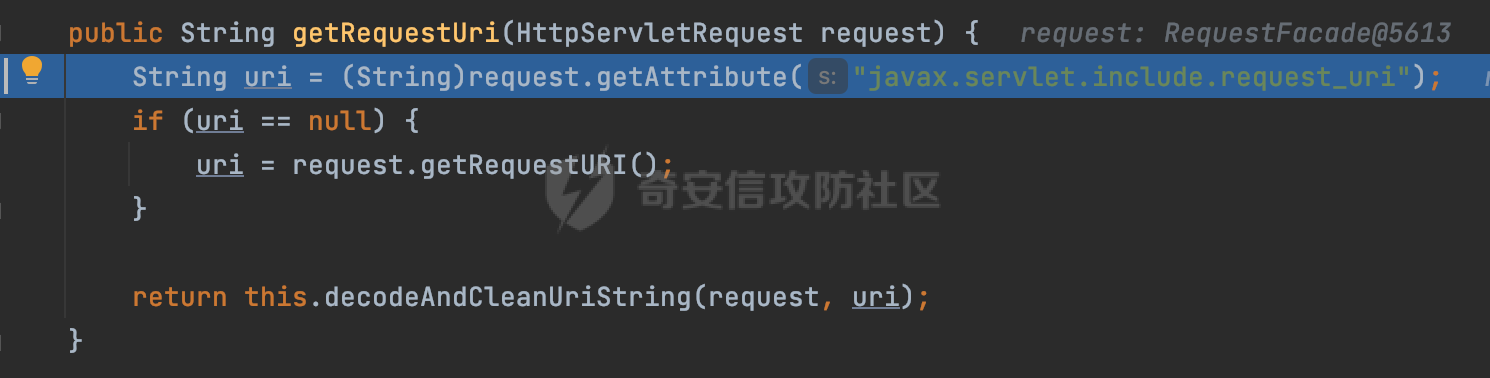 查看decodeAndCleanUriString方法的具体实现,主要有三个方法,看看具体的作用: 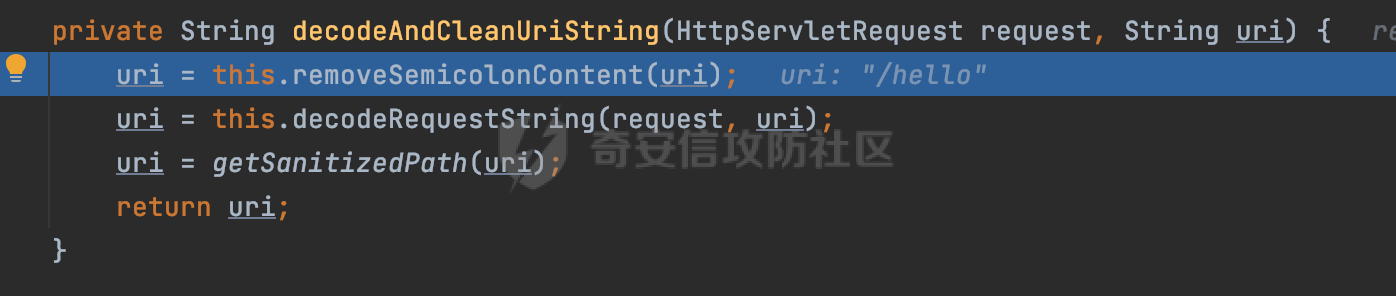 首先是removeSemicolonContent,对于当前处理的URI,如果设置了setRemoveSemicolonContent属性为true,则删除分号,否则删除Jsessionid:  然后是decodeRequestString,这里前面说过,如果设置了解码属性便进行对应的解码操作。 最后是getSanitizedPath方法,这个方法主要是将`//`替换为`/`: 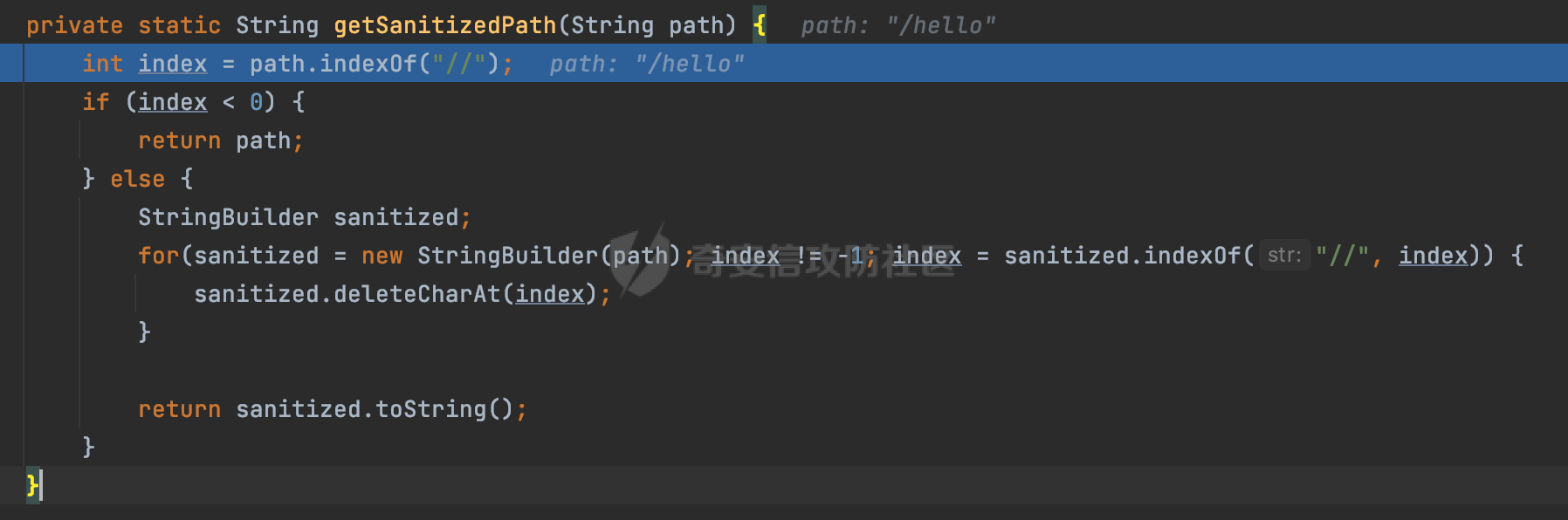 此时ContextPath和requestUri已经处理完成,继续调用getRemainingPath方法进行处理,这里主要是将mapping字符(实际上传入的是ContextPath)与requestUri字符串相匹配,把requestUri中的分号部分忽略掉: 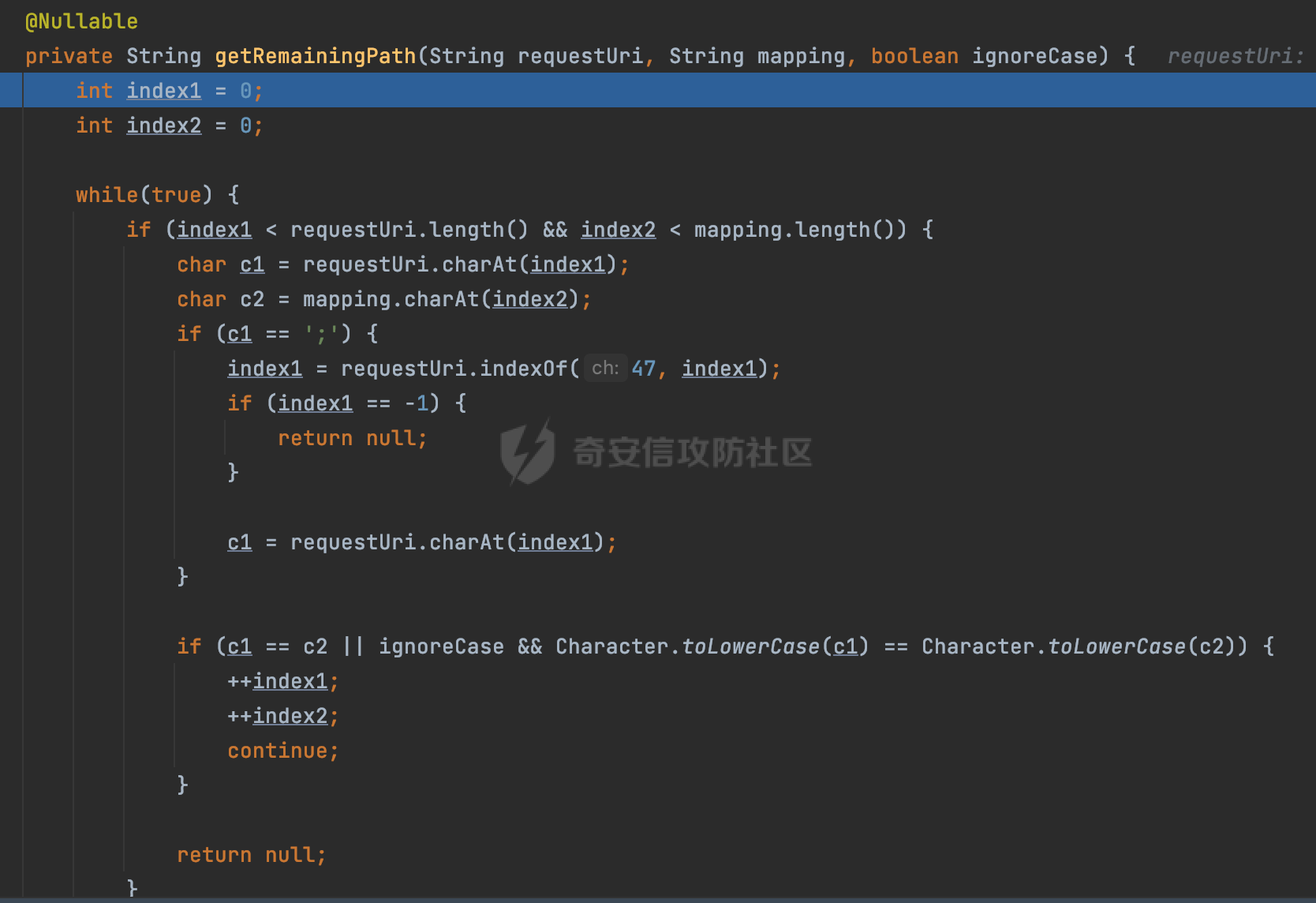 到这里整个getPathWithinApplication方法处理完成,这时候涉及到一个属性`alwaysUseFullPath`,不同的值将会决定是否经过getPathWithinServletMapping方法处理(当Spring Boot版本在小于等于2.3.0.RELEASE的情况下,alwaysUseFullPath为默认值false,当前版本会直接返回处理后的pathWithinApp): 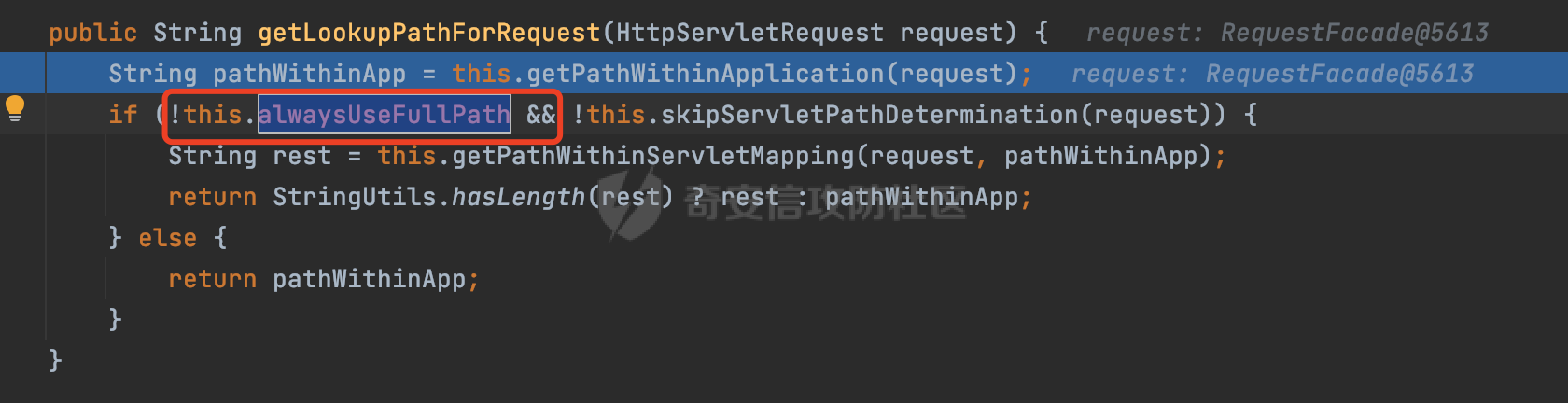 到此整个`String lookupPath = this.initLookupPath(request);`解析完成。 ### 2.1.1 其他 前面提到在initLookupPath方法中,主要用于初始化请求映射的路径,主要会通过**UrlPathHelper**类进行路径的处理,这里还有一段逻辑,当this.usesPathPatterns()为true时会执行另外一段逻辑: 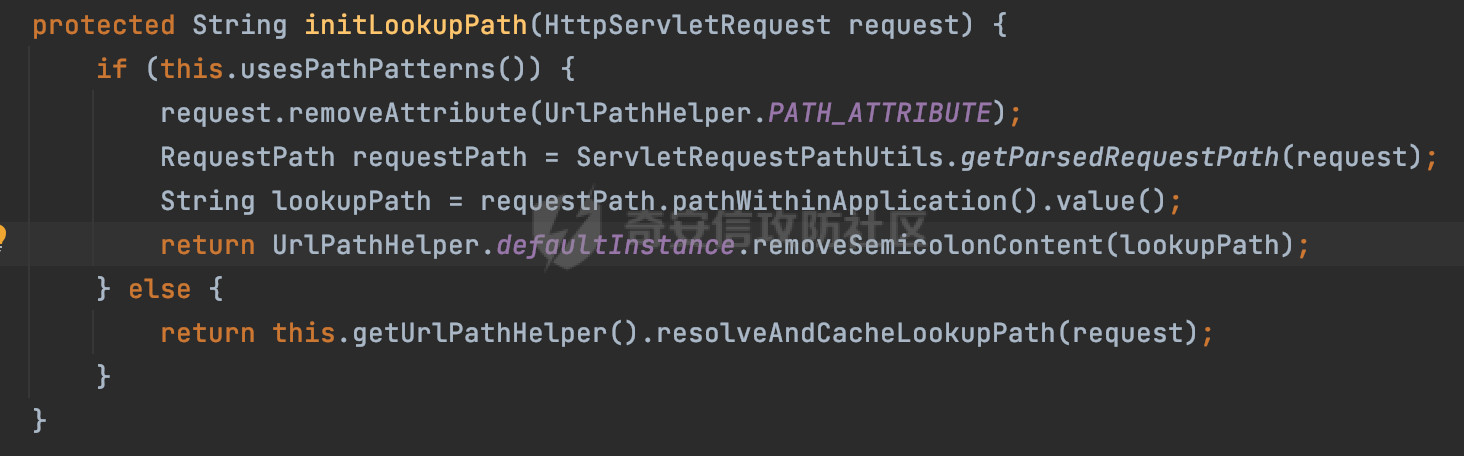 当使用PathPattern进行解析时,this.usesPathPatterns()为true,以spring-webmvc-5.3.25为例,查看具体的解析过程: 首先从request域中获取PATH\_ATTRIBUTE属性的内容,然后使用defaultInstance对象进行处理:  这里会根据removeSemicolonContent的值(默认为true)确定是移除请求URI中的所有分号内容还是只移除jsessionid部分: 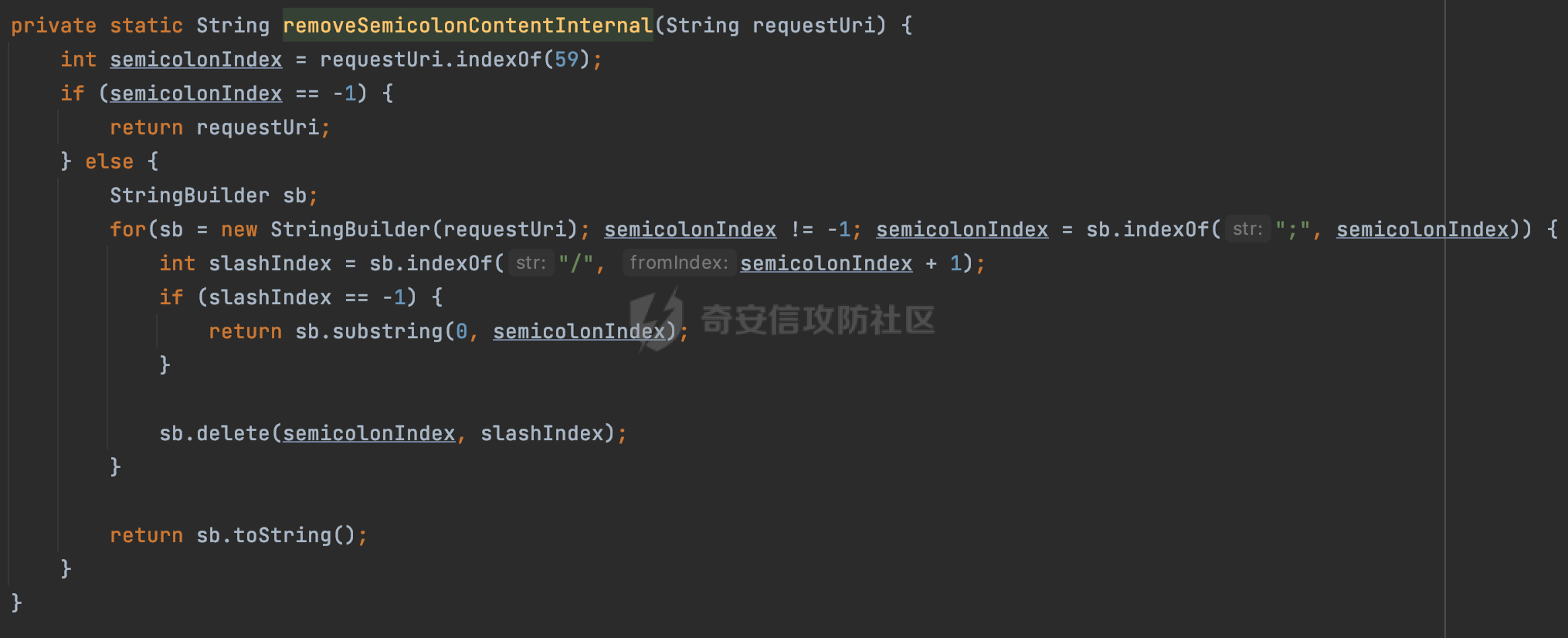 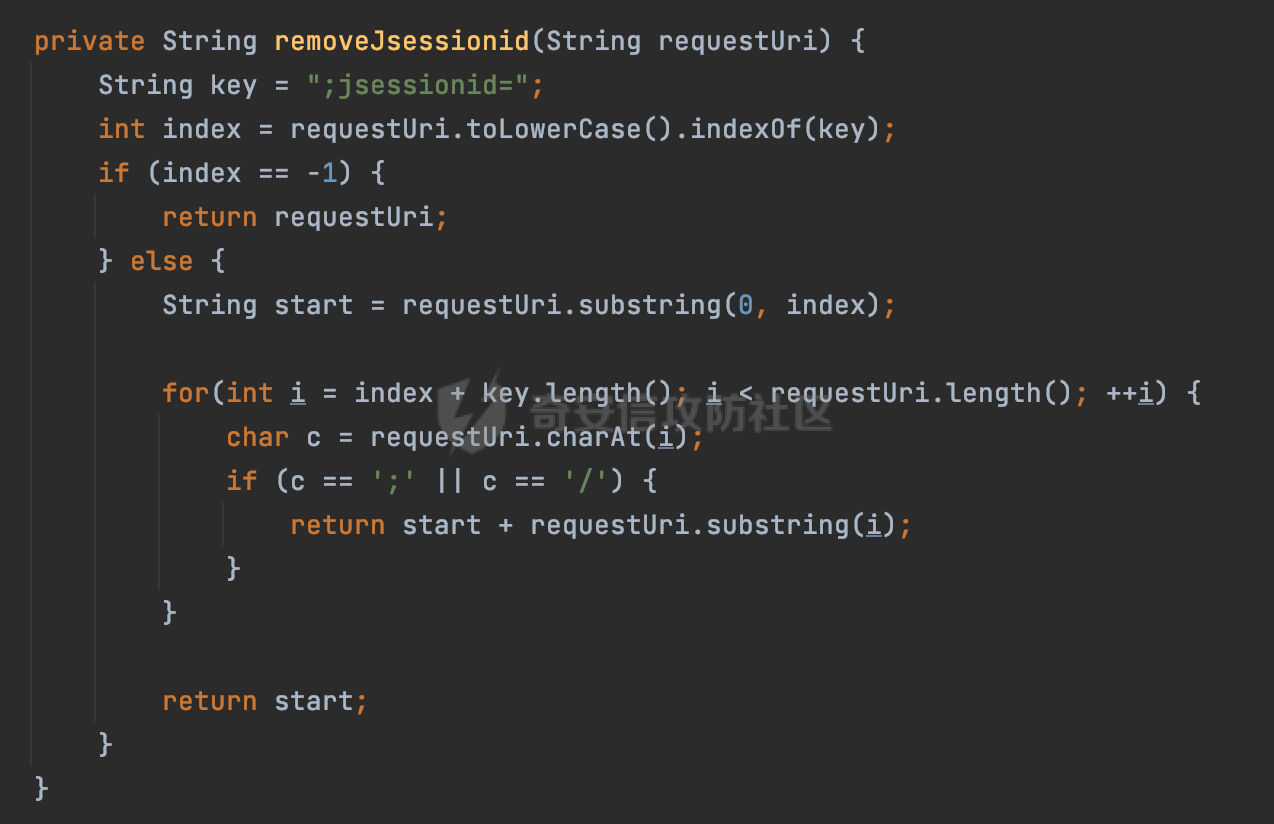 到此整个`String lookupPath = this.initLookupPath(request);`解析完成。 这里并没有前面调用resolveAndCacheLookupPath的逻辑复杂,例如并不会将`//`处理成`/`,结合PathPattern的解析逻辑,如果此时Controller配置如下: ```Java @RequestMapping("/admin/page") @ResponseBody public String hello() { return "admin page"; } ``` 那么访问/admin//page是无法匹配的: 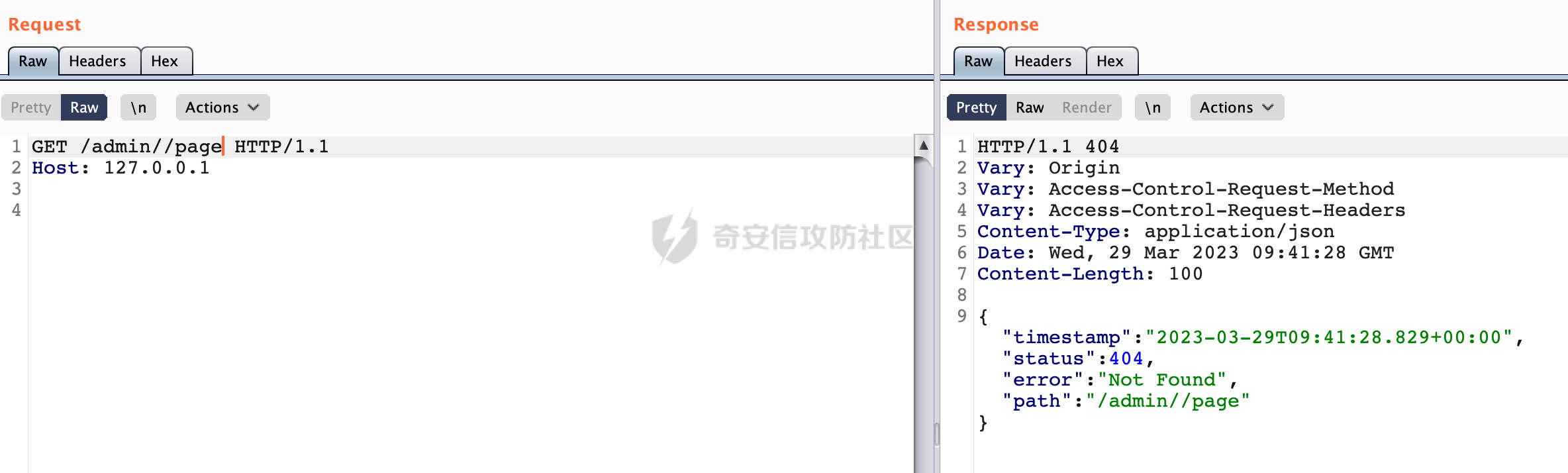 0x03 关键属性 ========= 3.1 SuffixPatternMatch/TrailingSlashMatch(后缀/结尾匹配模式) ---------------------------------------------------- 前面提到的模式匹配的两个属性**SuffixPatternMatch&TrailingSlashMatch**。看看具体的代码实现: **SuffixPatternMatch**是后缀匹配模式,用于能以 .xxx 结尾的方式进行匹配。这里46对应的Ascii码是`.`,根据具体代码可以知道,当启用后缀匹配模式时,例如/hello和/hello.do的匹配结果是一样的: 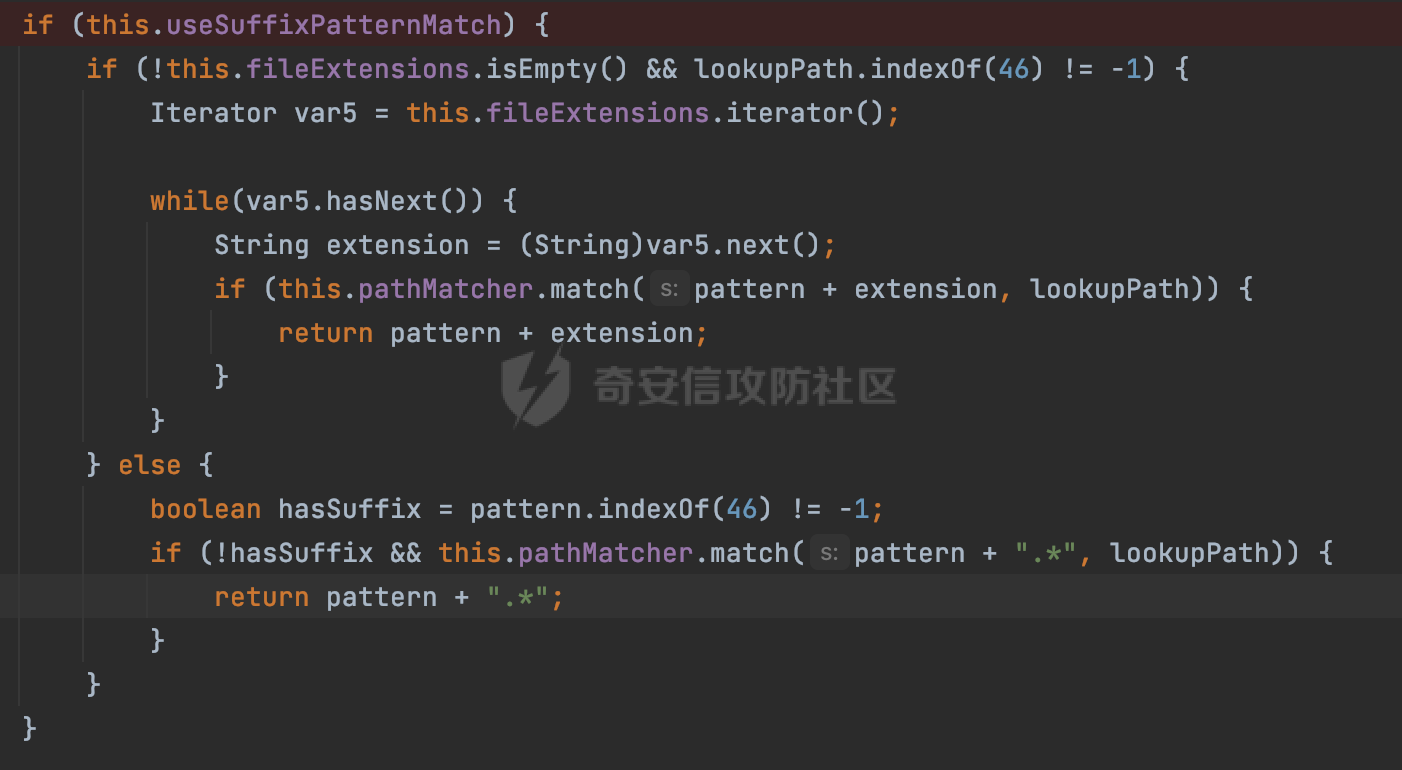 当**TrailingSlashMatch**为true时,会应用尾部的/匹配,例如/hello和/hello/的匹配结果是一样的:  ### 3.1.1 各版本差异 5.3后相关useSuffixPatternMatch的默认值会由true变为false,参考<https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-framework/issues/23915>  从`org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping`中可以看到对应属性的改变: - spring-webmvc:5.3.9 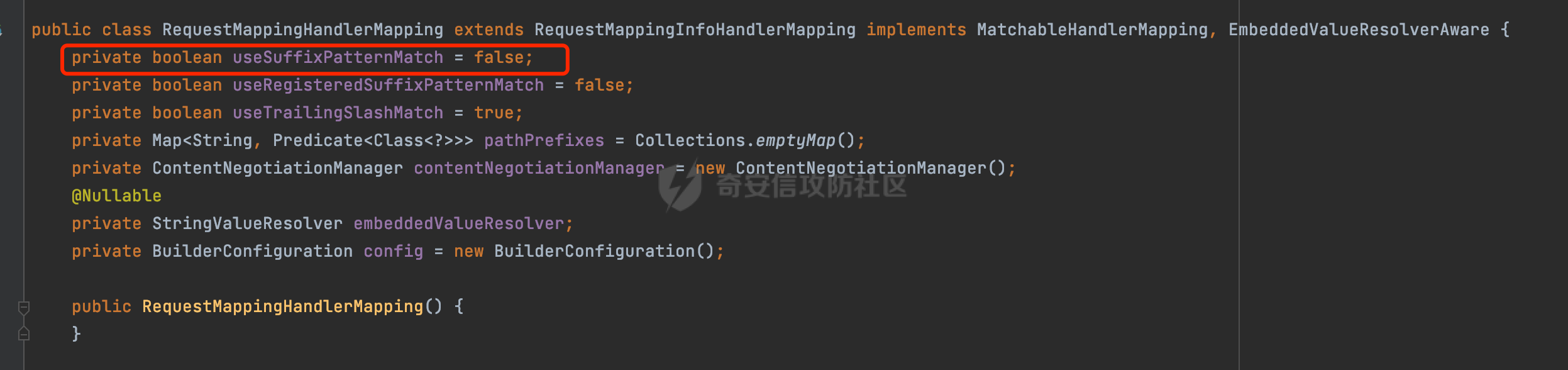 - spring-webmvc-5.2.22.RELEASE 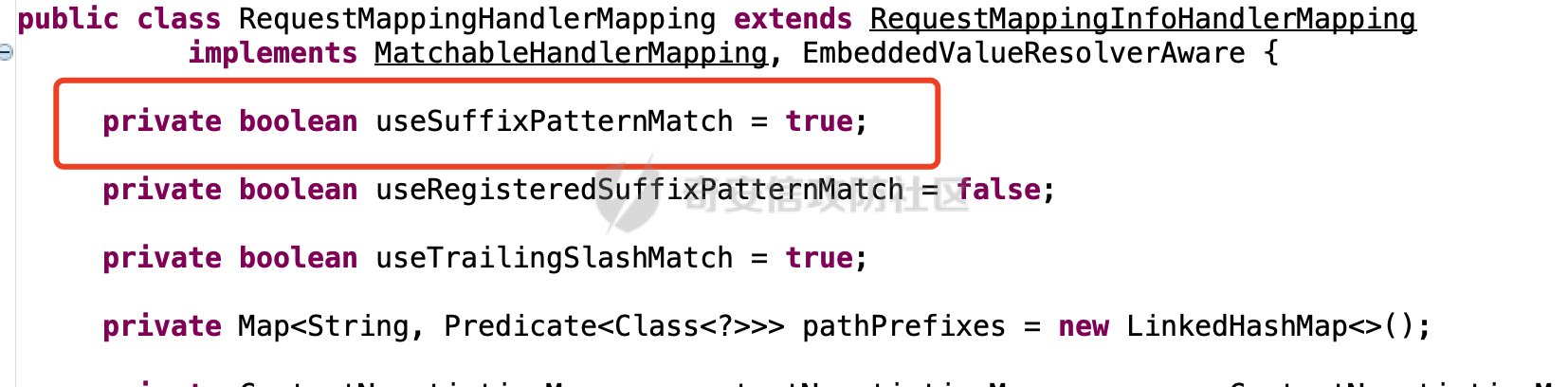 3.2 alwaysUseFullPath --------------------- alwaysUseFullPath主要用于判断是否使用servlet context中的全路径匹配处理器。 ### 3.2.1 各版本差异 WebMvcAutoConfiguration是Spring Boot中关于Spring MVC自动配置类。在org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration#configurePathMatch方法中可以配置URL路径的匹配规则。 主要是这两个分界点: - spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.3.0.RELEASE 在2.3.0以及之前版本,在configurePathMatch中,没有对UrlPathHelper的alwaysUseFullPath属性进行设置,默认为False: 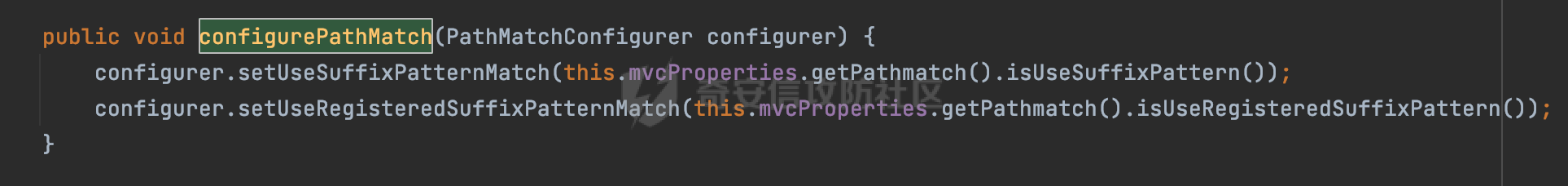 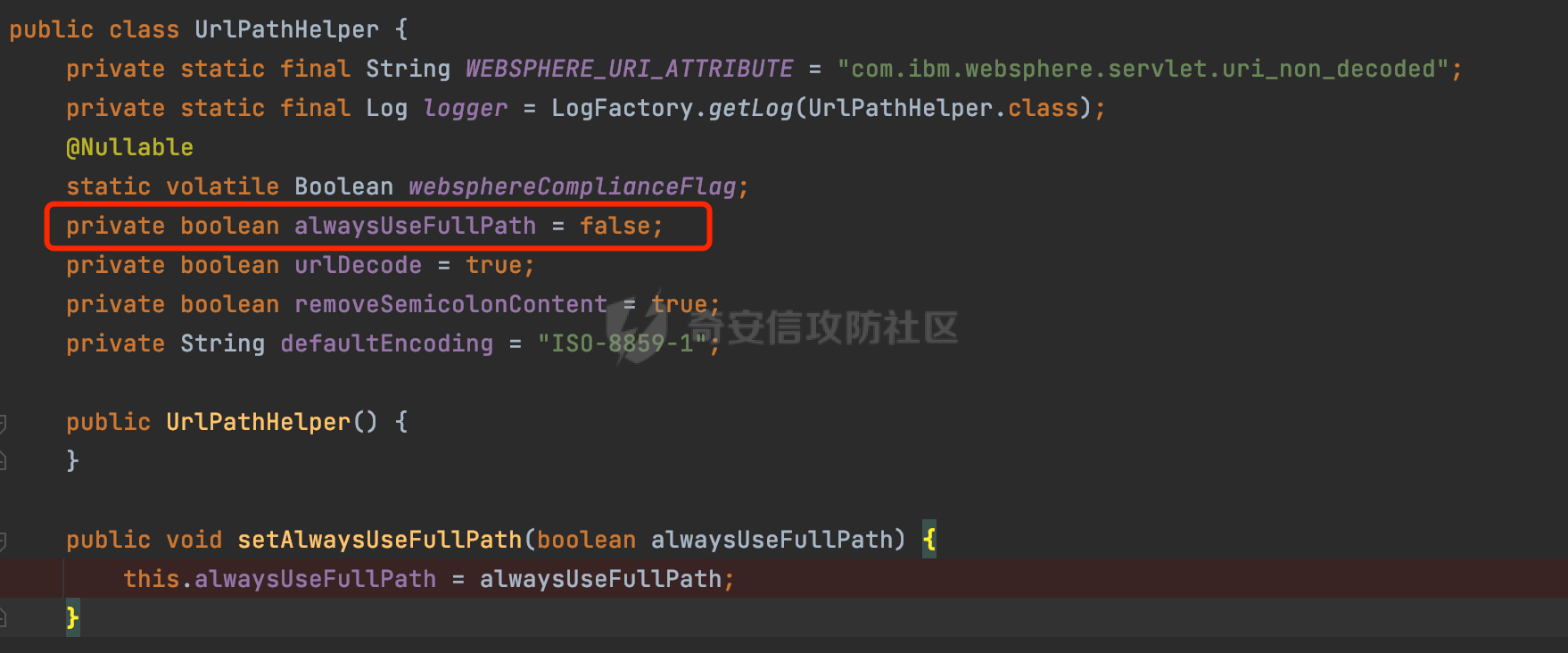 - spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.3.1.RELEAS 在2.3.1及之后版本,在configurePathMatch方法中,通过实例化UrlPathHelper对象并调用对应的setAlwaysUseFullPath方法将alwaysUseFullPath属性设置为true: 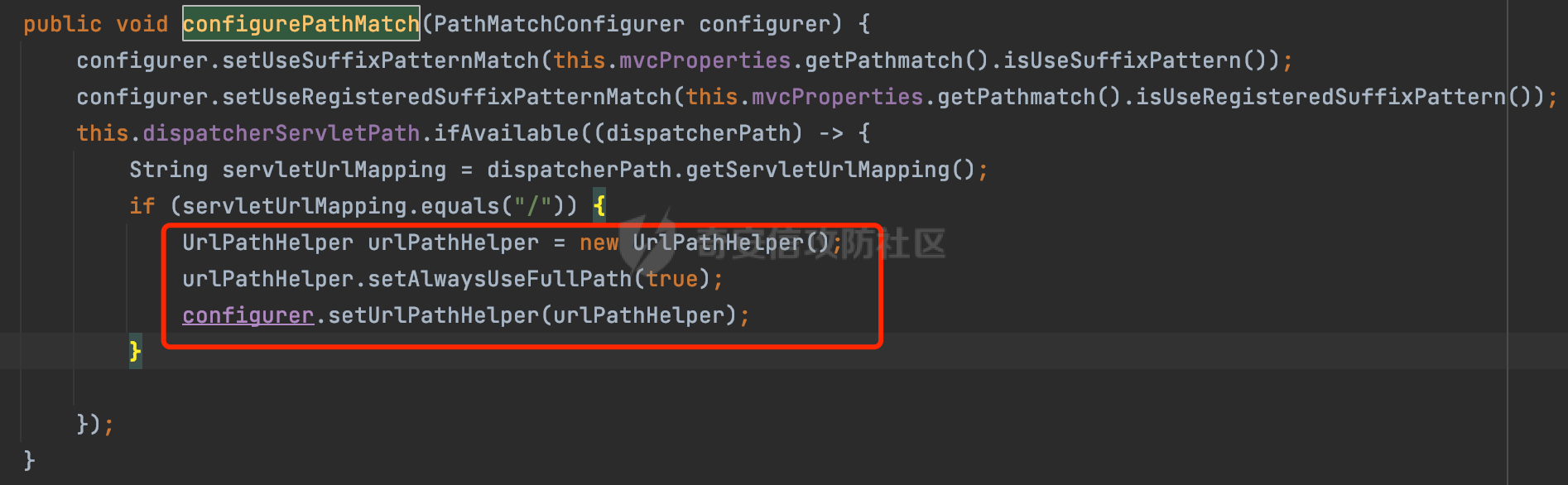 ### 3.2.2 getPathWithinServletMapping方法 接之前Spring MVC发接收到请求时的分析,`alwaysUseFullPath`属性不同的值将会决定是否经过getPathWithinServletMapping方法处理。这里以2.3.0.RELEASE版本为例,其值默认为false,会经过getPathWithinServletMapping方法进行处理,跟进查看具体的过程: 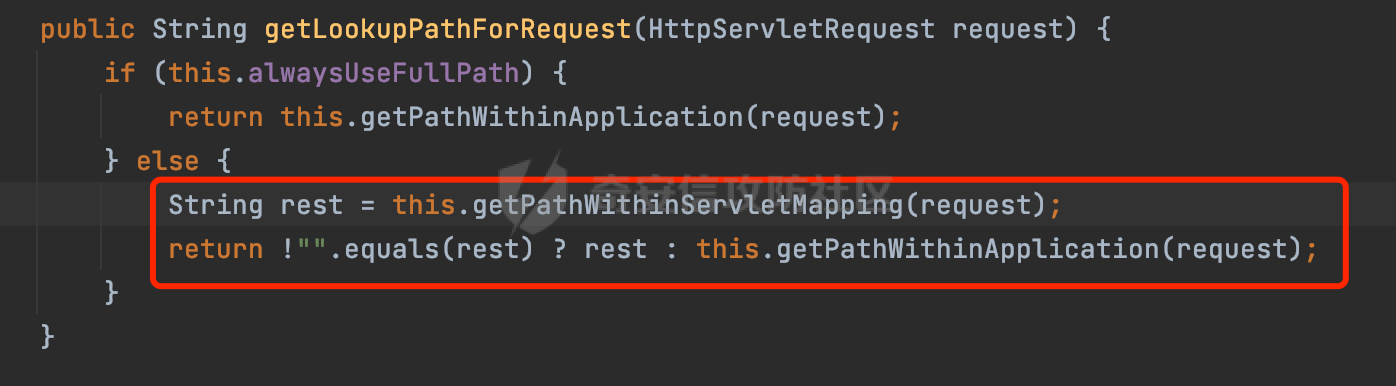 首先会调用getPathWithinApplication方法进行处理,前面已经分析过具体的行为了,主要是进行了URI解码、移除分号内容并清理斜线等一系列操作,不再赘述:  跟getPathWithinApplication不同的是,getPathWithinServletMapping会获取ServletPath并进行对应的处理,这里主要是调用request.getServletPath(主要是对uri标准化处理,例如解码然后处理跨目录等一系列操作)方法: 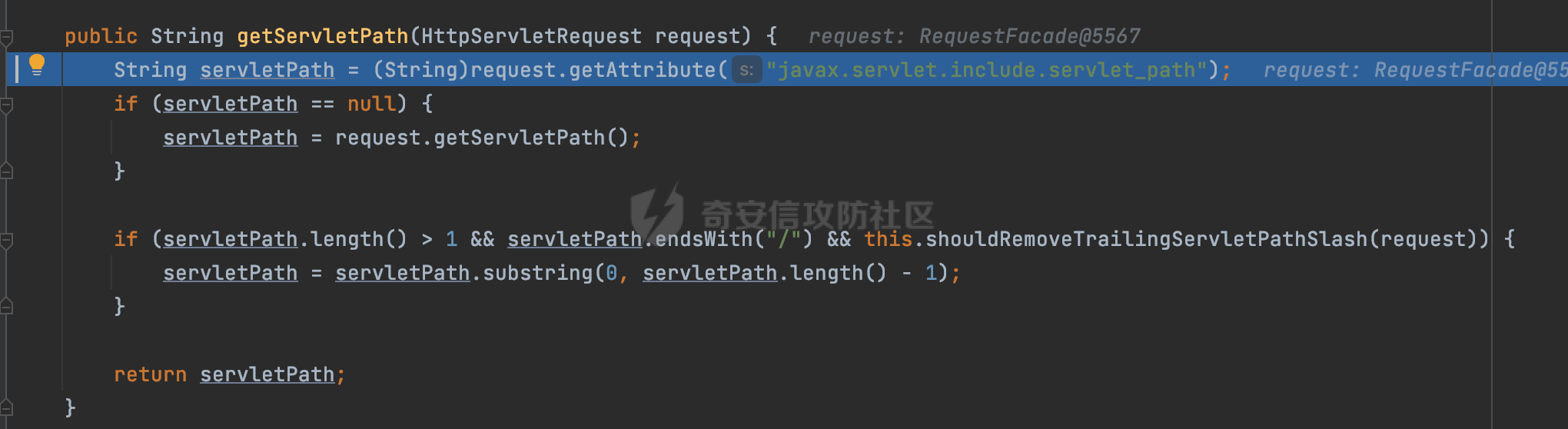 再往后就是一系列熟悉的操作了,例如调用getSanitizedPath方法将`//`替换为`/`。调用getRemainingPath进行处理。还有request.getPathInfo()等一系列的组合后,返回对应的值给lookupPath,然后就是熟悉的操作了,调用lookupHandlerMethod方法,遍历所有的ReuqestMappingInfo对象并进行匹配,进行对应的解析。 ### 3.2.3 与getPathWithinApplication的区别 根据前面的分析,getPathWithinServletMapping会对uri进行标准化处理(也就是说**当SpringBoot 版本在小于等于2.3.0.RELEASE时,会对路径进行规范化处理**),而getPathWithinApplication是通过request.getRequestURI()方法获取当前request中的URI/URL,并不会对获取到的内容进行规范化处理。 当请求路径中包括类似`..`的关键词时,调用getPathWithinApplication方法解析后,会因为没有处理跨目录的字符,导致找不到对应的Handler而返回404。 看一个具体的实例,注册的路由如下,尝试访问`/file/../hello`路径,看看不同版本的解析情况: ```Java @GetMapping({"/hello"}) public String index() { return "hello"; } ``` 当alwaysUseFullPath为false时,调用了getPathWithinServletMapping进行处理,跨目录字符解码并规范化后,成功匹配对应的handler并访问成功: 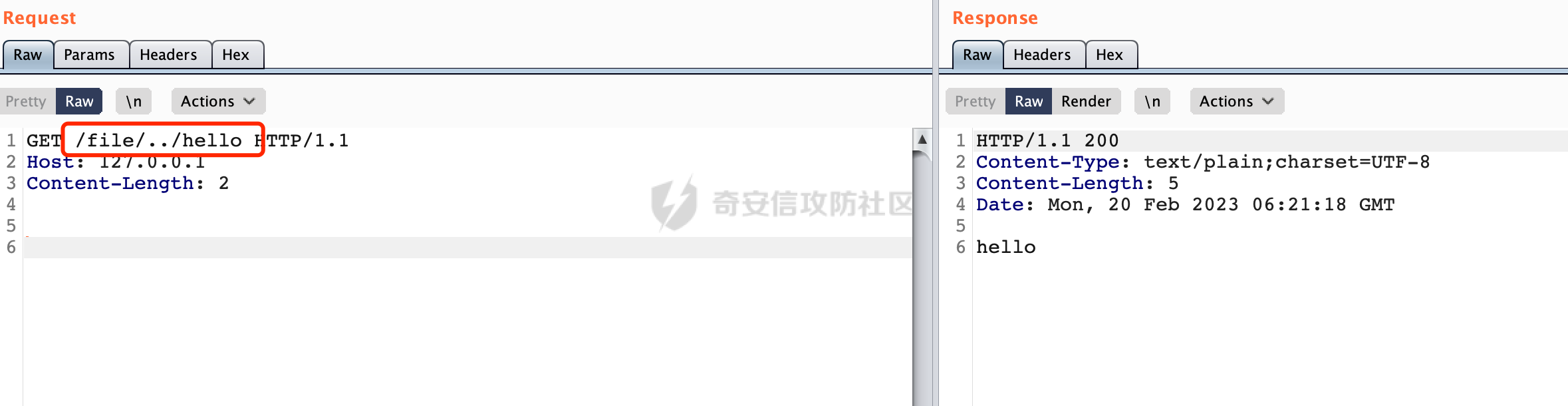 当alwaysUseFullPath为true时,调用的是getPathWithinApplication,没有对跨目录进行标准化处理,最终找不到对应的handler,返回404状态码: 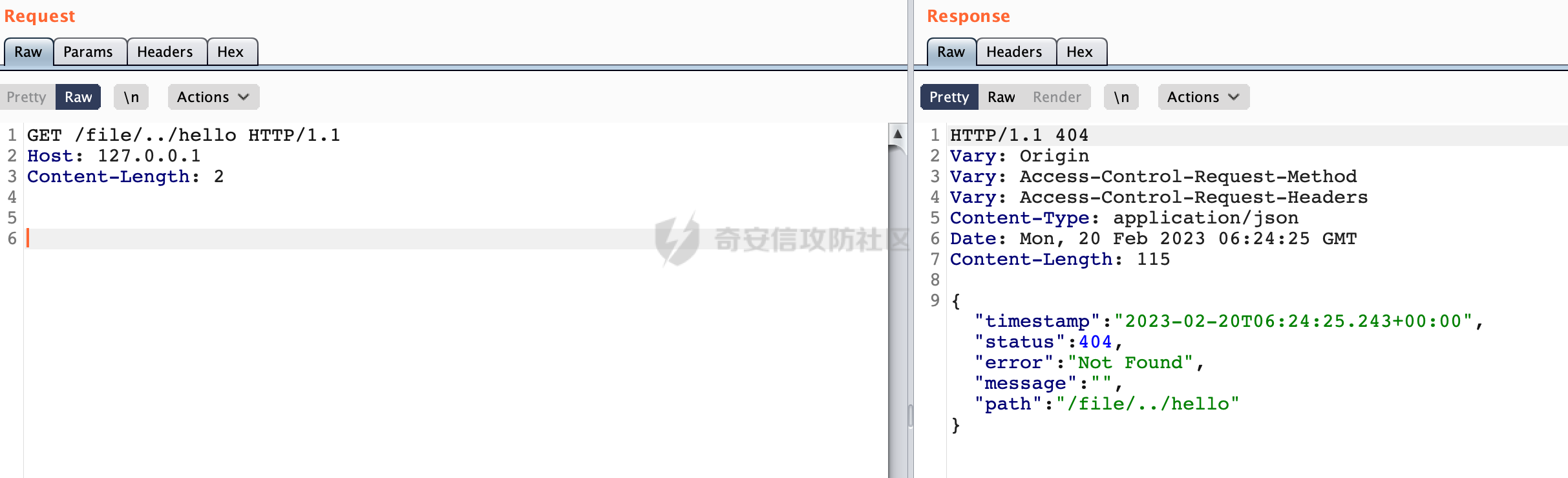 这里也解释了类似平时审计中遇到的一些鉴权措施缺陷,为什么没办法结合`../`进行绕过的原因。例如如下的例子: 在Filter中以/system/login开头的接口是白名单,不需要进行访问控制(登陆页面所有人都可以访问),其他接口都需要进行登陆检查,防止未授权访问: ```Java String uri = request.getRequestURI(); if(uri.startsWith("/system/login")) { //登陆接口设置白名单 filterChain.doFilter(request, response); } ..... ..... ``` 从代码上看确实可以通过构造类似`/system/login/../admin/userInfo`的方式进行访问,绕过鉴权Filter的处理,但是在后续解析时,若当前alwaysUseFullPath为true时,此时解析调用的是getPathWithinApplication,不会对跨目录进行标准化处理,最终找不到对应的handler,返回404状态码,即使绕过了Filter也没办法进行漏洞利用。 0x04 解析器 ======== 4.1 AntPathMatcher&PathPattern ---------------------------------- ### 4.1.1 各版本差异 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration是Spring Boot中关于Spring MVC自动配置类,对比下2.6之前之后的两个版本,可以发现2.6及之后版本多了个PathPatternParser的实现: 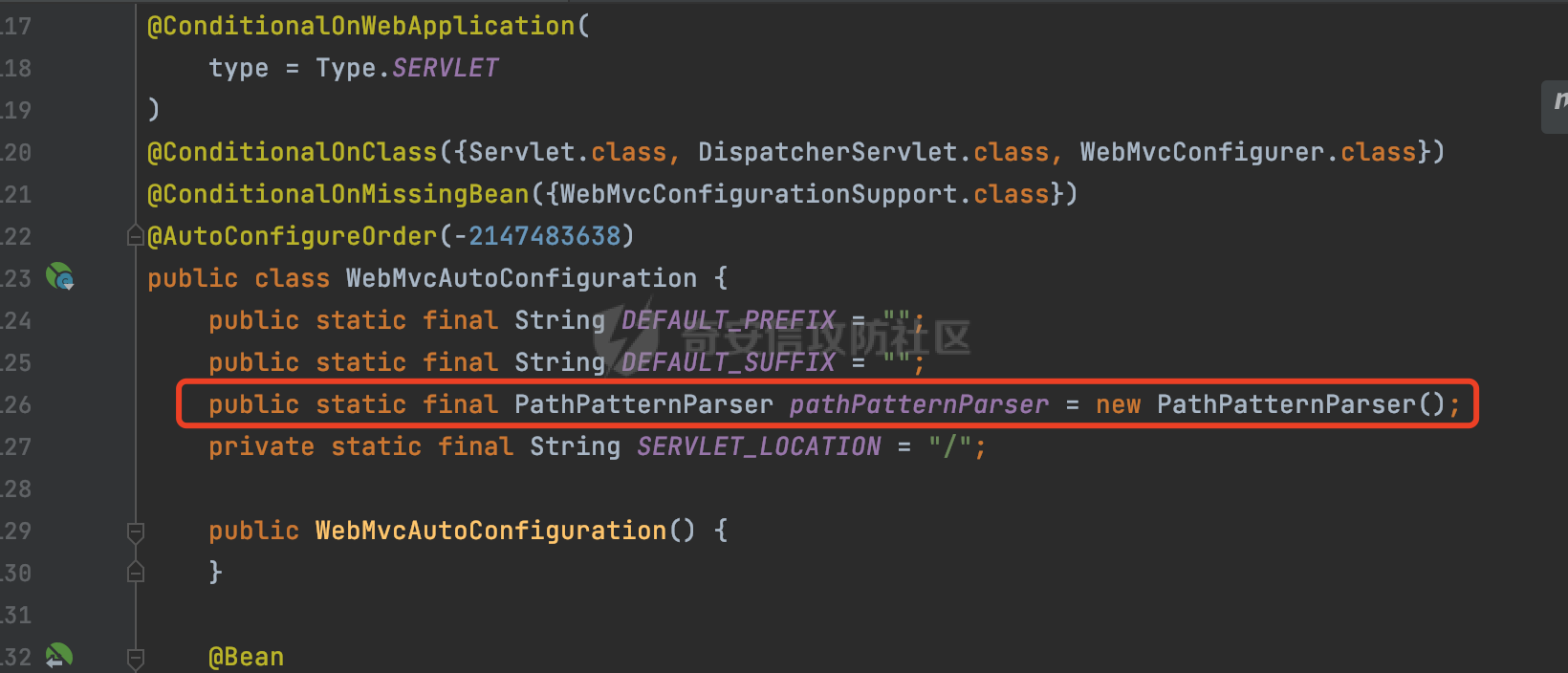 此外,WebMvcAutoConfiguration自动配置类中包含了一个静态类WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter,通过这里加载的WebMvcProperties内容也可以看出来具体的差异: - 在 2.6之前,默认使用的是AntPathMatcher(具体配置在org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcProperties.Pathmatch),查看具体的代码: 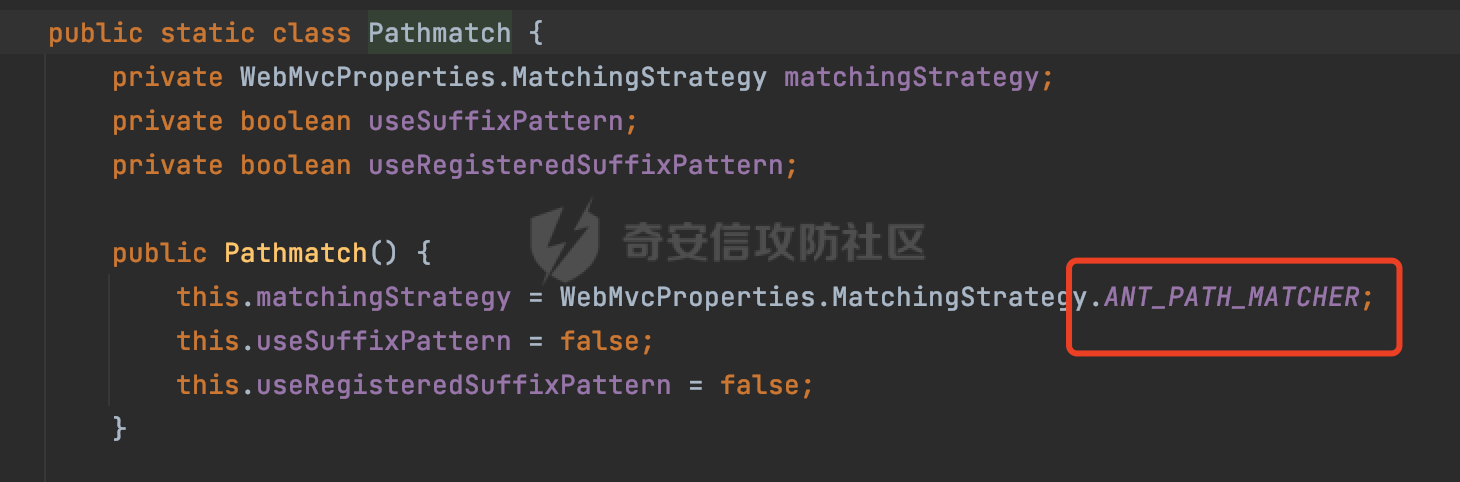 - 2.6.0及之后就变成了PathPattern了: 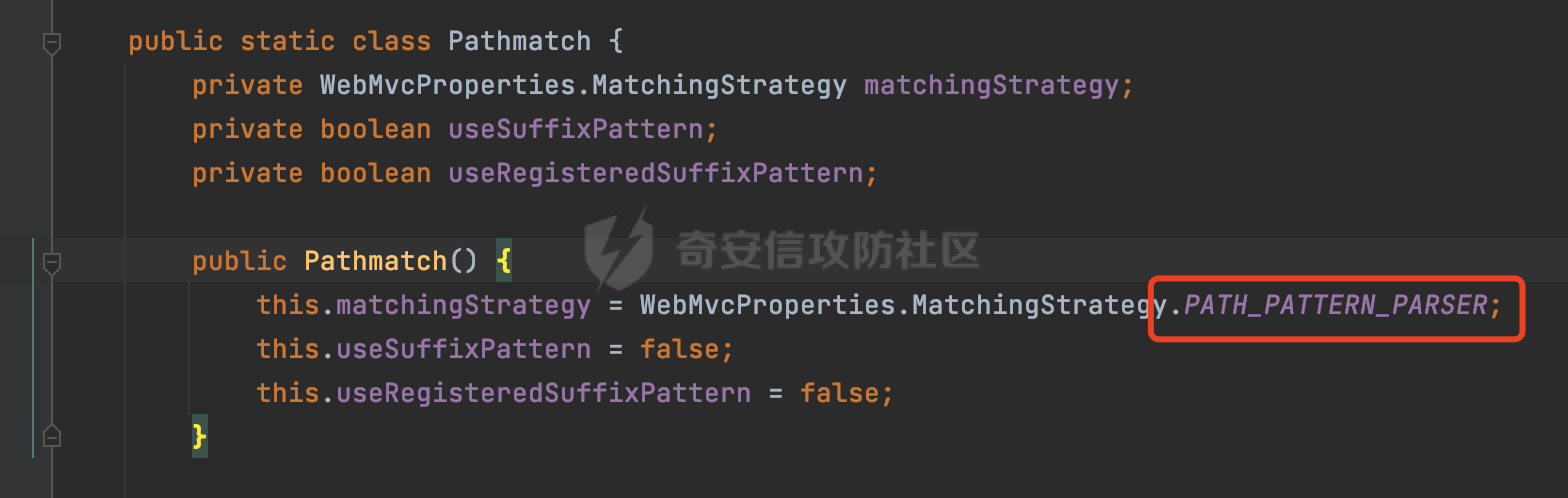 ### 4.1.2 AntPathMatcher AntPathMatcher所属模块为`spring-core`,对应class`org.springframework.util.AntPathMatcher`。一般用于类路径、文件系统和其它资源的解析。 查看官方文档,可以知道AntPathMatcher支持的Path匹配规则如下: | 规则 | 作用 | |---|---| | ? | 匹配任意单字符 | | \* | 匹配0或者任意数量的字符 | | \*\* | 匹配0或者任意层级的目录 | | {spring:正则表达式} | 匹配到的path内容赋值给spring变量 | 简单分析下具体的解析过程: 2.6之前的Spring会使用PatternsRequestCondition通过AntPathMatcher来进行URL匹配:  具体的匹配在org.springframework.util.AntPathMatcher#doMatch方法,首先调用tokenizePattern()方法将pattern分割成了String数组,如果是全路径并且区分大小写,那么就通过简单的字符串检查,看看path是否有潜在匹配的可能,没有的话返回false: 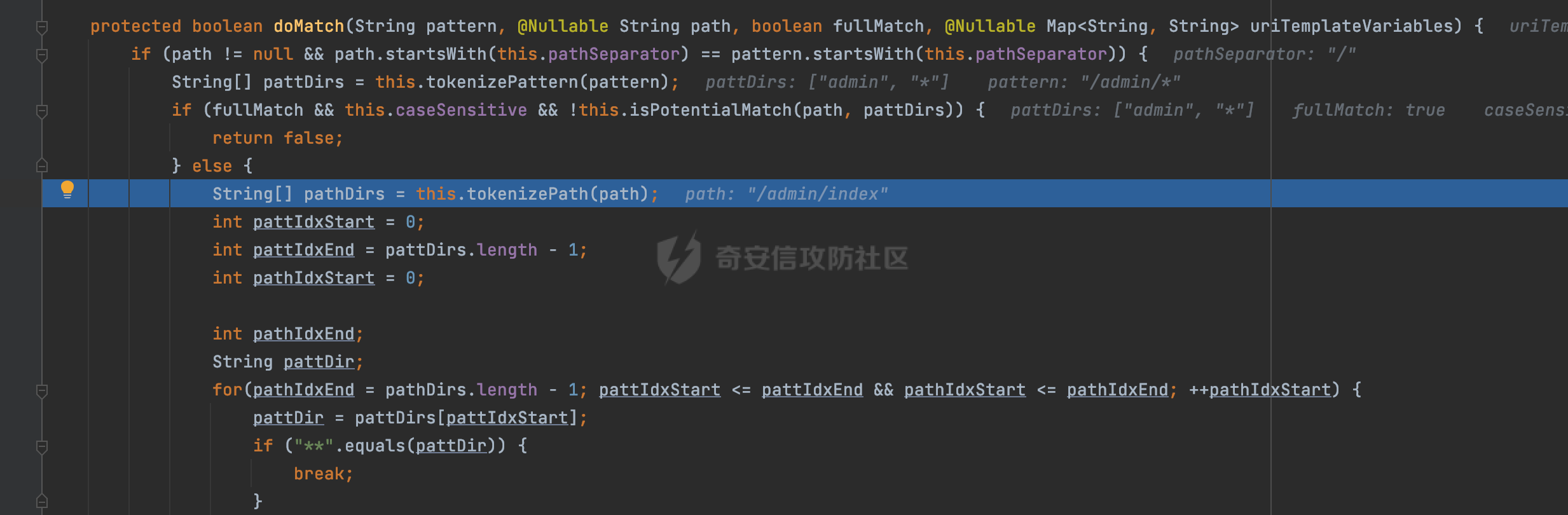 然后调用tokenizePath()方法将需要匹配的path分割成string数组,主要是通过java.util 里面的StringTokenizer来处理字符串:  这里有个属性trimTokens(**从Spring Framework 4.3.0+开始, AntPathMatcher将 trimTokens 设置为false**):  可以看到这个属性主要是用于消除path中的空格(之前由于与SpringSecurity的解析差异导致了CVE-2016-5007、CVE-2020-17523): 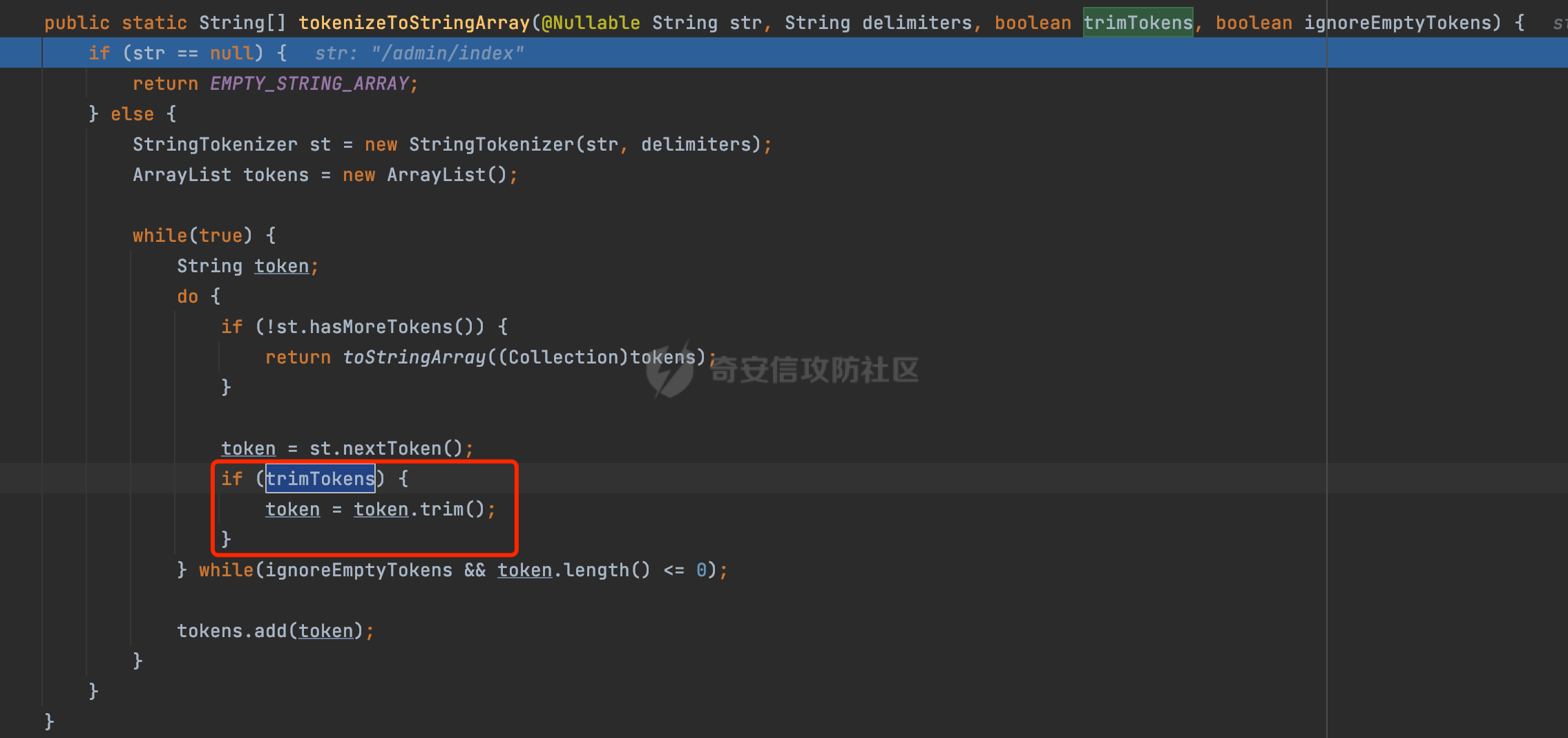 后面就是pathDirs和pattDirs两个数组从左到右开始匹配,主要是一些正则的转换还有通配符的匹配。例如/admin/\*的`*`实际上是正则表达式`.*`通过java.util.regex.compile#matcher进行匹配: 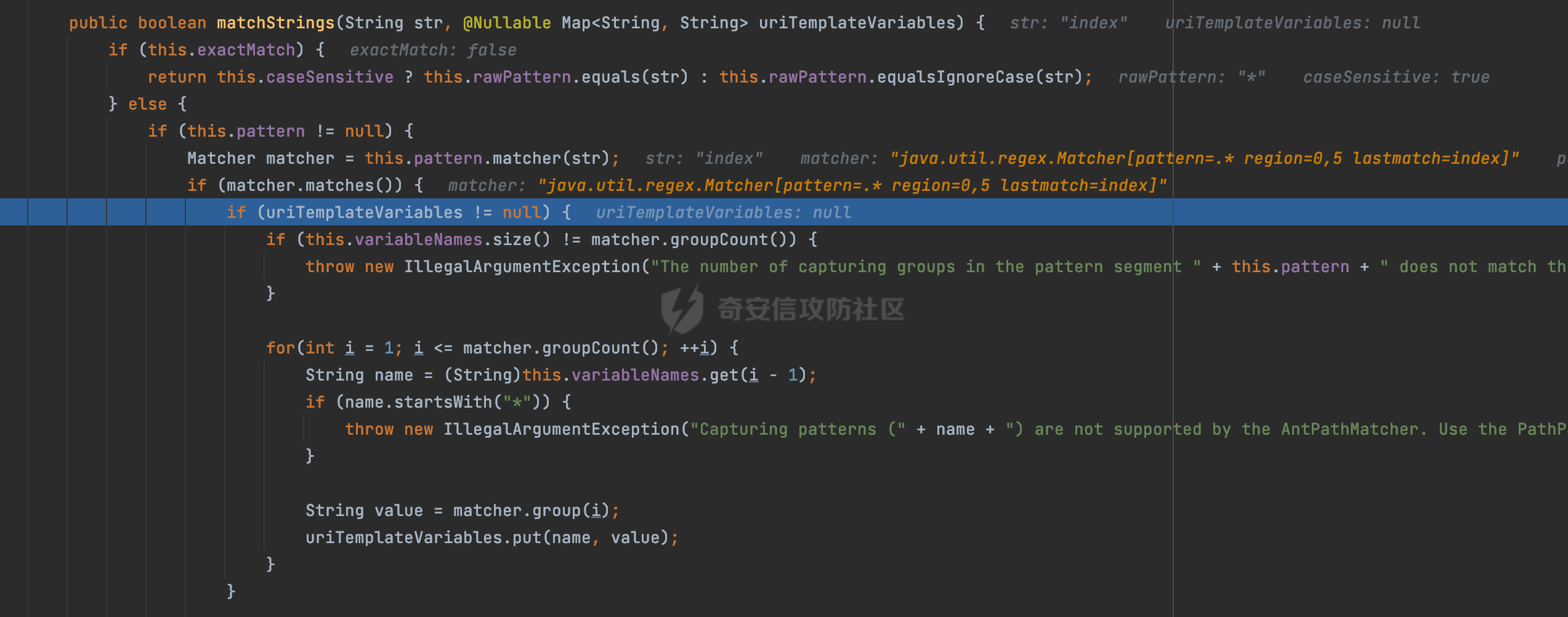 ### 4.1.3 PathPattern PathPattern是Spring5新增的API,所属模块为`spring-web`,对应class `org.springframework.web.util.pattern.PathPattern`。 查看官方文档: Representation of a parsed path pattern. Includes a chain of path elements for fast matching and accumulates computed state for quick comparison of patterns. `PathPattern` matches URL paths using the following rules: - `?` matches one character - `*` matches zero or more characters within a path segment - `**` matches zero or more *path segments* until the end of the path - `{spring}` matches a *path segment* and captures it as a variable named "spring" - `{spring:[a-z]+}` matches the regexp `[a-z]+` as a path variable named "spring" - `{*spring}` matches zero or more *path segments* until the end of the path and captures it as a variable named "spring" **Note:** In contrast to `[AntPathMatcher](https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/current/javadoc-api/org/springframework/util/AntPathMatcher.html)`, `**` is supported only at the end of a pattern. For example `/pages/{}` is valid but `/pages/{}/details` is not. The same applies also to the capturing variant `{*spring}`. The aim is to eliminate ambiguity when comparing patterns for specificity. 根据官方文档的描述,其实\**跟AntPathMatcher匹配规则区别不大,PathPattern在保持其匹配规则的基础上,新增了`{*spring}`的语法支持。\*\* `{*spring}`表示匹配余下的path路径部分并将其赋值给名为spring的变量(变量名可以根据实际情况随意命名,与`@PathVariable`名称对应即可)。同时,\**`{*spring}`是可以匹配剩余所有path的,类似`/**`,只是功能更强,可以获取到这部分动态匹配到的内容。** 简单分析下具体的解析过程: 2.6以及之后的Spring会使用PathPatternsRequestCondition通过PathPattern来进行URL匹配: 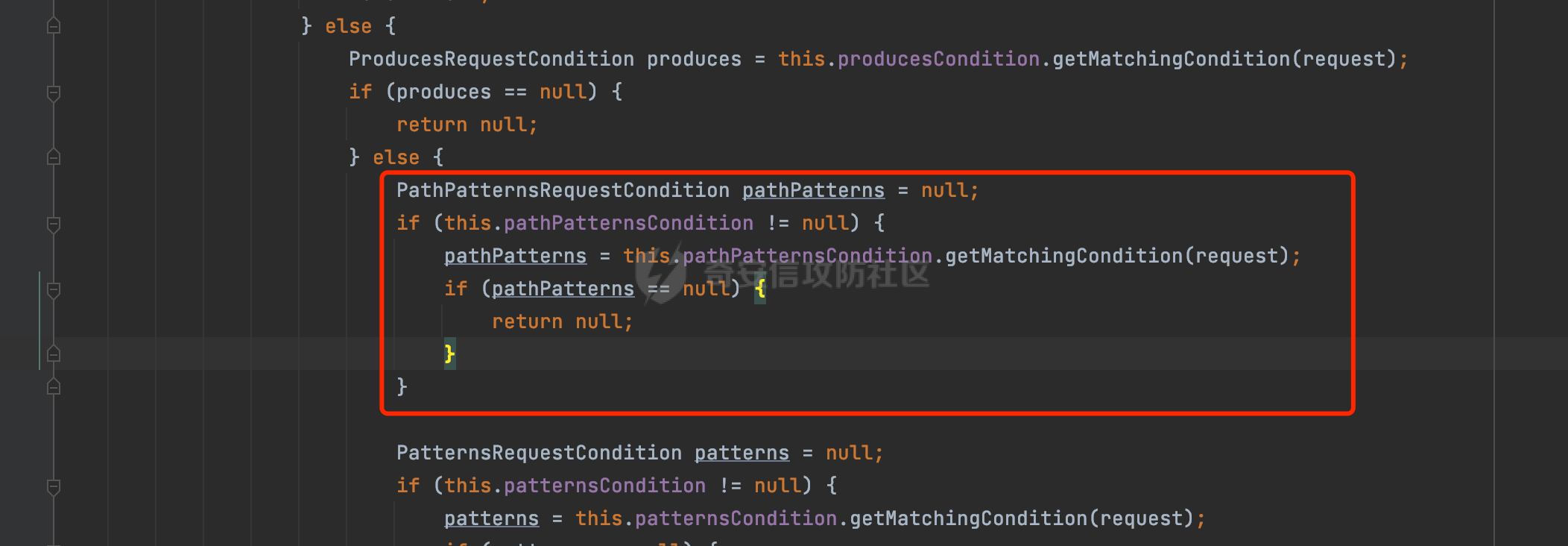 可以看到跟之前版本使用的PatternsRequestCondition不同的是,此时的路径解析已经不受到类似SuffixPatternMatch属性的影响了: 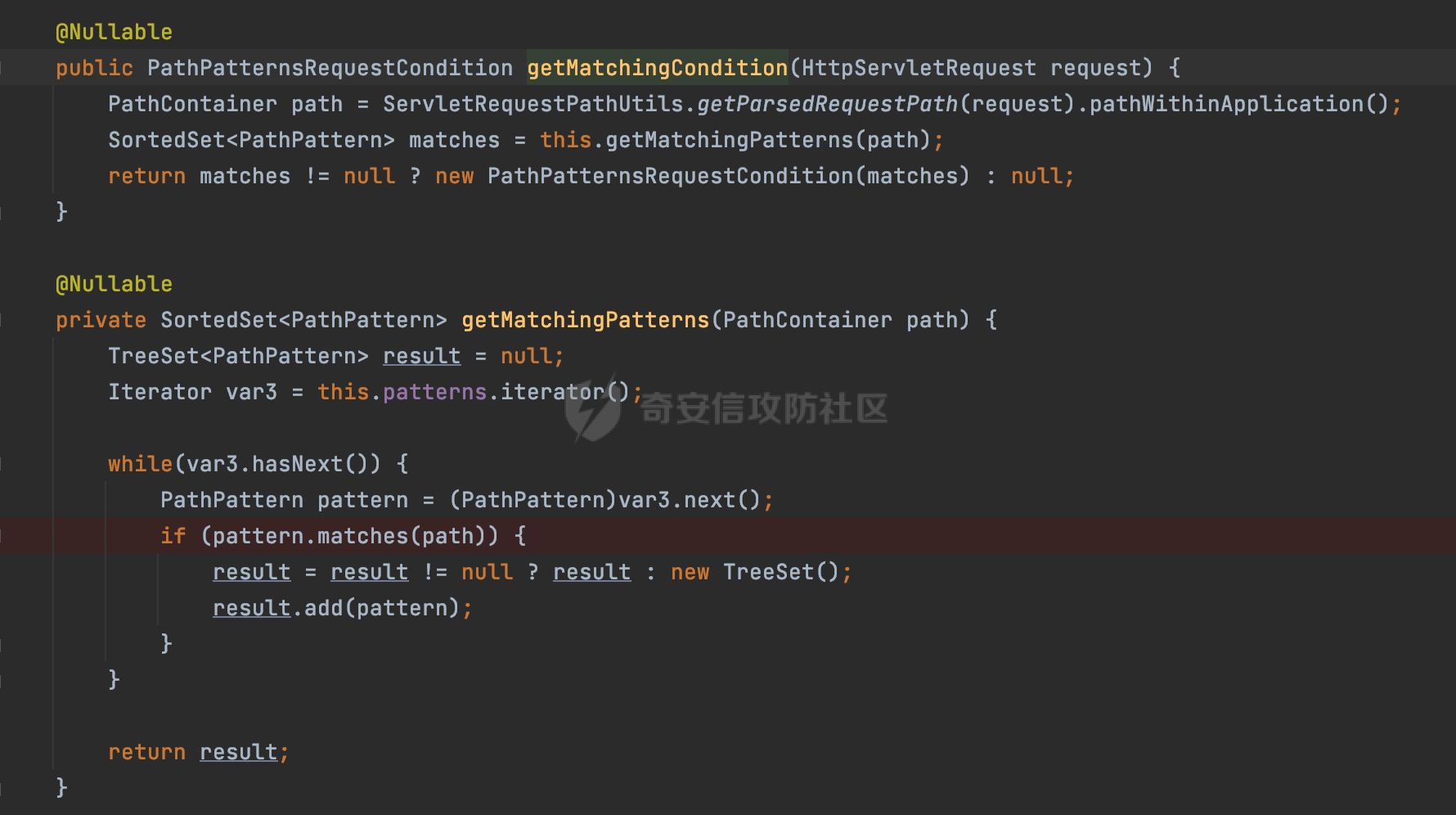 主要在org.springframework.web.util.pattern.PathPattern#matches方法: 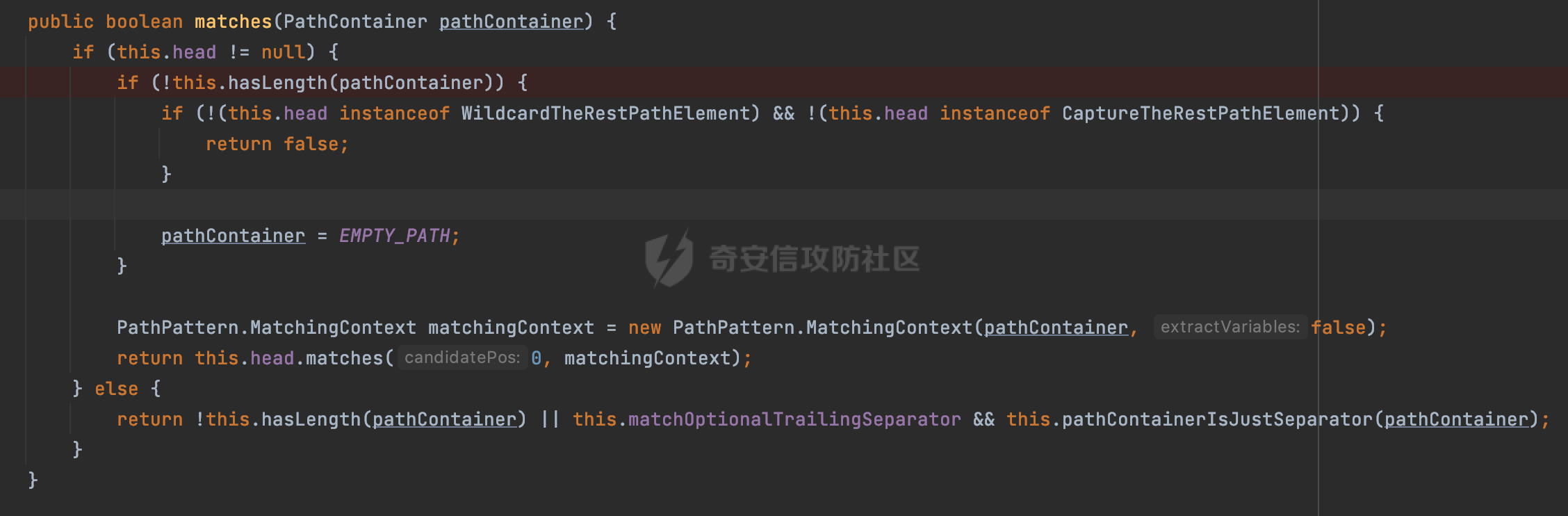 首先会根据/将URL拆分成多个**PathElement**对象,以/admin/index/为例,这里会分割成多个对象,然后根据PathPattern的链式节点中对应的PathElement的matches方法逐个进行匹配: 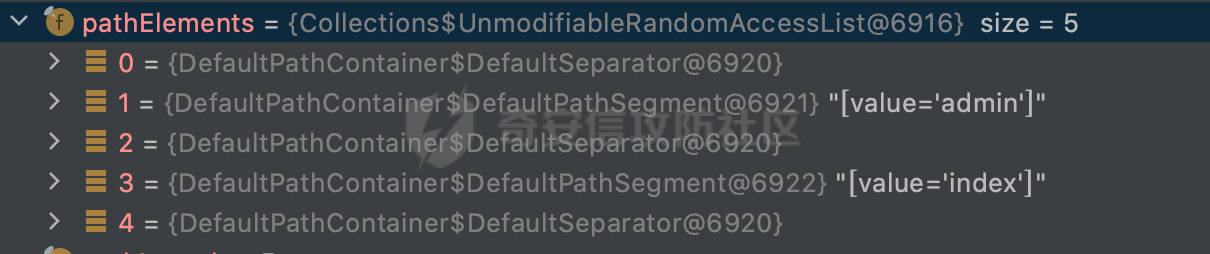 以Pattern为/admin/\*为例,首先第一个元素是分隔符`/`,会调用SeparatorPathElement的matches方法进行处理: 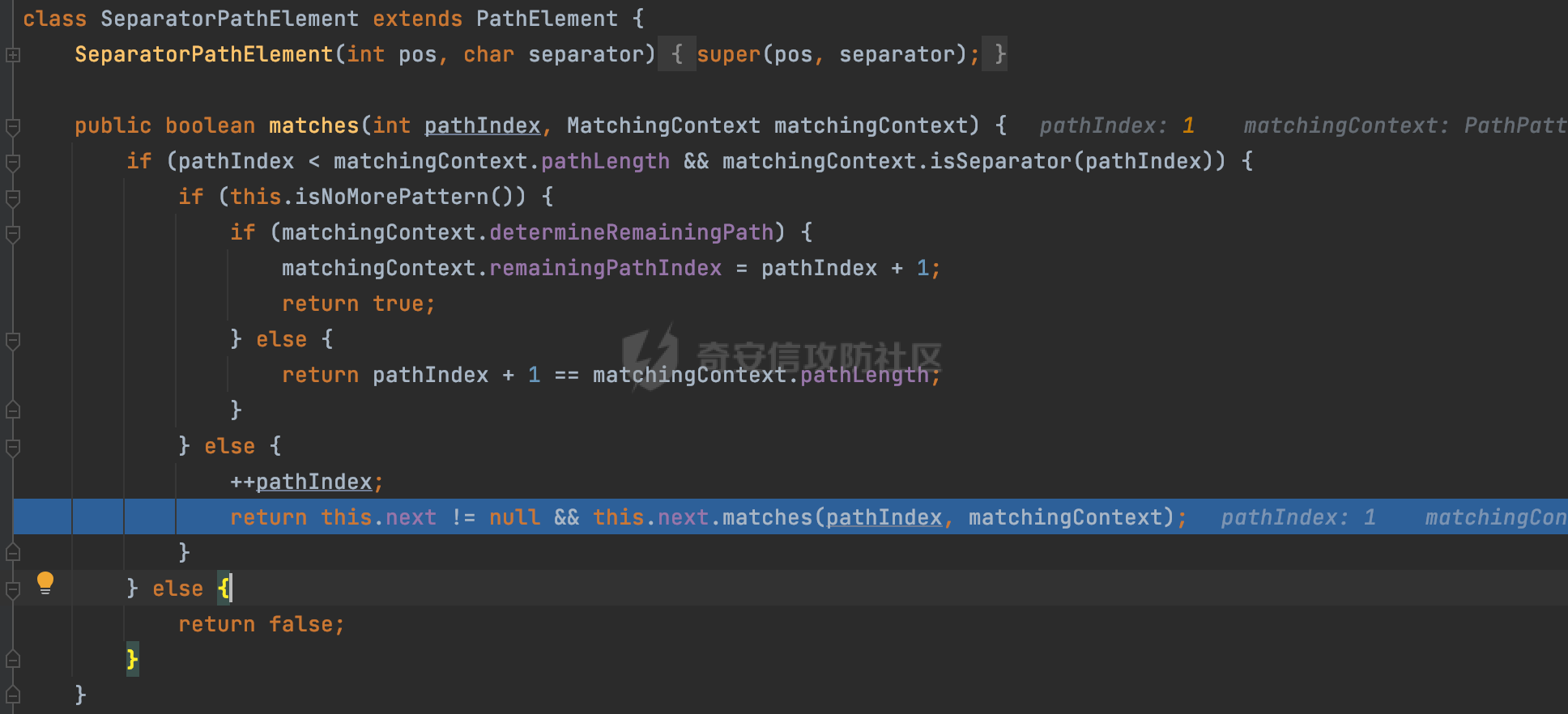 处理完后pathIndex++,继续遍历下一个元素进行处理,下一个是admin,会通过LiteralPathElement#matches进行处理,同样的最后会对pathindex进行+1,然后继续遍历PathElement元素直到遍历结束为止: 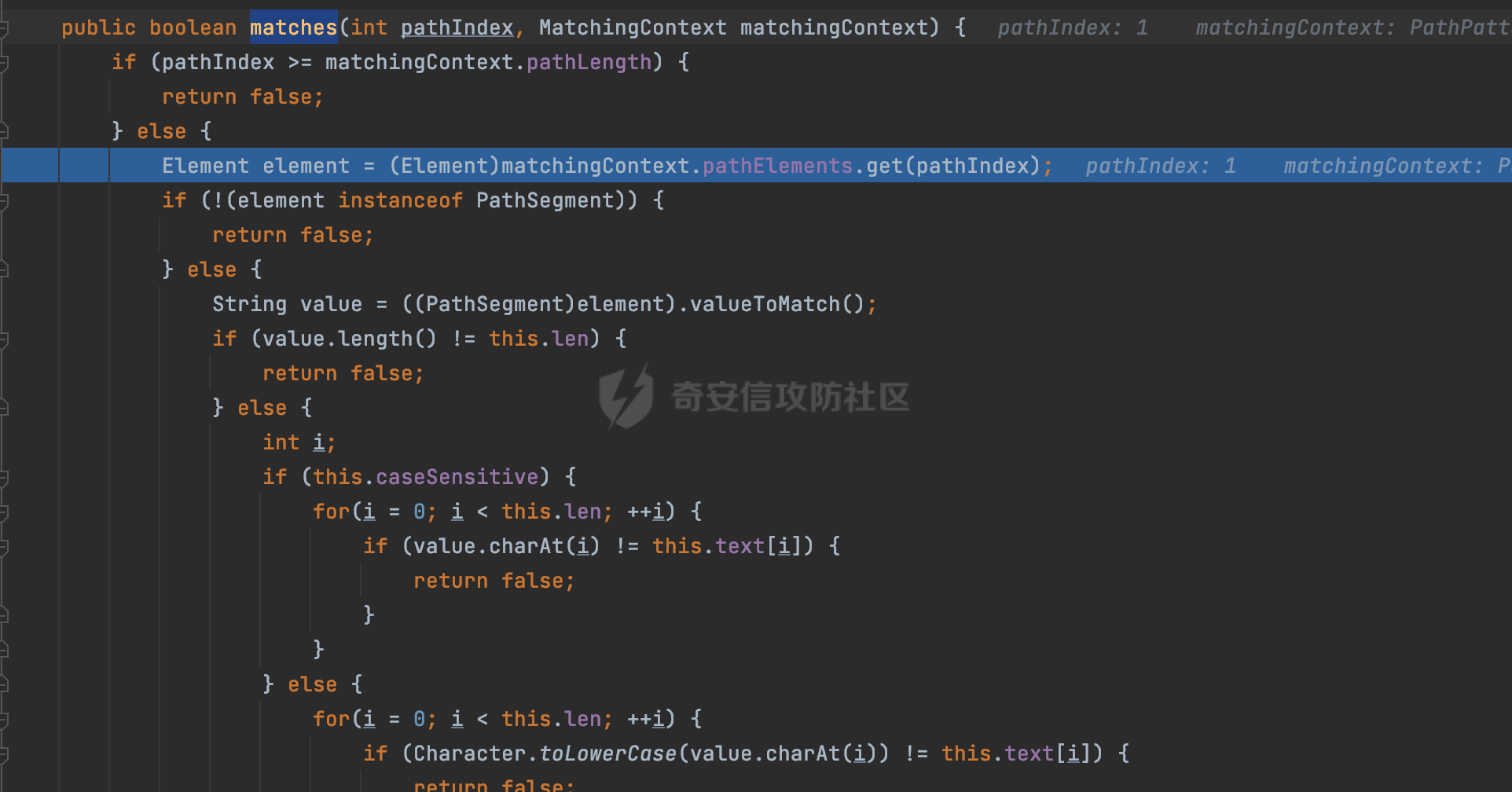 在最后会根据matchOptionalTrailingSeparator(此参数为true时,默认为true)进行一定的处理,如果Pattern尾部没有斜杠,请求路径有尾部斜杠也能成功匹配(类似TrailingSlashMatch的作用):  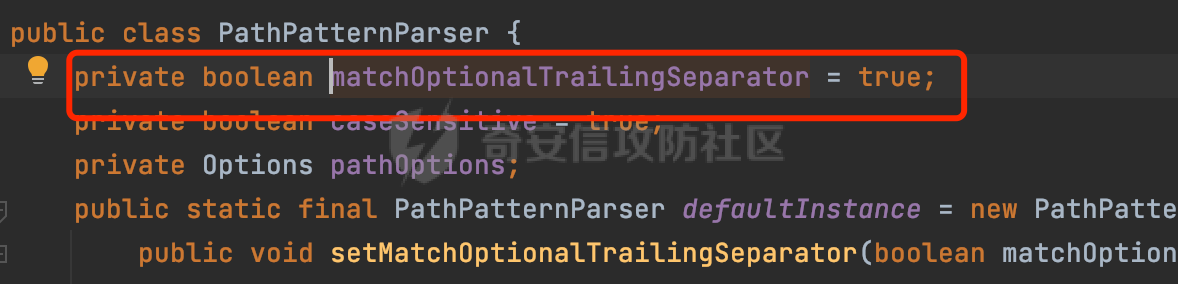 所以这里/admin/index和/admin/index/都是可以访问到对应的路由的。 除此之外,根据不同Pattern的写法,还有很多PathElement。 ### 4.1.4 两者的区别 首先,PathPattern新增{\*spring}语法支持,功能更加的强大。除此以外,相比AntPathMatcher,还有以下区别: - PathPattern通配符只能定义在尾部,而AntPathMatcher可以在中间:  - AntPathMatcher默认使用`/`作为分隔符。也可以根据实际情况自行指定分隔符(例如windows是`\`,Linux是`/`,包名是`.`),这点从其构造器可以看出:  因为PathPattern的构造器不是public的,只能通过`PathPatternParser`创建其实例,这里构造方法初始化了pathOptions变量:  查看Options.HTTP\_PATH,可以看到跟AntPathMatcher一样,默认使用`/`作为分隔符:  但是**PathPattern只支持两种分隔符(/和.)**。
发表于 2023-04-12 09:00:02
阅读 ( 11487 )
分类:
代码审计
2 推荐
收藏
0 条评论
请先
登录
后评论
tkswifty
66 篇文章
×
发送私信
请先
登录
后发送私信
×
举报此文章
垃圾广告信息:
广告、推广、测试等内容
违规内容:
色情、暴力、血腥、敏感信息等内容
不友善内容:
人身攻击、挑衅辱骂、恶意行为
其他原因:
请补充说明
举报原因:
×
如果觉得我的文章对您有用,请随意打赏。你的支持将鼓励我继续创作!