问答
发起
提问
文章
攻防
活动
Toggle navigation
首页
(current)
问答
商城
实战攻防技术
活动
摸鱼办
搜索
登录
注册
浅谈Spring与安全约束SecurityConstraint
渗透测试
在Java Web应用程序中,可以通过安全约束(Security Constraint)来实现访问控制。在Spring应用中,同样可以通过相应的安全约束进行访问控制,但是各个中间件与Spring两者间是存在一定的解析差异的,在某种情况下可能存在绕过的可能。
0x00 前言 ======= 在Java Web应用程序中,可以通过安全约束(Security Constraint)来实现访问控制。 安全约束是一种安全配置,可用于保护Web应用程序中的资源,如Servlet、JSP、HTML文件等。它定义了可以访问资源的身份验证要求以及访问资源时必须满足的安全约束。 在Servlet规范中定义了如何在Java Web服务器(如Jetty、Tomcat、Wildfly等)上配置安全约束,安全约束是通过定义一组约束来实现的,其中每个约束都是由以下三个元素组成: 1.安全约束名称(Security Constraint Name):这是可选的元素。它主要用于管理和调试安全约束等方面。 2.Web资源集合(Web Resource Collection):这是要保护的Web资源集合,如Servlet、JSP、HTML文件等。 3.角色名(Role Name):这是允许访问该Web资源集合的角色。角色名可以是已知的角色(如tomcat、root)或应用程序中定义的角色名称。如果用户已经验证并且具有访问角色,则可以访问该Web资源集合。 0x01 关于SecurityConstraint ========================= 1.1 常见使用方式 ---------- 3通常,安全约束通过在web.xml文件中配置实现。在这个xml文件中,我们可以定义角色,如何验证用户,以及哪些角色可以访问哪些受保护的Web资源集合。 3例如如下的例子: 3通过定义SecurityConstraint元素,定义了一个名为"Private"的Web资源集合,它包括URL模式`/private/*`和HTTP GET方法。它还指定只有具有“admin”角色的用户才能访问这些资源。 ```XML <security-constraint> <web-resource-collection> <web-resource-name>Private</web-resource-name> <url-pattern>/private/*</url-pattern> <http-method>GET</http-method> </web-resource-collection> <auth-constraint> <role-name>admin</role-name> </auth-constraint> </security-constraint> ``` 为了充分利用Spring Boot提供的自动配置和灵活性,除了使用web.xml进行配置以外,还可以通过@Configuration的方法进行配置,例如Tomcat的话,可以通过TomcatServletWebServerFactory来配置Tomcat中的安全约束。 1.2 具体实现原理 ---------- 为了方便环境的搭建,下面的场景都是基于Springboot的场景进行讨论。Spring Boot默认支持Tomcat,Jetty,和Undertow作为底层容器,简单看看各个场景下的具体实现原理: ### 1.2.1 tomcat Springboot默认使用的是tomcat,只需要引入spring-boot-starter-web依赖,应用程序就默认引入了tomcat。在Tomcat中,可以通过`TomcatServletWebServerFactory`来配置安全约束,例如如下的例子,对于`/admin/*`的路径,只有admin角色才可以访问: ```Java @Configuration public class SecurityConfig { @Bean public TomcatServletWebServerFactory servletContainer() { TomcatServletWebServerFactory tomcatServletContainerFactory = new TomcatServletWebServerFactory(); tomcatServletContainerFactory.addContextCustomizers(new TomcatContextCustomizer() { @Override public void customize(Context context) { SecurityConstraint securityConstraint = new SecurityConstraint(); SecurityCollection collection = new SecurityCollection(); collection.addPattern("/admin/*"); securityConstraint.addCollection(collection); securityConstraint.addAuthRole("admin"); context.addConstraint(securityConstraint); } }); return tomcatServletContainerFactory; } } ``` 在Tomcat中,主要是在`org.apache.catalina.authenticator.AuthenticatorBase#invoke`处理安全约束的。在这里会根据请求的 URI 和配置的安全约束来确定是否需要进行身份验证和授权。 查看具体的解析流程: 首先判断了是否启用了缓存`this.cache`。如果启用了缓存,会尝试从缓存中获取用户的身份信息: 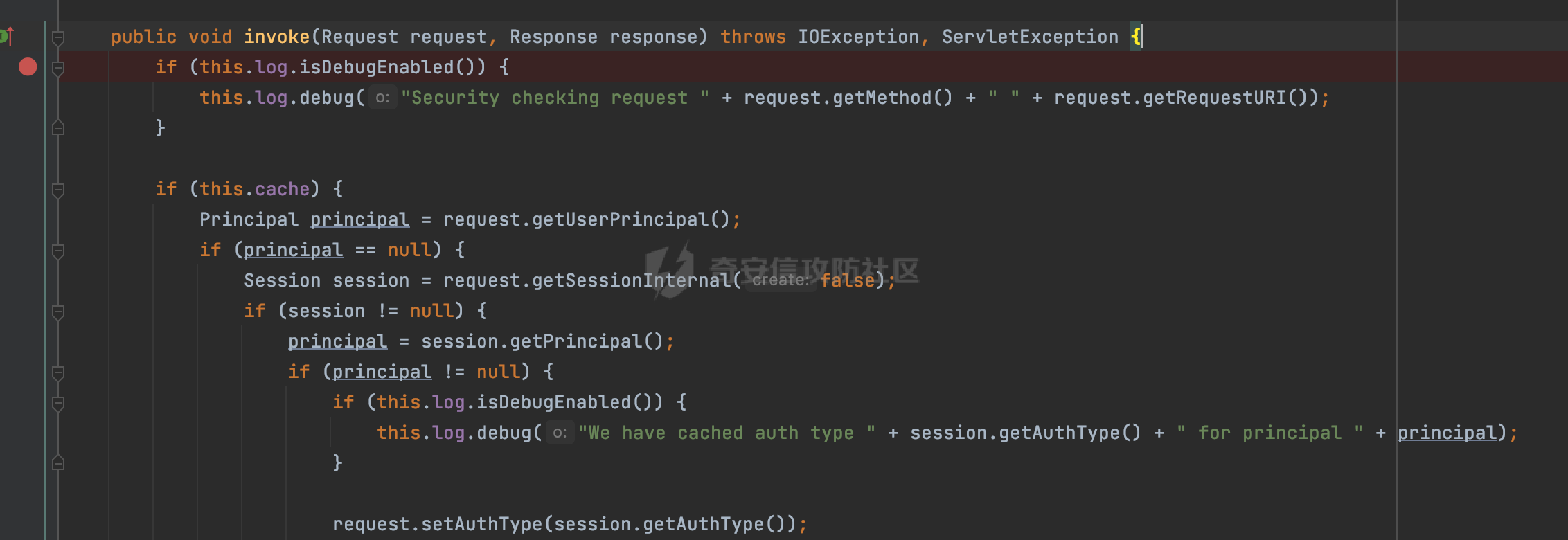 然后获取到当前请求上下文的 `Realm` 对象,并通过调用`realm.findSecurityConstraints(request, this.context)` 查找与请求匹配的安全约束:  查看`findSecurityConstraints`方法的具体实现,首先如果配置了安全约束的话,会从reqeust请求中国呢获取当前请求的uri,用于遍历`SecurityConstraint[]`,查找适用于当前请求的安全约束: 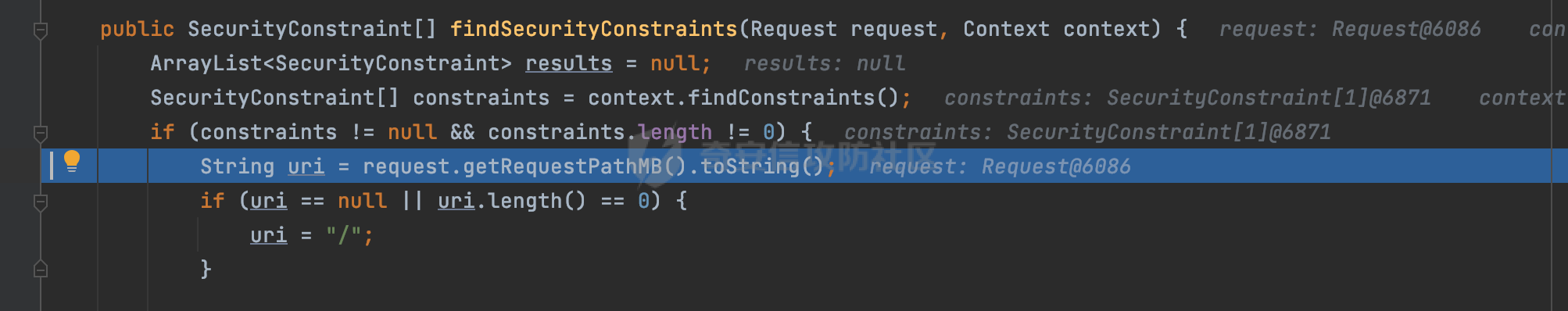 然后获取当前安全约束的路径模式,如果与当前请求的uri相等,或者路径模式为空字符串并且请求的 URI 为根路径`/`,则匹配成功,然后继续检查当前请求的 HTTP 方法是否在安全约束定义的方法列表中,是的话把当前的安全约束添加到结果中: 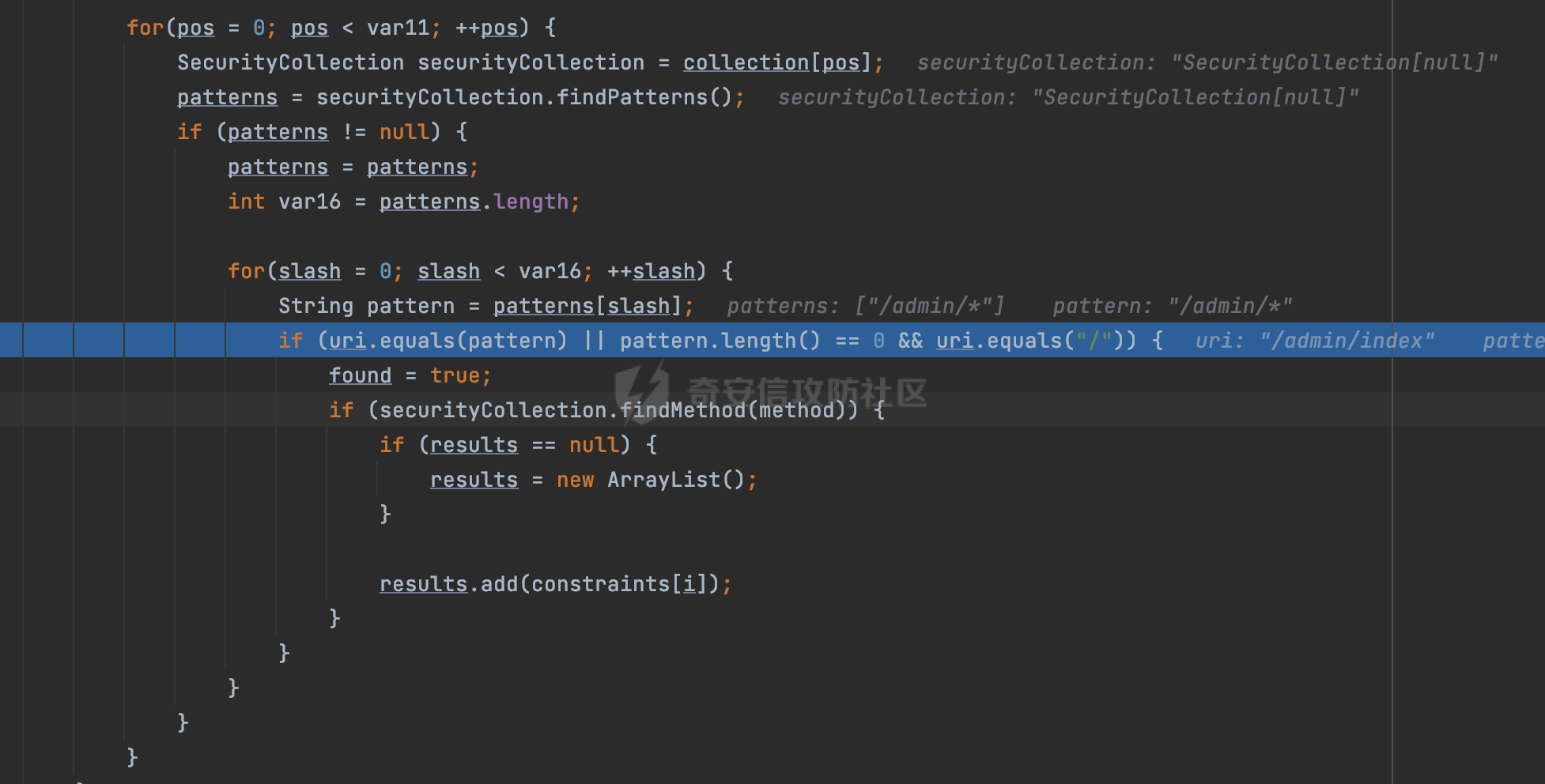 如果直接匹配失败的话,会继续执行其他匹配逻辑。 同样的首先获取路径模式,然后检查路径模式是否以 `/` 开头、以 `/*` 结尾,并且长度大于等于当前最长匹配路径长度。是的话首先判断路径模式pattern长度是否是2,其实就是匹配`/*`的模式(表示匹配任意路径),如果是的话说明匹配成功: 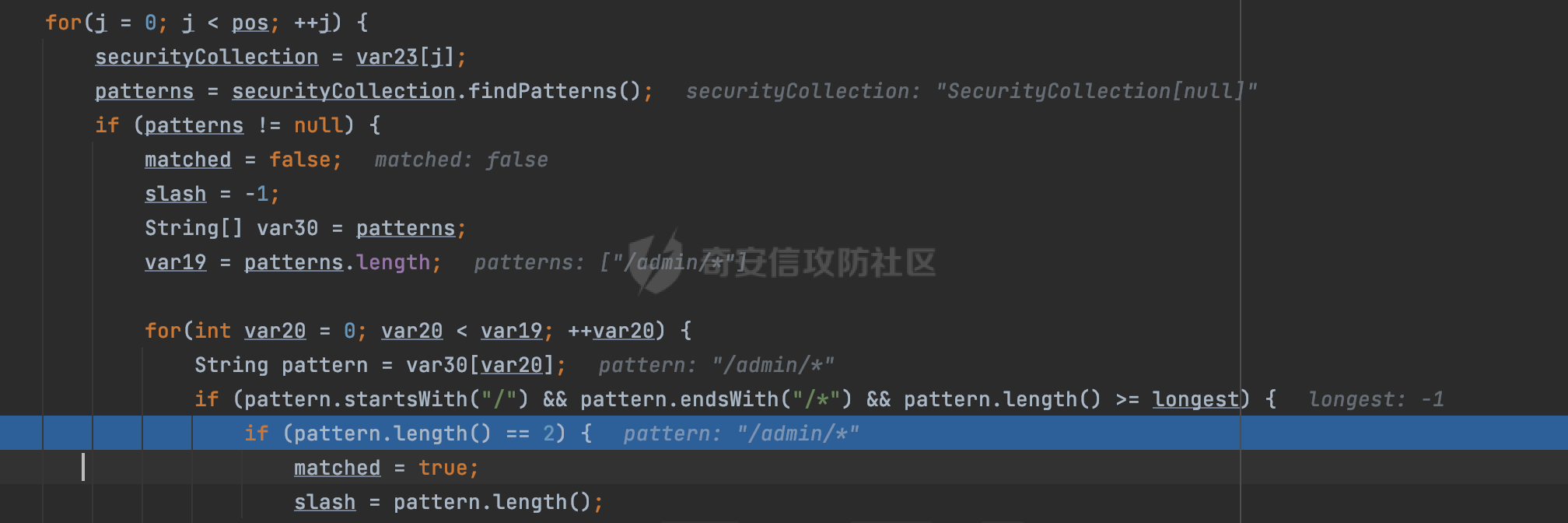 另一种情况会调用regionMatches方法比较字符串的一部分区域是否与另一个字符串的相应区域相等。这里主要是检查路径模式与请求的 URI 在除最后两个字符(`/*`)外的部分是否完全匹配:  如果匹配成功的话,同样的会检查当前请求的 HTTP 方法是否在安全约束中定义的方法列表中,是的话把当前的安全约束添加到结果中。 如果匹配失败的话,会检查路径模式是否以 `*.` 开头,用于匹配以指定后缀结尾的 URI:  最后还有一种情况是检查路径模式是否与根路径(`/`)完全匹配: 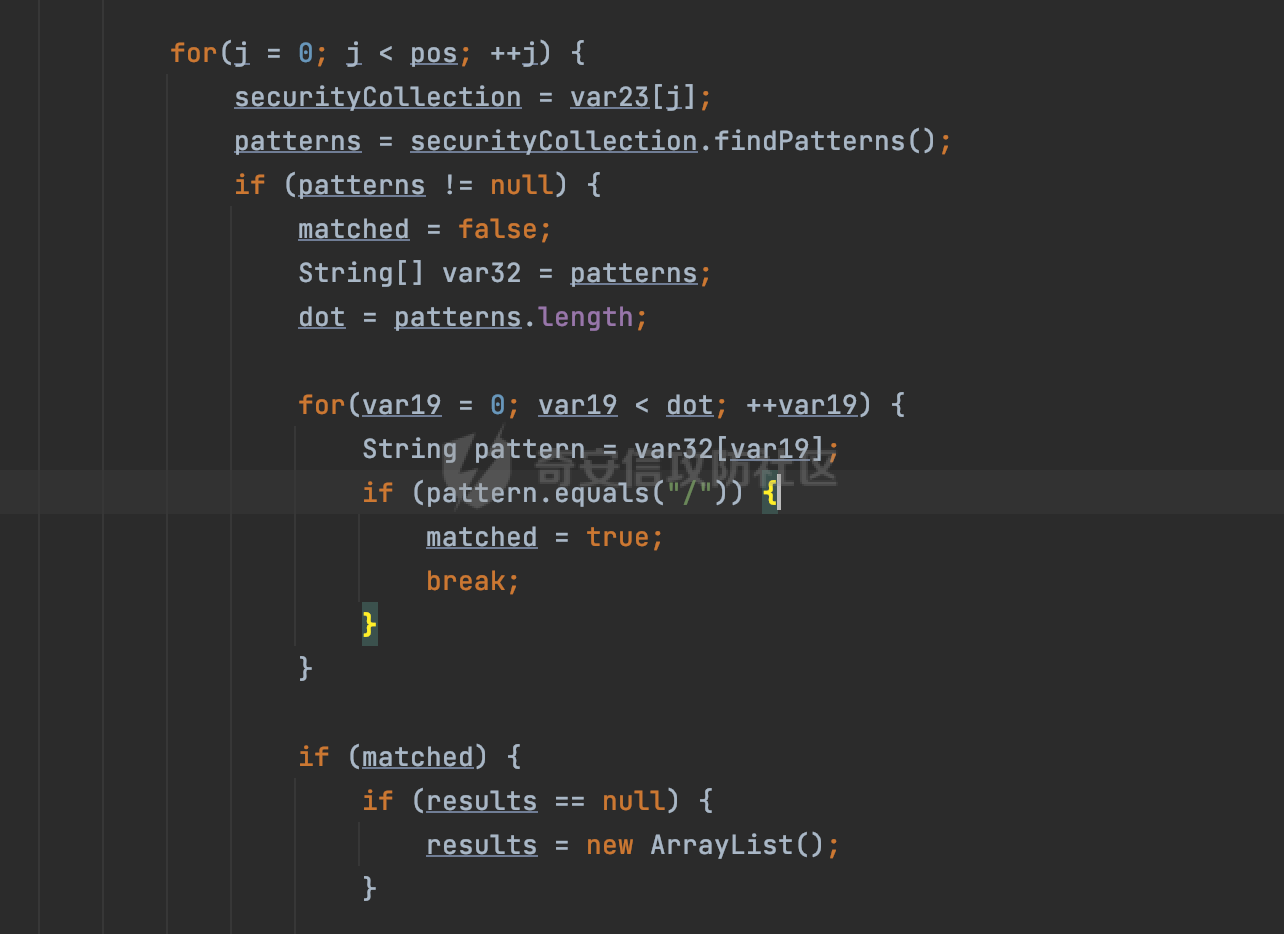 处理完上述逻辑后会返回包含匹配当前请求的安全约束结果列表。如果返回的constraints为null,说明请求不受任何安全约束的限制,则直接调用下一个处理器进行请求处理。  否则会进行对应权限的检查,例如如下是进行资源权限的检查:如果请求不满足资源权限要求,则直接返回,不继续处理请求。 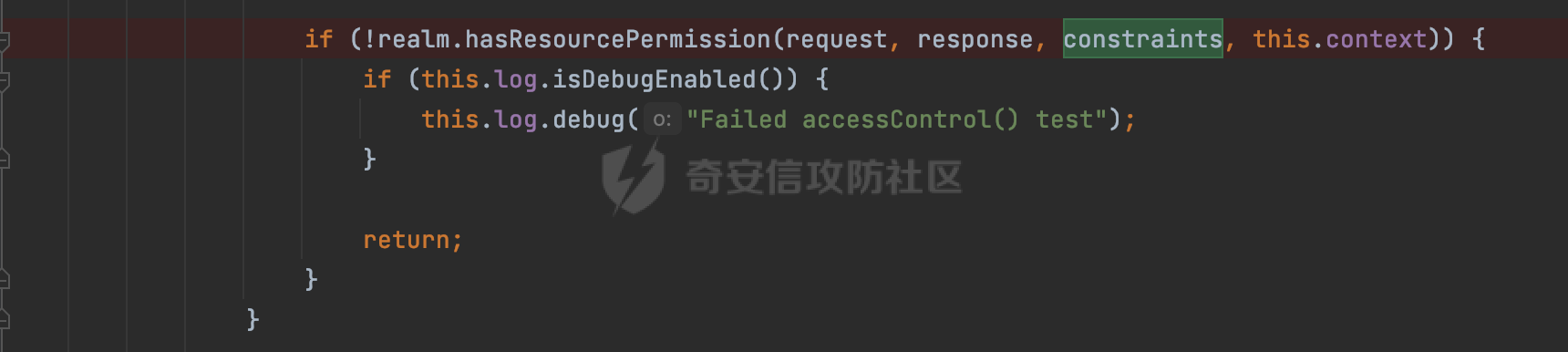 以上就是Tomcat中关于安全约束的大致解析逻辑。 ### 1.2.2 Jetty 使用Jetty的方式很简单,去除springboot 中默认的Tomcat 依赖后引入Jetty即可: ```XML <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jetty</artifactId> </dependency> ``` 在Jetty中,可以`JettyServletWebServerFactory` 来配置安全约束,例如如下的例子,对于`/admin/*`的路径,只有admin角色才可以访问: ```Java @Configuration public class SecurityConfig { @Bean public JettyServletWebServerFactory servletWebServerFactory() { JettyServletWebServerFactory factory = new JettyServletWebServerFactory(); factory.addServerCustomizers(server -> { ServletContextHandler contextHandler = (ServletContextHandler) server.getHandler(); ConstraintSecurityHandler securityHandler = (ConstraintSecurityHandler) contextHandler.getSecurityHandler(); ConstraintMapping mapping = new ConstraintMapping(); mapping.setPathSpec("/admin/*"); Constraint constraint = new Constraint(); constraint.setName("auth"); constraint.setRoles(new String[] { "admin" }); constraint.setAuthenticate(true); mapping.setConstraint(constraint); securityHandler.addConstraintMapping(mapping); }); return factory; } } ``` 可以看到请求/admin/page返回403: 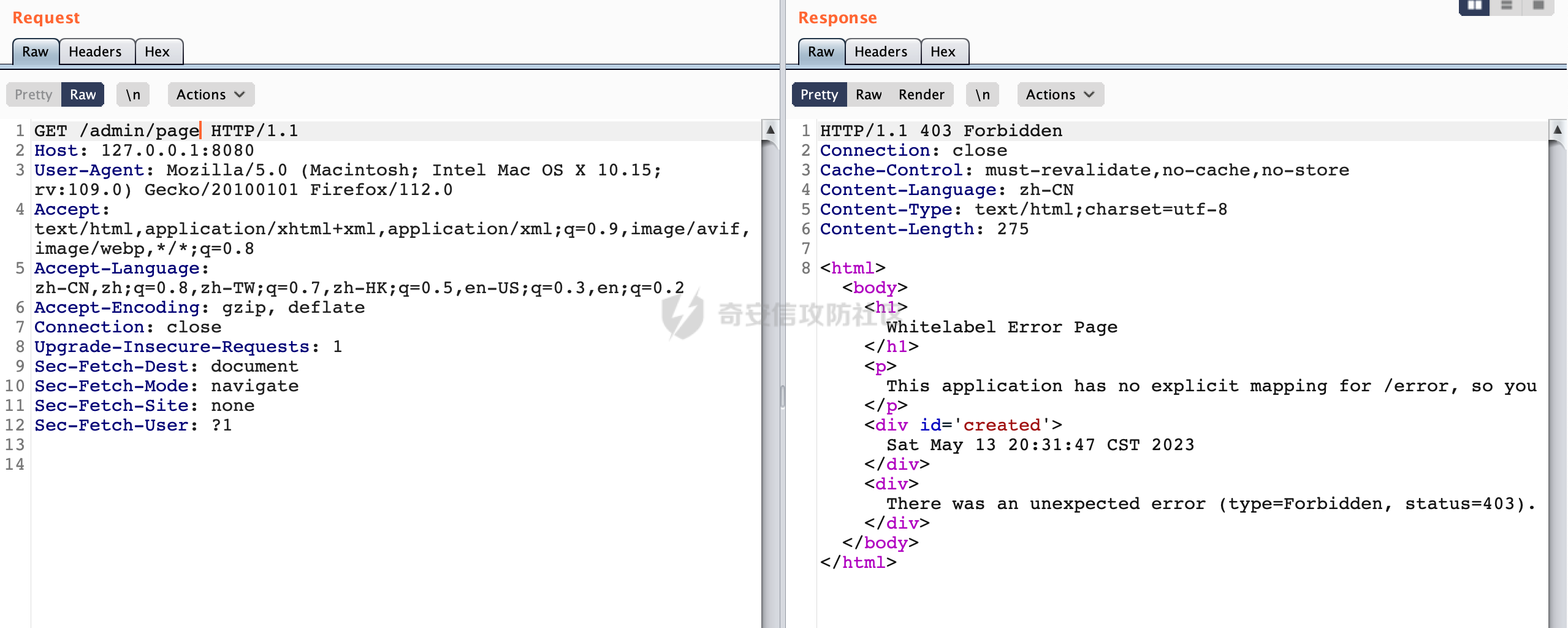 查看在Jetty中是如何实现安全约束的: 当一个HTTP请求到达Jetty服务器时,其请求处理流程大致如下: ```Java Server -> ServerConnector -> SelectChannelEndPoint -> HttpChannel -> HttpChannelState -> HttpChannelOverHttp -> HttpParser -> HttpRequest -> Handled By SecurityHandler ``` 其中,SecurityHandler是在HttpChannel的handle方法中被调用的。该方法是Jetty处理请求的核心方法之一。 `org.eclipse.jetty.security.SecurityHandler`是 Jetty 中进行安全控制的基础类,它提供了多种安全约束,可以根据需要组合使用。handle 方法是 SecurityHandler 的核心方法,它被 Jetty 容器调用,用于对请求进行安全约束匹配,会根据检查结果来决定是否允许请求继续进行处理。 在handle 方法的入口处下一个断点,查看具体的执行过程: 首先获得当前Handler对象和Authenticator对象。然后调用checkSecurity方法判断当前请求是否需要进行安全处理其法根据 request 对象的 DispatcherType 属性来决定请求的类型,如果是普通的REQUEST或者ASYNC或直接返回TRUE,在检查后,如果启用了 `authenticator` 功能,则会调用 `authenticator.prepareRequest()` 方法,为请求做必要的准备工作: 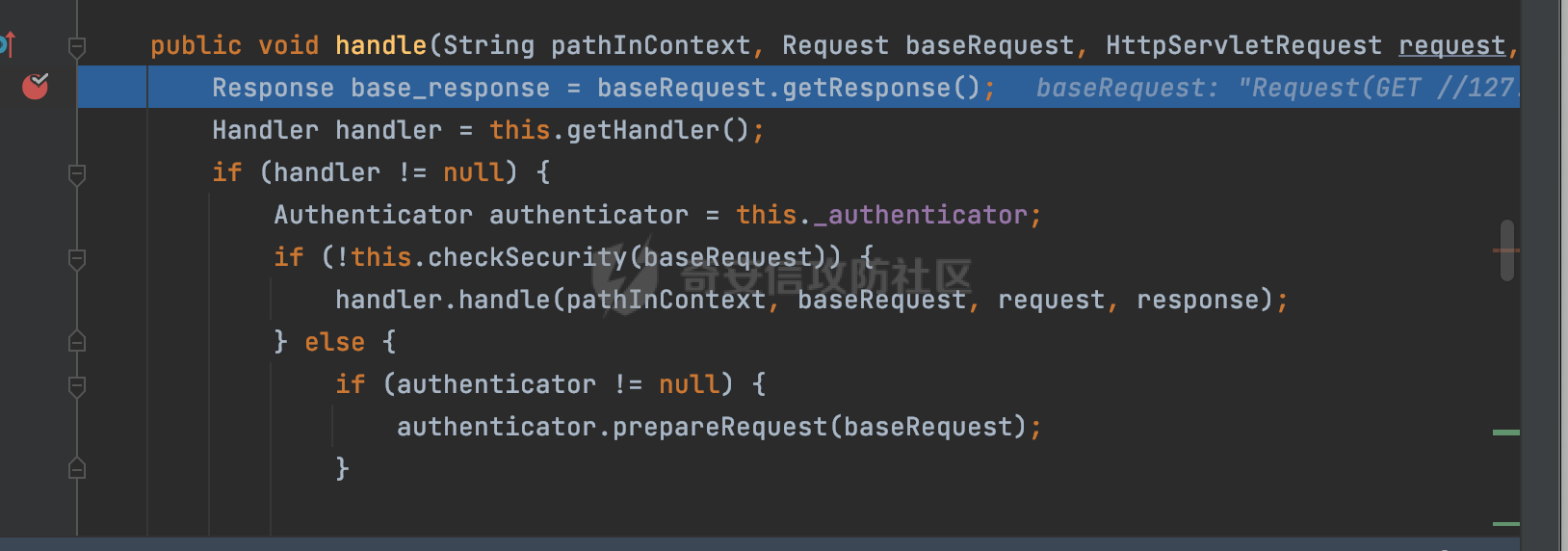 然后通过调用prepareConstraintInfo方法,根据传入的路径和请求信息,获取当前路径的访问限制信息,即 `RoleInfo` 。`RoleInfo` 封装了对当前路径的访问要求,包括需要具备的角色、权限等信息:  跟进查看该方法的具体实现: \_constraintMap 是一个 PathMap 对象,其中存储了在 SecurityHandler 中配置的所有路径和对应的访问权限控制信息。首先调用其match() 方法,根据当前请求的路径,在 \_constraintMap 中匹配到对应的数据,并返回匹配到的结果(该请求所对应的角色信息),以供后续的权限验证使用:  这里实际上是调用getMatch方法来处理的: 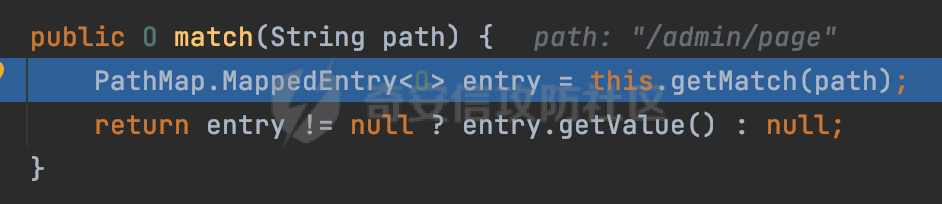 查看是如何匹配当前请求的路径的: 首先是对请求为`/`的情况进行处理,如果在 \_exactMap 中存在 path 对应的 MappedEntry 对象,直接返回。如果找不到,继续查找是否有该路径的精确匹配: 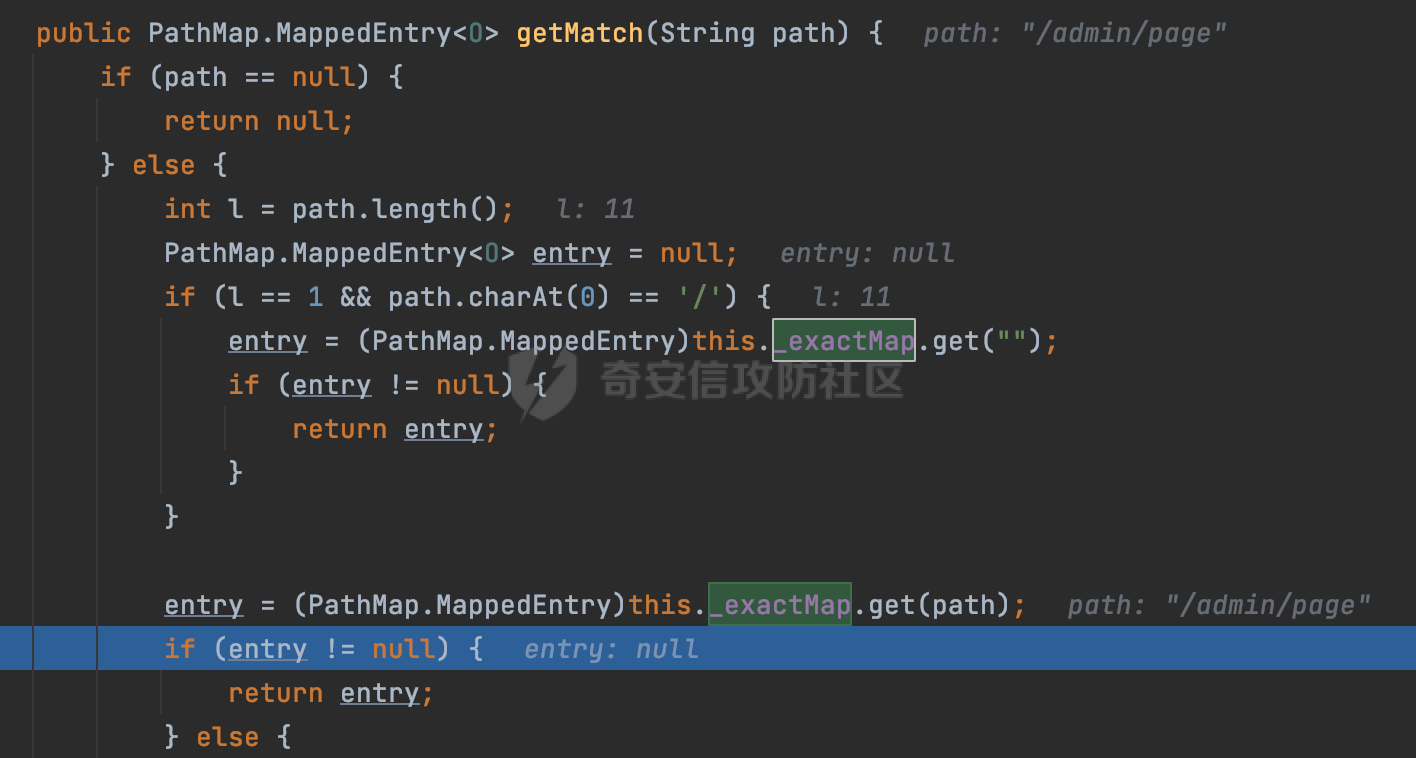 如果找不到,则在 `_prefixMap` 中查找以该路径为前缀的匹配。同样的会查找 path 对应的 MappedEntry 对象,如果找到了最佳匹配,会进一步判断最佳匹配结果的键值 `key` 是否真正匹配 `path`,若 key 的最后一个字符不是 /,会循环查找直到找到合适的结果: 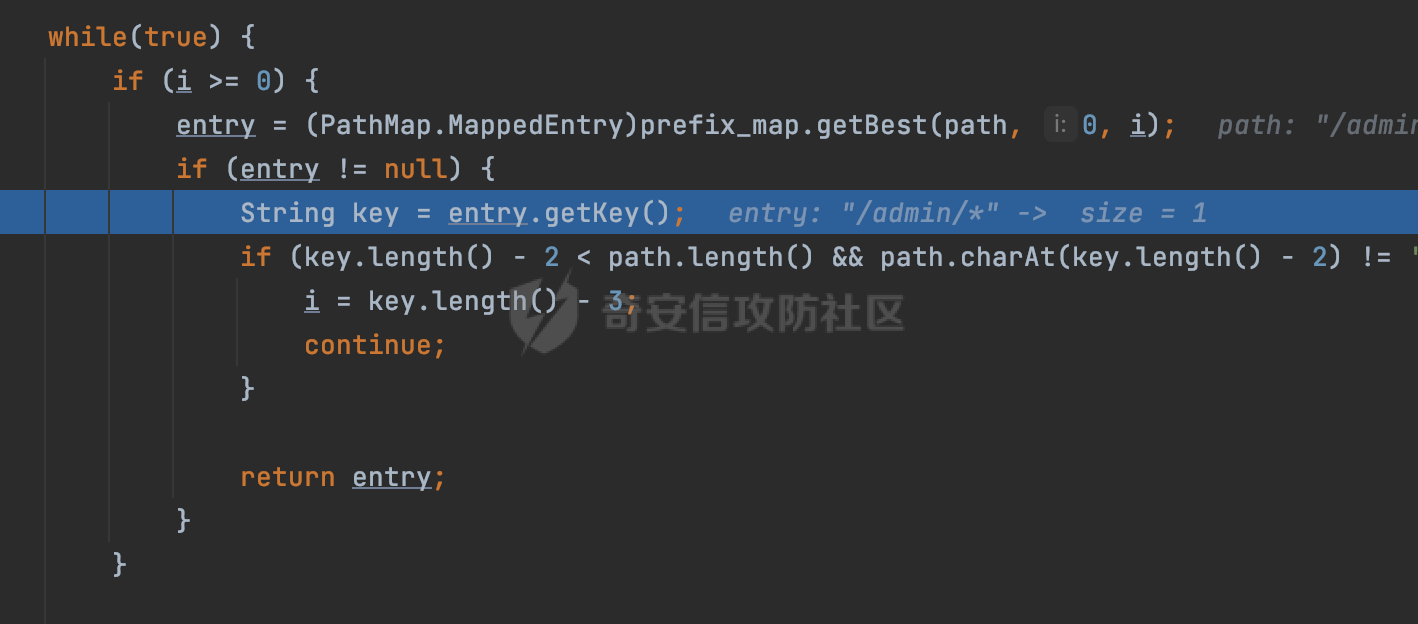 无法在 \_prefixMap 中找到匹配项,尝试返回默认值: 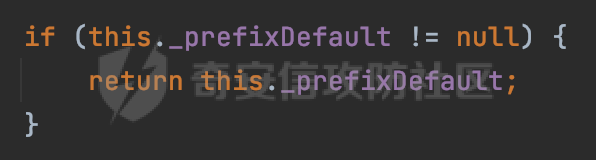 如果不存在则继续尝试在 \_suffixMap 中查找任何带有相应扩展名的 MappedEntry 对象返回: 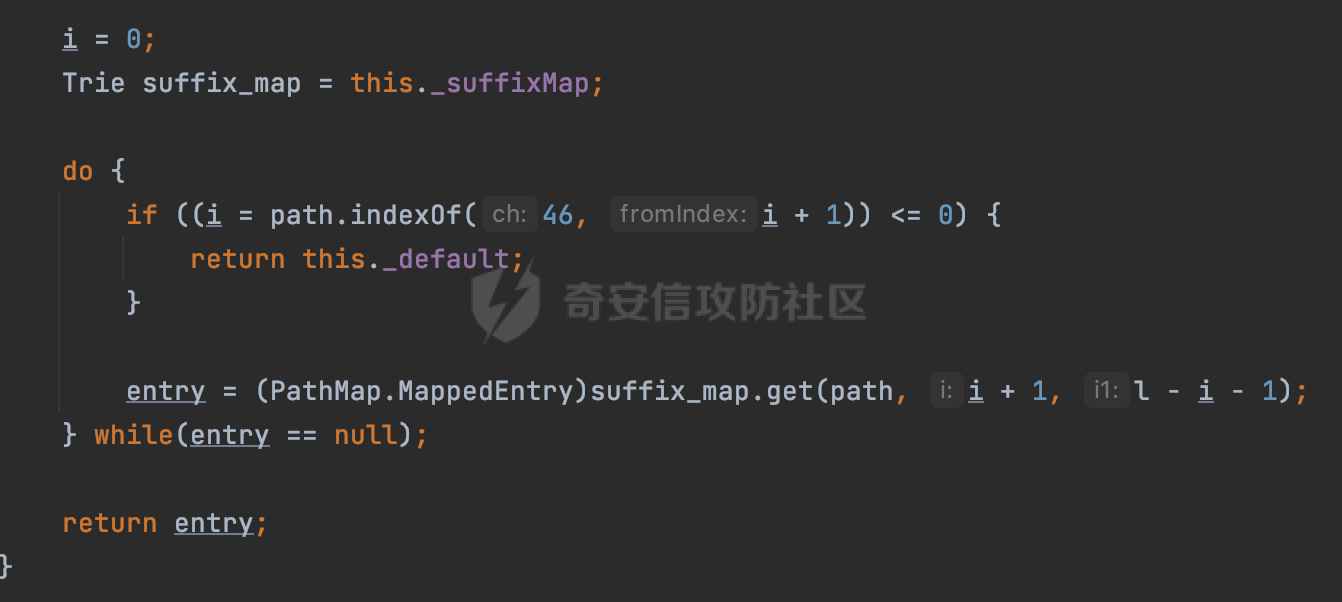 在获取完获取当前请求路径的访问限制信息后,重新回到prepareConstraintInfo方法的调用逻辑,这里根据请求方法(GET、POST 等)获取该方法下的角色信息,如果获取不到,则需要继续查找其他可用的限制映射或默认的全局映射: 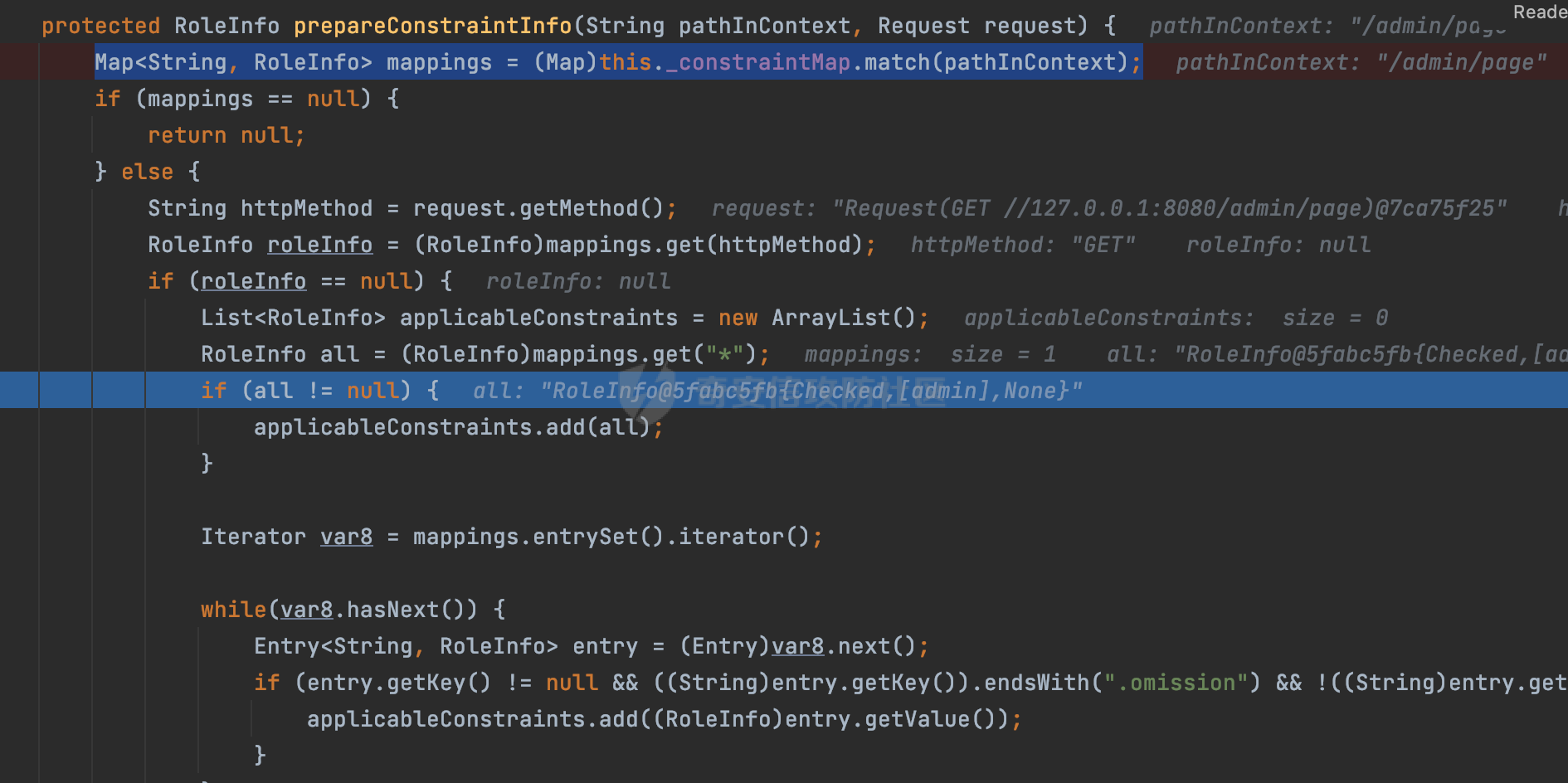 调用prepareConstraintInfo获取到RoleInfo后,会继续调用checkUserDataPermissions()方法检查用户是否有权访问特定路径,如果检查通过,则返回 `true`,表示用户/角色有权访问当前路径。否则返回`false`,此时说明没有权限,会将发送一个 403 禁止访问的错误响应,并将请求标记为已处理: 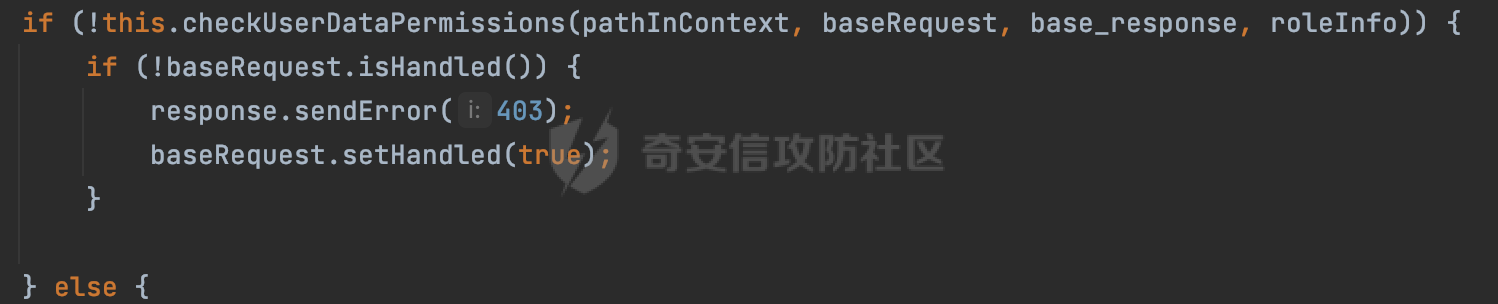 如果检查通过,会判断是否需要用户认证(isAuthMandatory)以及是否配置了 Authenticator(authenticator)。如果需要用户认证但没有配置 Authenticator,则抛出警告并返回 403 错误: 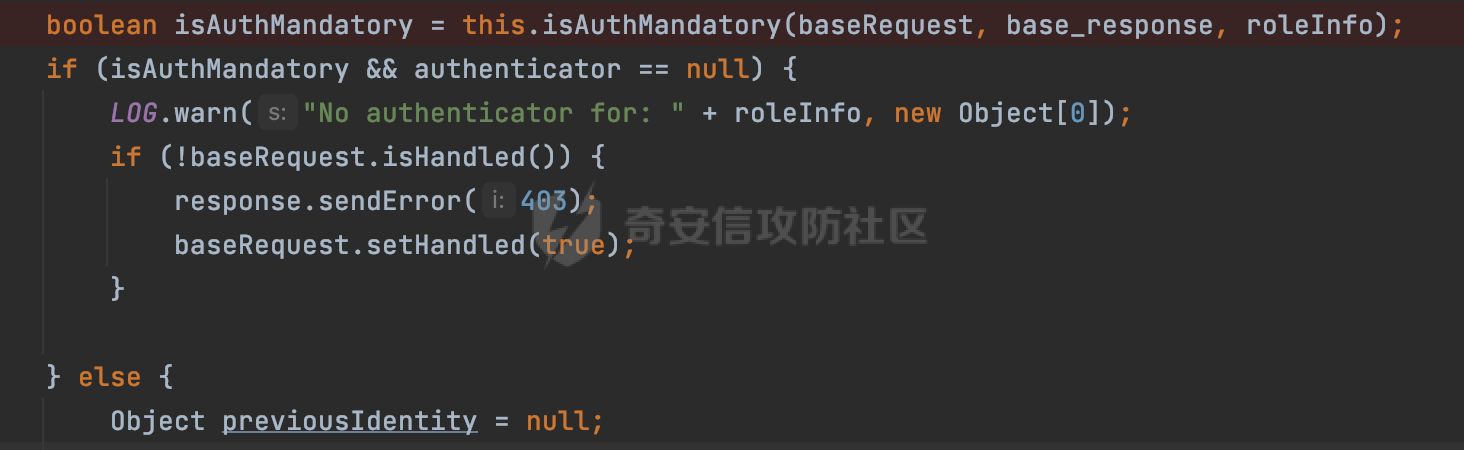 如果authenticator不为null,会获取请求对象中包含的 authentication 对象,如果为 null 或未经过验证,则使用 Authenticator 进行验证: 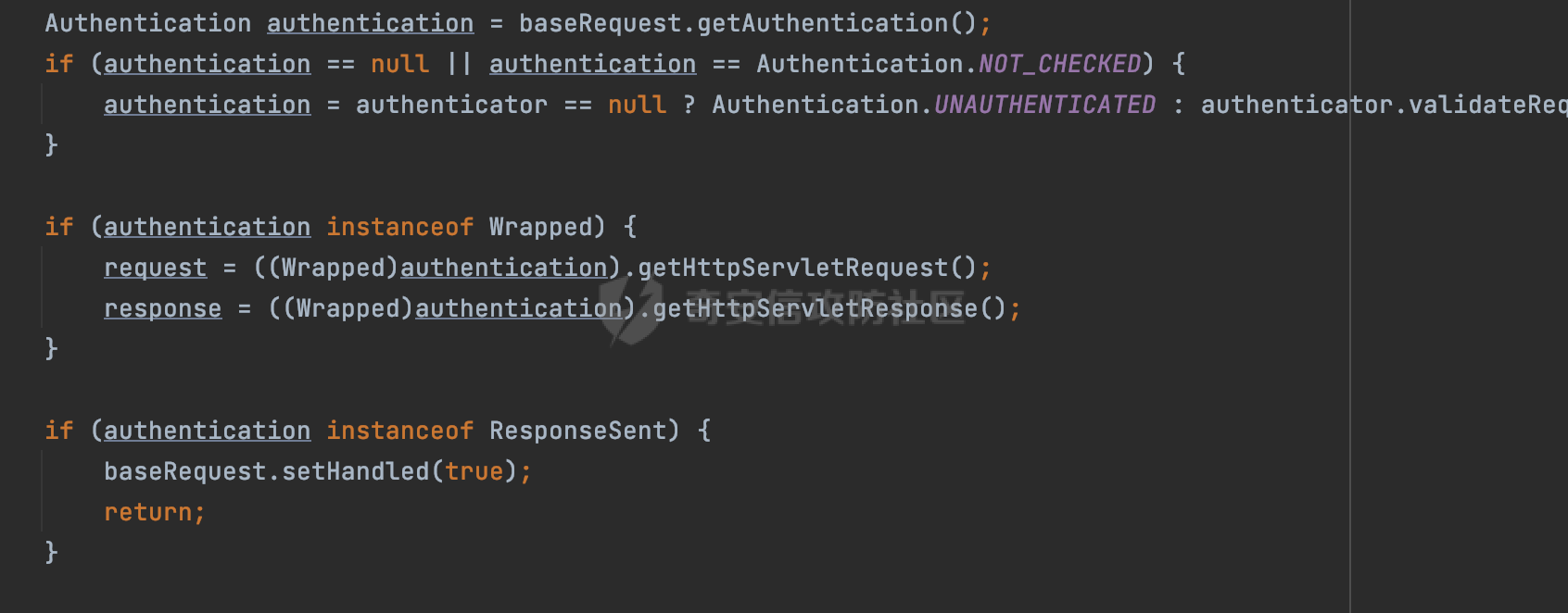 首先,代码检查 authentication 对象是否是 User 类型,如果不是则需要进一步处理。 如果 authentication 是 Deferred 类型,则说明权限验证还未完成,需要先将当前 authentication 对象保存,并直接返回到 Handler 中等待权限验证: 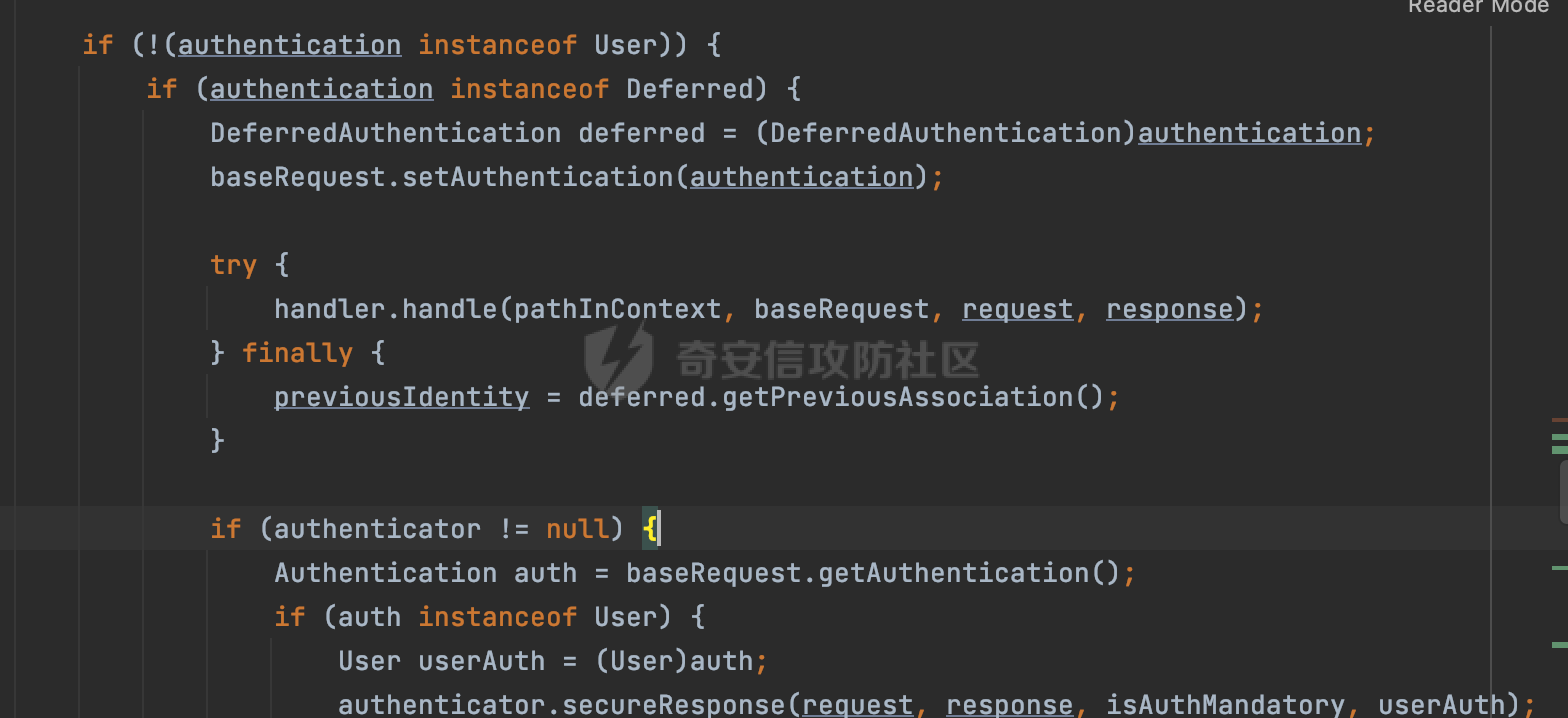 如果 authentication 既不是 User 也不是 Deferred 类型,需要根据是否是`isAuthMandatory`来返回错误信息或者继续处理请求: 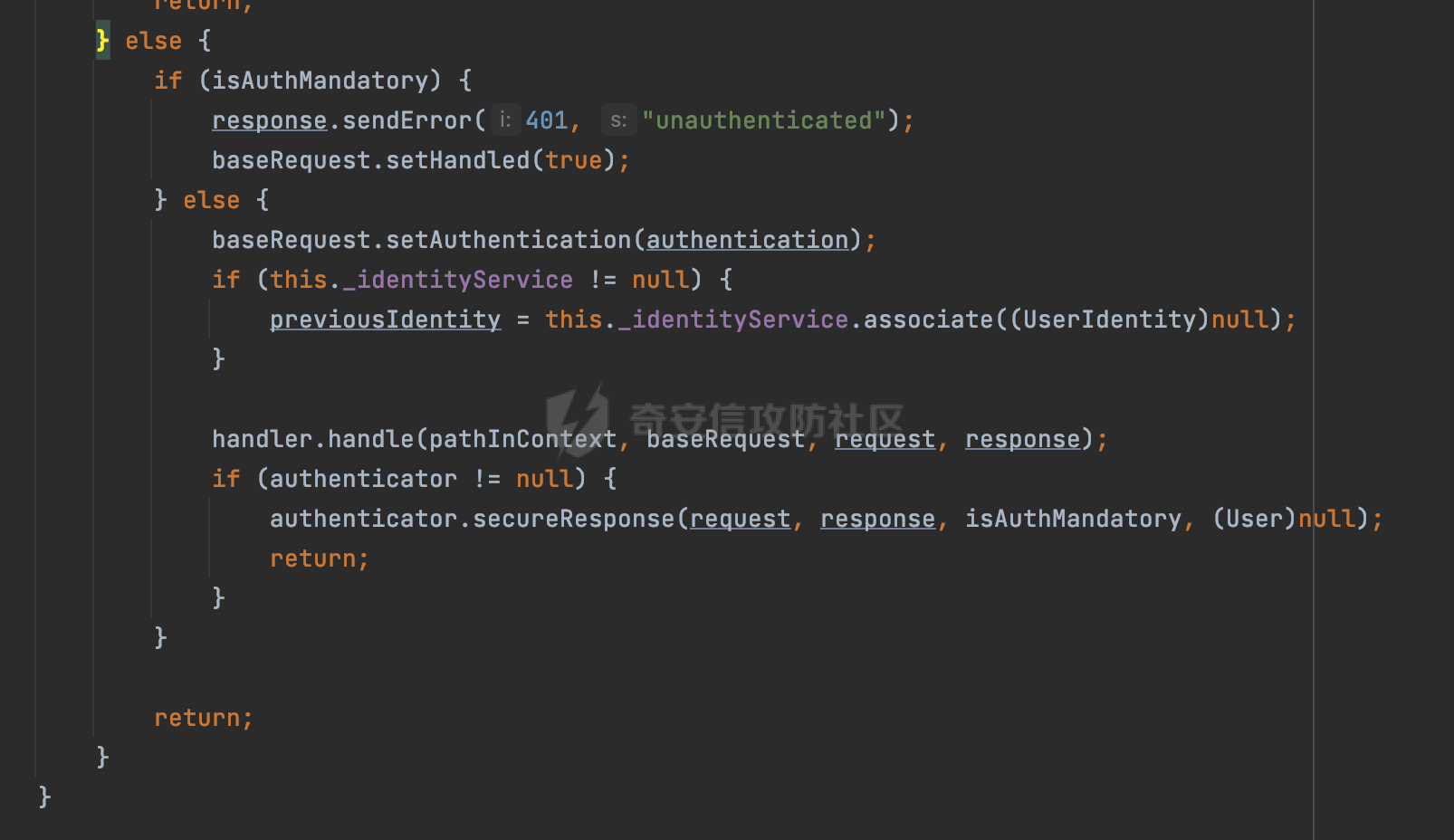 在认证通过后会对访问资源的授权管理,`isAuthMandatory` 为 `true`,则表示该资源需要进行认证才能访问,这里会调用 `checkWebResourcePermissions` 方法,会检查当前用户是否具有访问该资源所需的权限,如果当前用户没有权限访问该资源,则返回 HTTP 状态码 `403`,即禁止访问,并打上 `!role` 的错误信息: 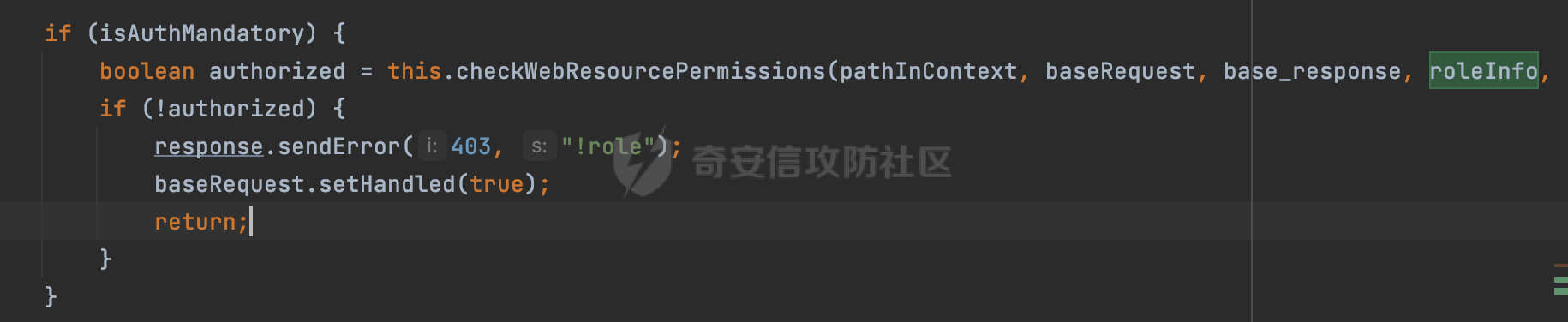 以上就是Jetty中关于安全约束的大致解析逻辑。 ### 1.2.3 undertow 使用udertow的方式很简单,去除springboot 中默认的Tomcat 依赖后引入undertow即可: ```XML <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-undertow</artifactId> </dependency> ``` 在udertow中,可以`UndertowServletWebServerFactory`来配置安全约束,例如如下的例子,对于`/admin/*`的路径,只有admin角色才可以访问: ```Java @Configuration public class SecurityConfig { @Bean public UndertowServletWebServerFactory undertowServletWebServerFactory() { UndertowServletWebServerFactory factory = new UndertowServletWebServerFactory(); factory.addDeploymentInfoCustomizers(deploymentInfo -> { deploymentInfo.addSecurityConstraint( new SecurityConstraint() .addWebResourceCollection( new WebResourceCollection() .addUrlPattern("/admin/*") ) .setEmptyRoleSemantic(SecurityInfo.EmptyRoleSemantic.DENY) .addRoleAllowed("admin")); }); return factory; } } ``` `io.undertow.servlet.handlers.security.ServletSecurityConstraintHandler` 类是 Undertow Web 服务器中处理 Servlet 安全约束的处理器。 查看具体的解析流程,主要是在 `handleRequest` 方法中进行处理,其会根据配置的安全约束对请求进行检查,包括路径匹配、HTTP 方法匹配等: 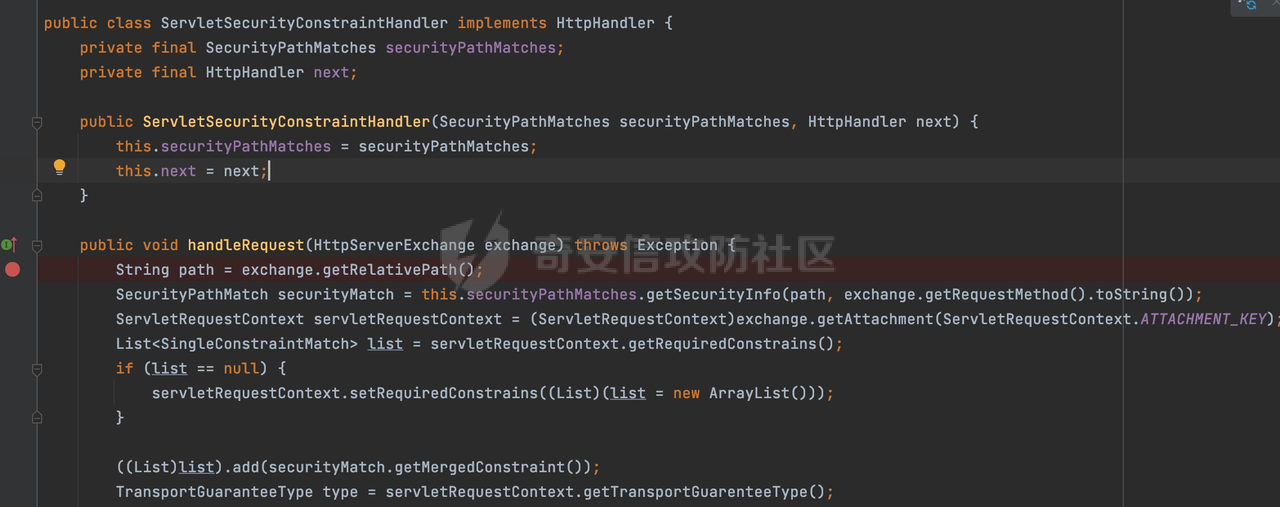 主要是通过调用`securityPathMatches.getSecurityInfo(path, exchange.getRequestMethod().toString())`来获取当前请求匹配的安全约束,首先会`this.handleMatch(method, this.defaultPathSecurityInformation, currentMatch);`匹配默认的路径安全信息:  然后会根据当前请求的path,从`exactPathRoleInformation`这个map结构尝试获取对应的value,如果匹配成功,调用handleMatch处理并返回当前请求安全约束相关信息:  否则会继续尝试从`prefixPathRoleInformation`尝试获取当前path对应的value: 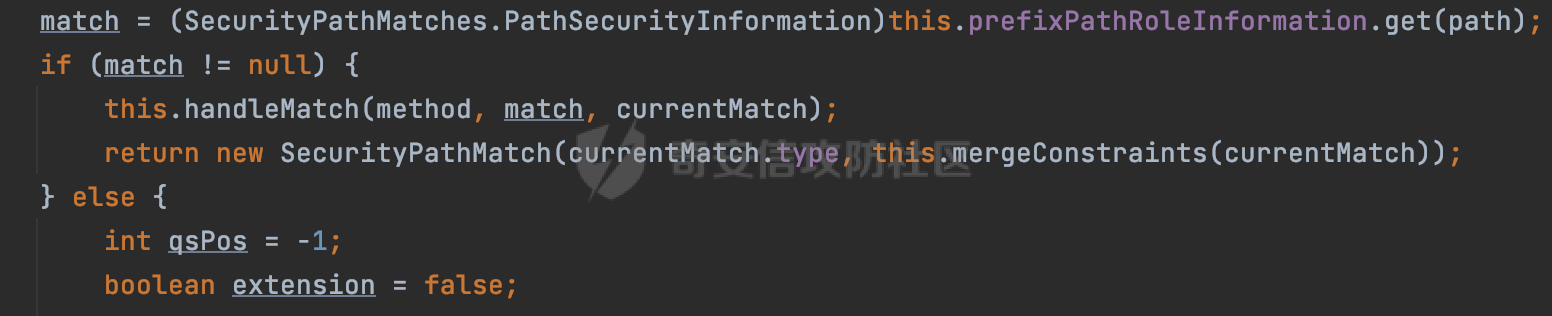 如果不能直接以path作为key获取value,此时会对path的资格字符串从尾部进行遍历,主要是做以下的处理: 1.如果匹配到`?`,说明包含url请求参数,此时会从`?`进行截断,然后继续上述`exactPathRoleInformation`的匹配过程; 2.如果匹配`/`,此时包含目录结构,说明很可能匹配类似`/admin/*`的约束,此时或进行截断继续`prefixPathRoleInformation`的匹配过程; 3.最后是后缀模式`.`的匹配,会从`extensionRoleInformatio`这个map结构进行获取: 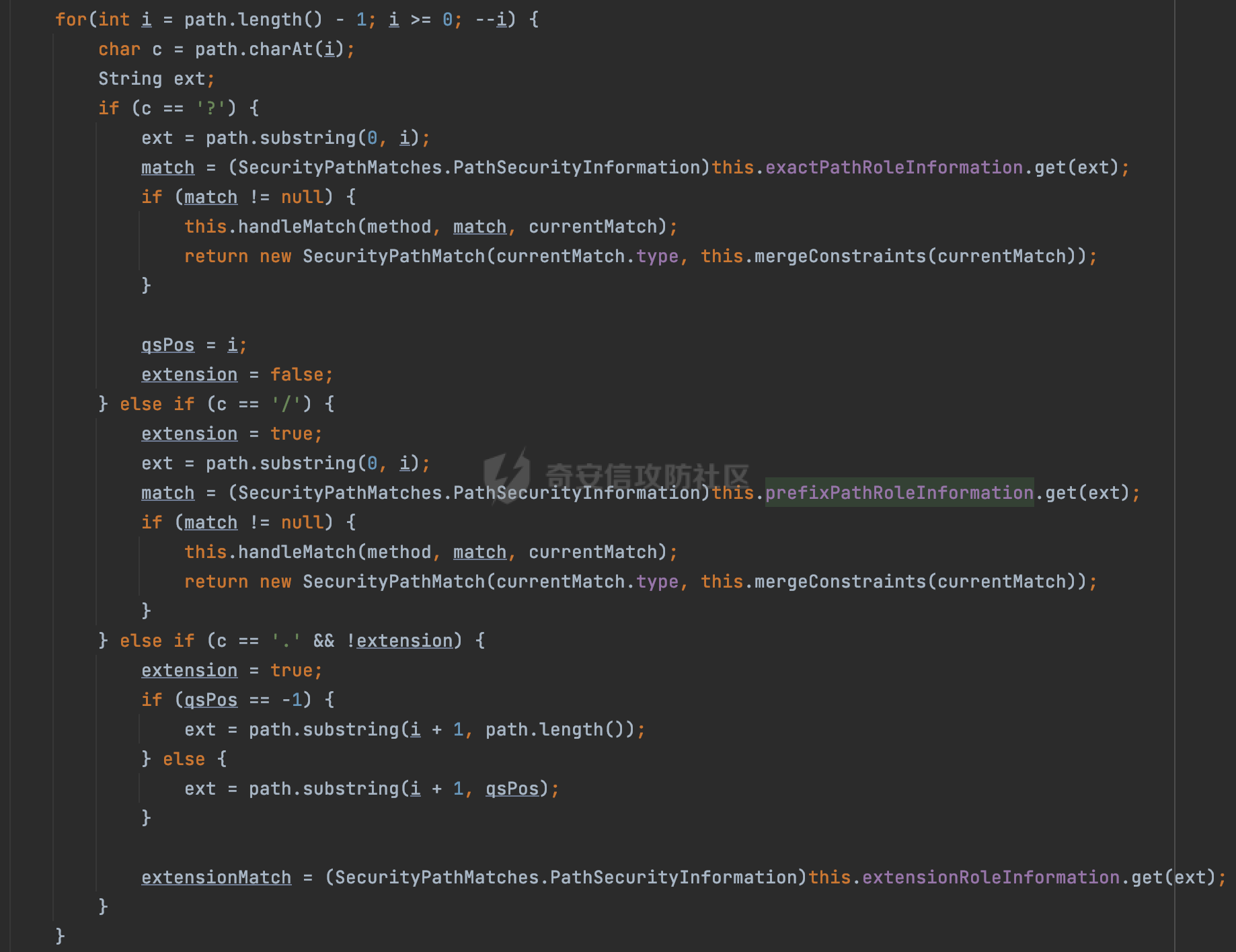 在获取到当前请求匹配的安全约束后,在`handleRequest` 方法中,会交给后面的处理器进行处理,如果请求满足安全约束的要求,即通过了验证和授权检查,那么请求将被允许继续处理,进入下一个处理阶段:  以上就是undertow中关于安全约束的大致解析逻辑。 0x02 潜在的绕过风险 ============ 2.1 中间件处理请求Path的方式 ================== 根据前面的分析,当接收到请求后,中间件会使用对应的模块来处理SecurityConstraint 。它会根据具体的配置对请求的 Path进行匹配。如果匹配成功,会检查请求是否满足定义的访问控制规则,包括认证和授权条件。如果满足规则,则请求被允许继续处理;否则,会返回相应的错误响应或重定向到登录页面等。下面看下各个中间件是怎么处理请求Path的然后进行SecurityConstraint的匹配的。 2.1.1 tomcat ------------ 在`org.apache.catalina.authenticator.AuthenticatorBase#invoke`中,会调用`realm.findSecurityConstraints(request, this.context)` 是用于查找与给定请求相关的安全约束: 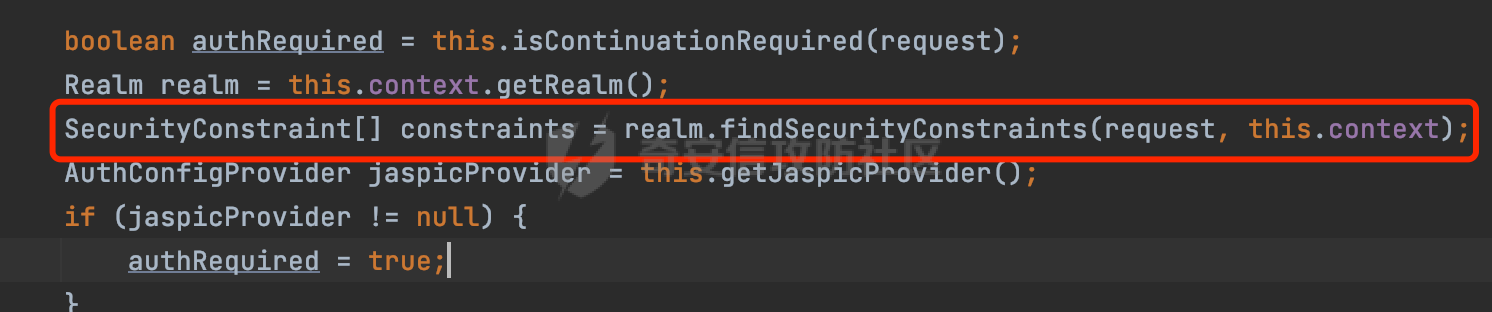 查看具体的实现,这里实际上会根据请求的 URI 查找相关配置的 `<security-constraint>`,而URI是从request对象的getRequestPathMB方法获取的: 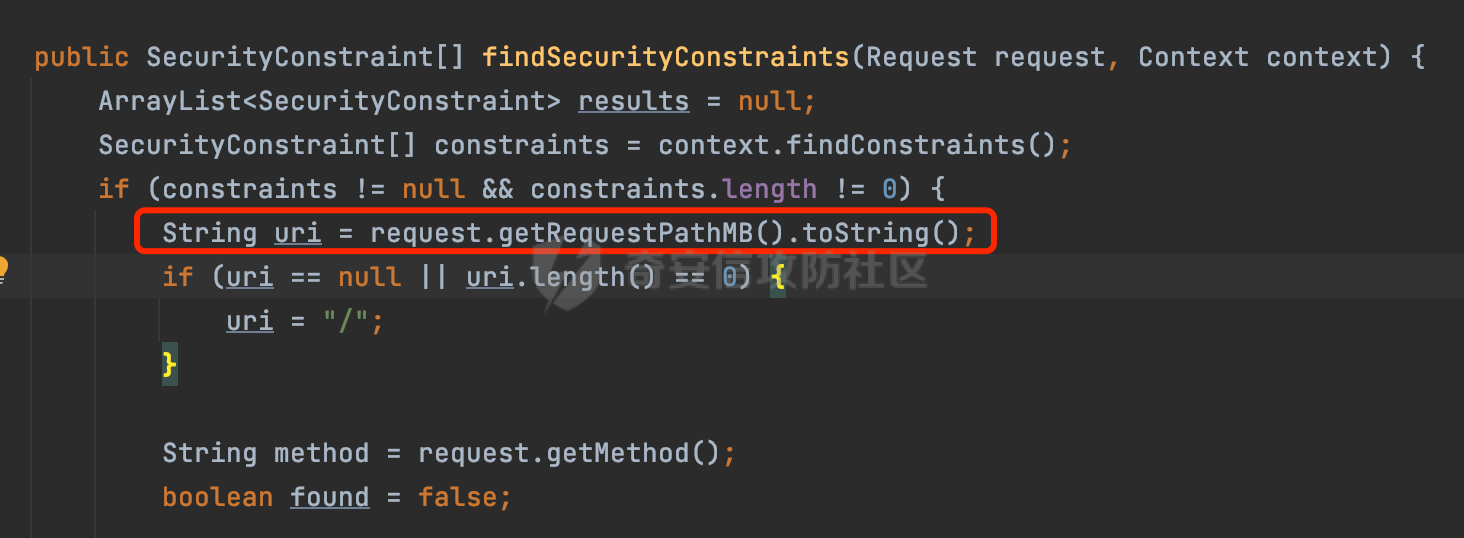 这里获取uri的方式实际是从mappingData的requestPath属性获取的: 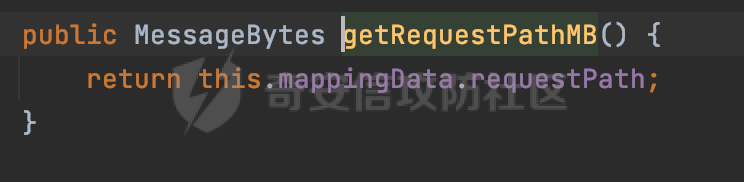 `org.apache.catalina.mapper.MappingData`的封装是在`CoyoteAdapter`中进行的。在`CoyoteAdapter`的`service`方法中,会通过prepareRequest方法设置Request对象的相关属性,包括uri、queryString、mappingData等。 在prepareRequest方法中,会调用MappingData类的recycle方法对mappingData对象进行重置,然后调用Mapper类的map方法对请求进行映射,最后将解析后的结果封装到MappingData对象中: 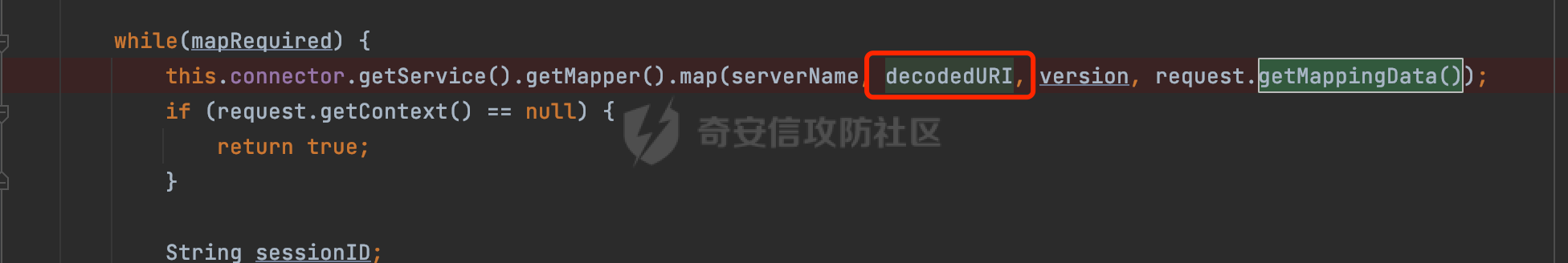 查看具体的逻辑可以看到这里会设置mappingData的requestPath属性: 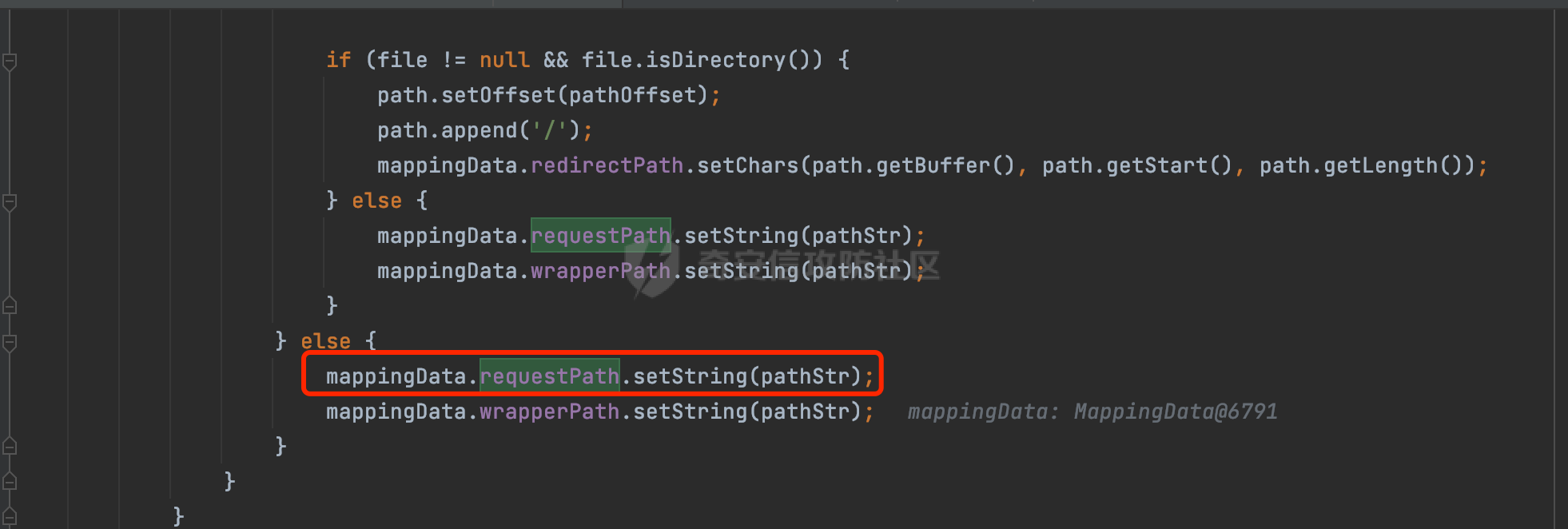 也就是说只要关注decodedURI即可。在Tomcat中,主要是在CoyoteAdapter.service()函数上对请求URL进行解析处理的,其会调用postParseRequest()函数来解析URL请求内容,主要处理逻辑如下,会调用parsePathParameters()和normalize()函数对请求内容进行解析处理: 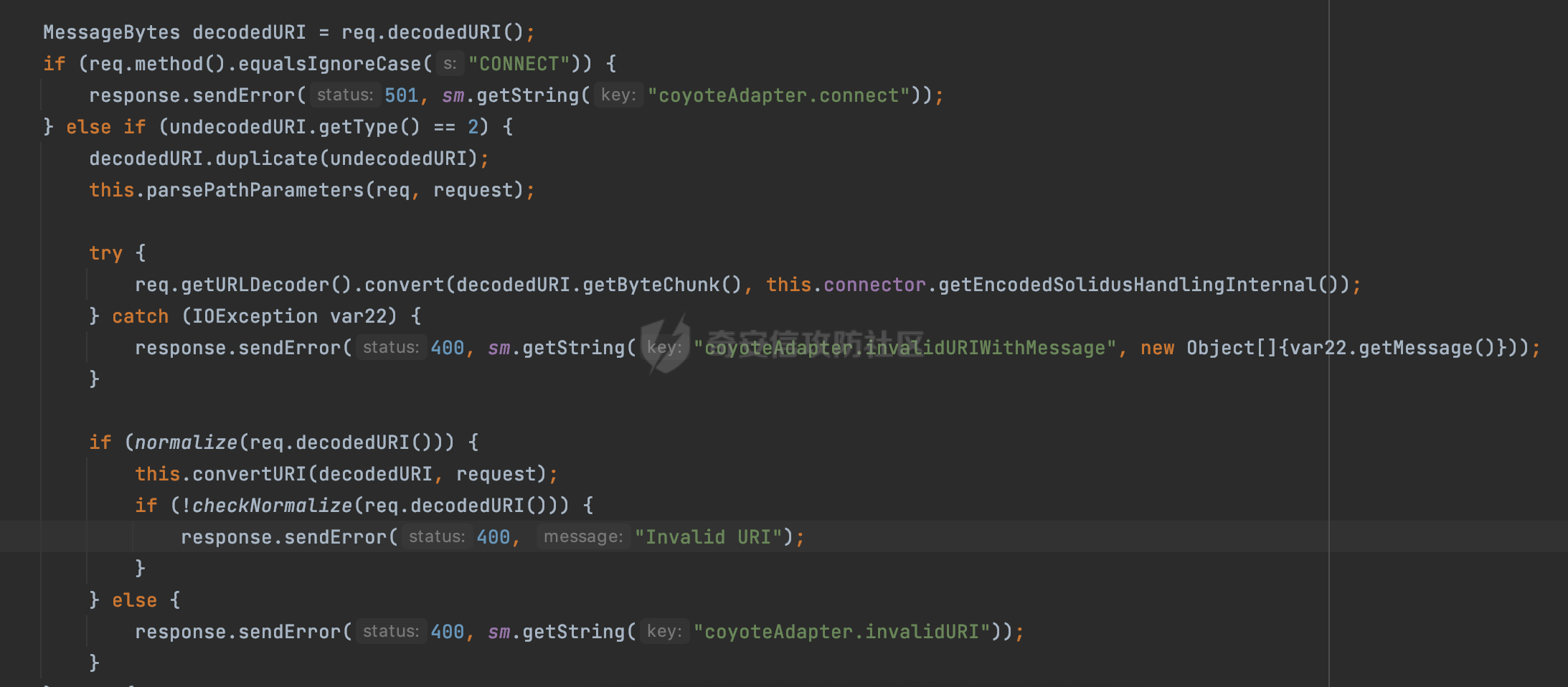 在parsePathParameters()中,先是寻找URL中是否存在`;`号,存在的话会将`;xxx/`中的分号与斜杠之间的字符串以及分号本身剔除: 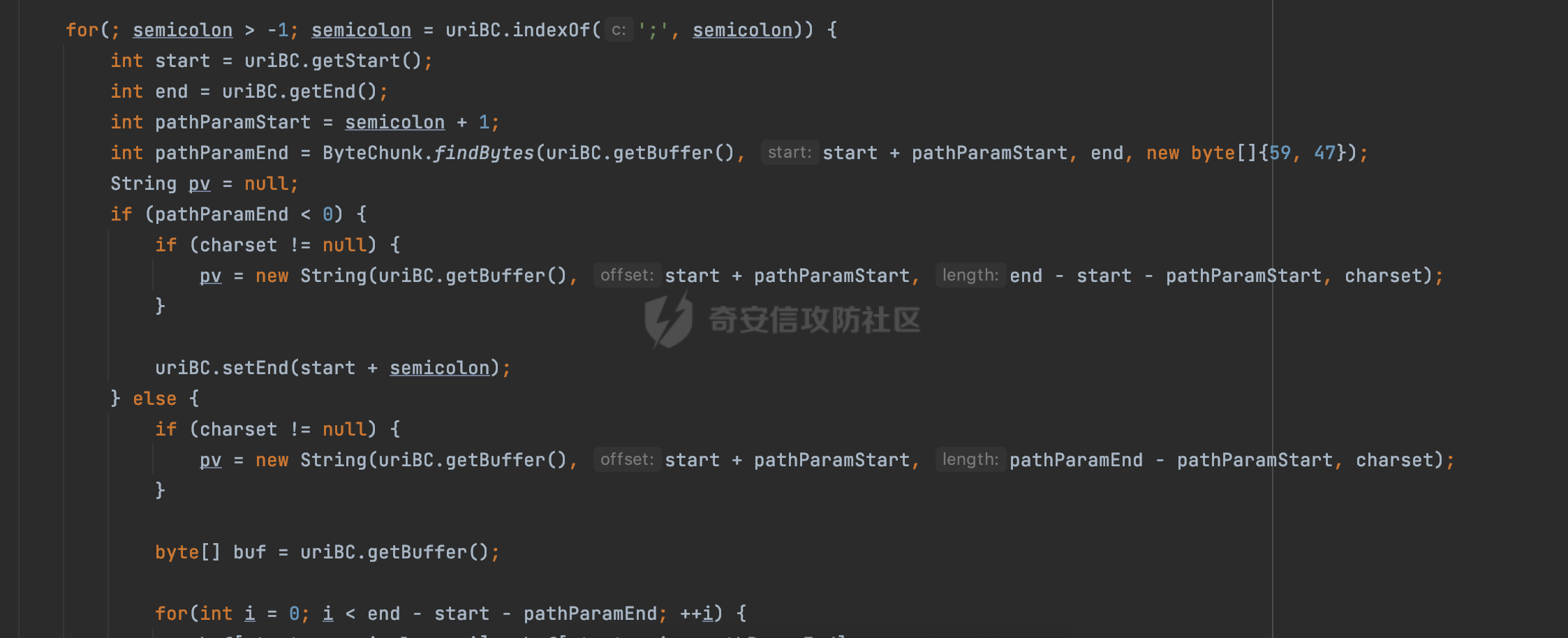 normalize()主要是对请求URL进行标准化处理,例如循环删除掉多余的`/`,处理目录穿越符号`/../`进行路径的回溯等: 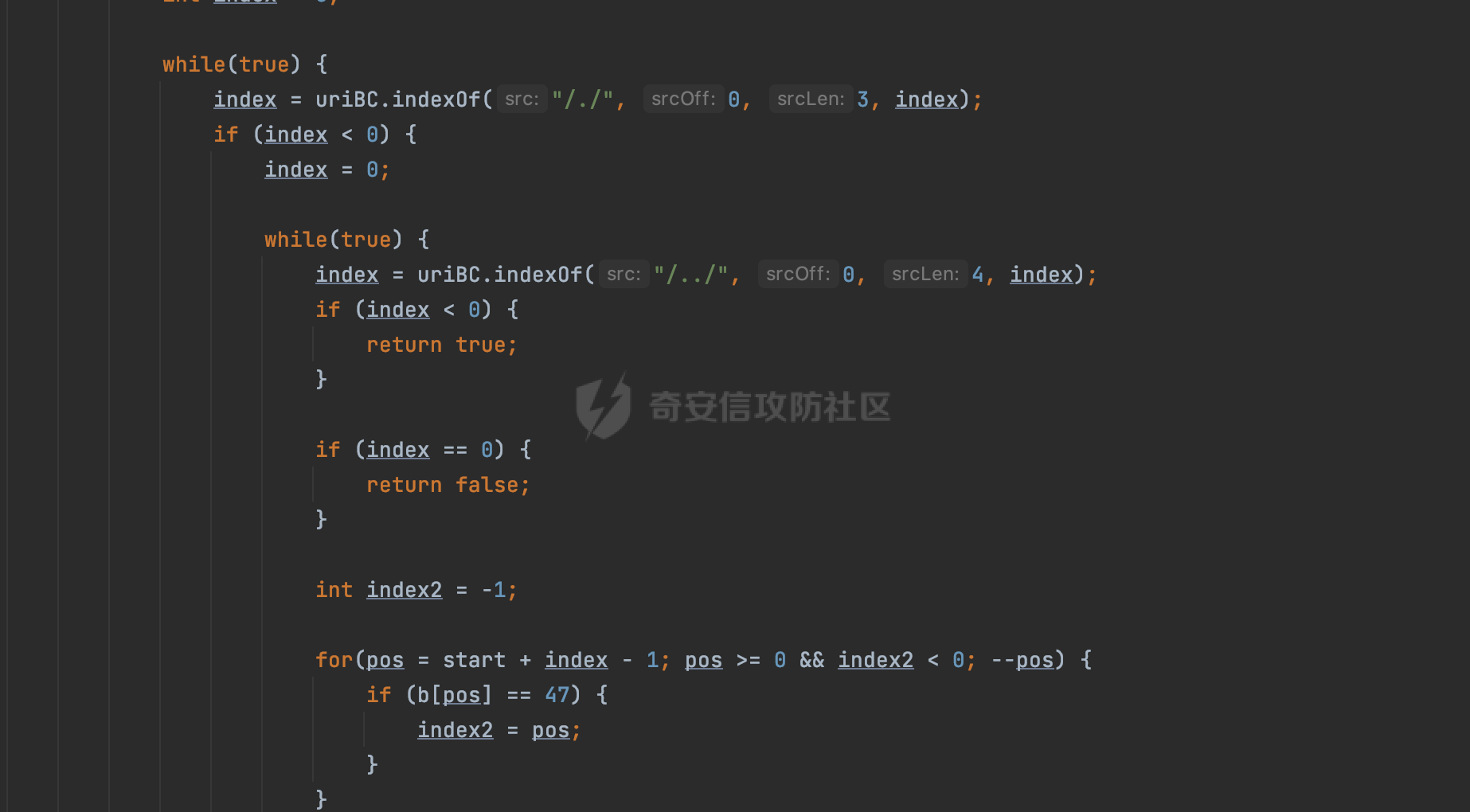 2.1.2 Jetty ----------- 从前面Jetty对于相关安全约束的解析可以看到,`RoleInfo` 封装了对当前路径的访问要求,包括需要具备的角色、权限等信息。而其主要是根据根据传入的路径和请求信息来获取的,对应的路径是在调用handle方法时通过pathInContext参数传入的: 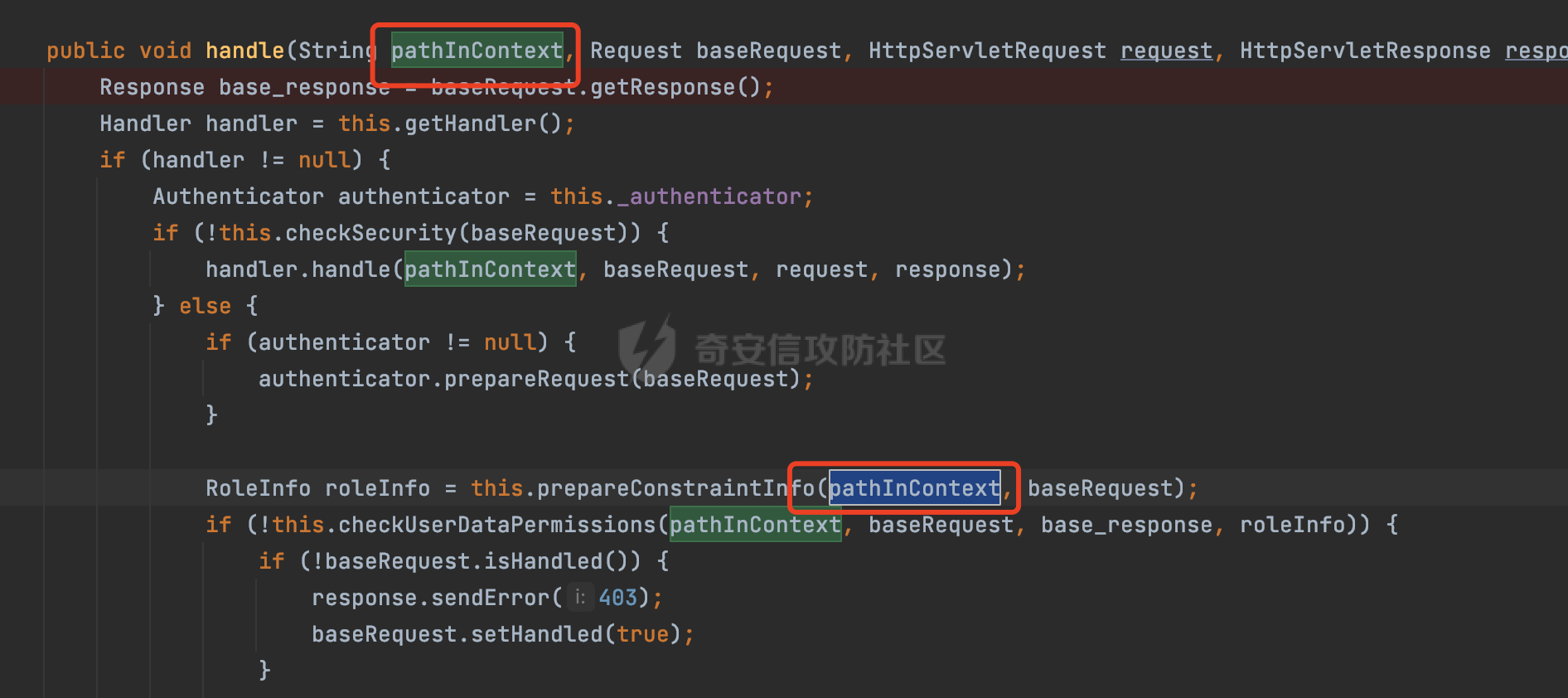 查看pathInContext具体是怎么生成的: 当Jetty接收到一个请求时,会在`org.eclipse.jetty.http.HttpURI#parse`方法中进行URI的处理。这里首先会对请求的URI进行解码操作,然后调用`org.eclipse.jetty.util.URIUtil#canonicalPath`方法进行规范化处理,如果返回结果为null,说明是个Bad URI,会抛出异常: 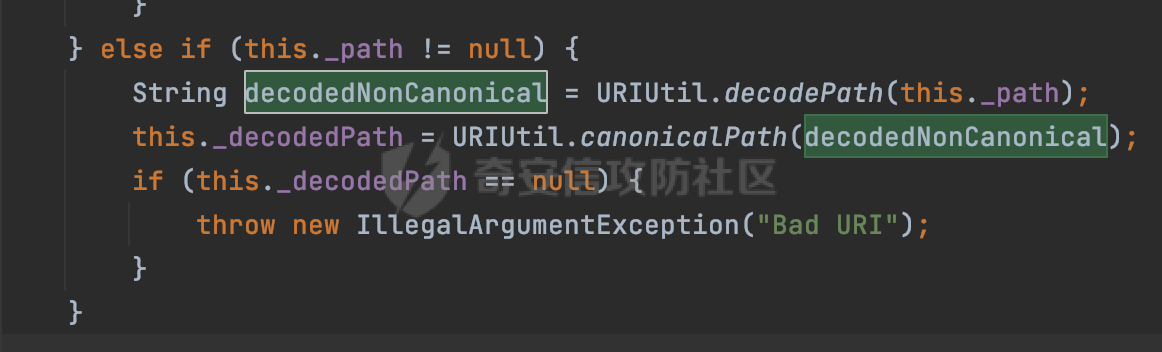 在`canonicalPath`方法主要是处理`/./`或`/../`形式的url: 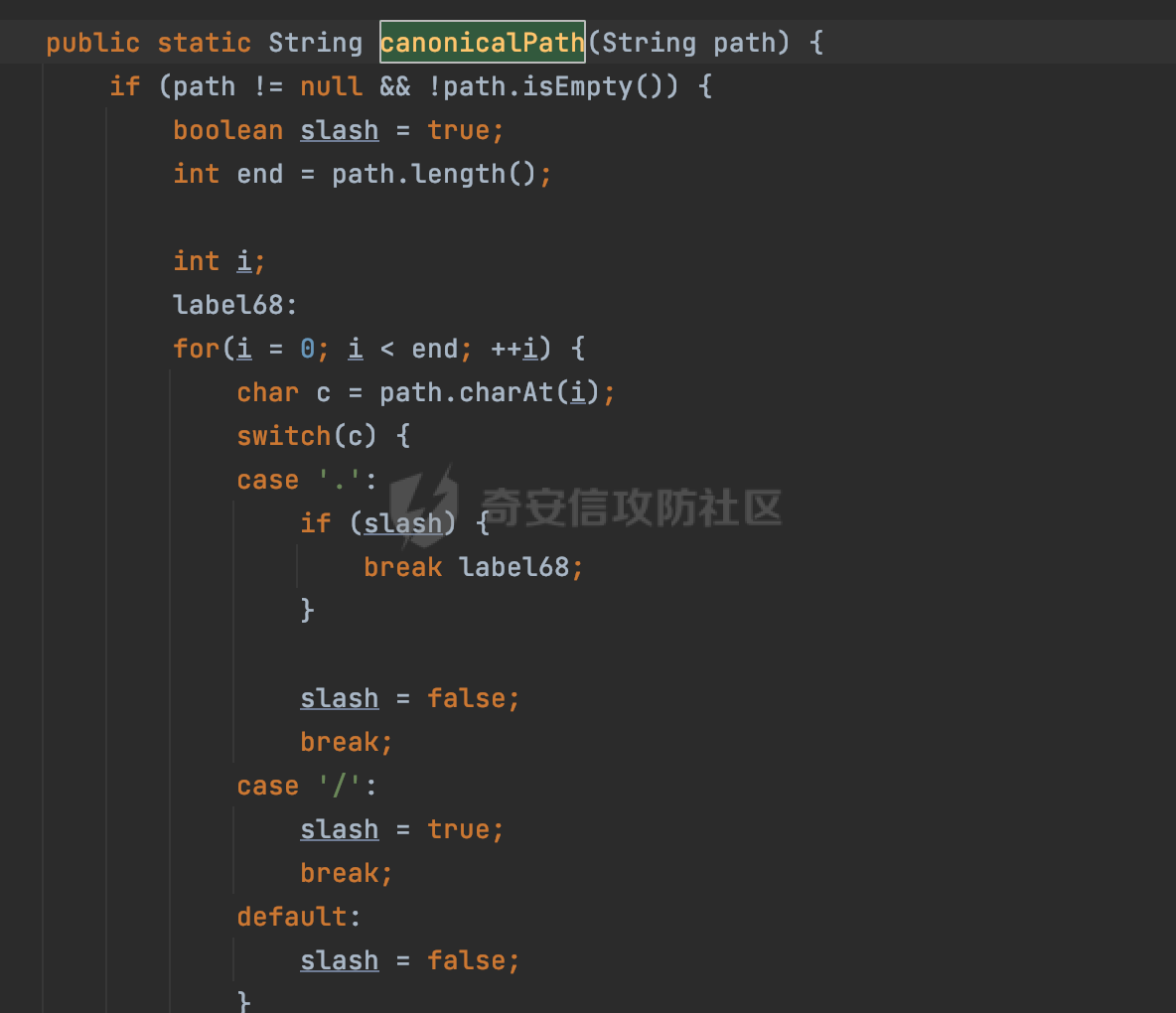 也就是说类似`/admin/..`的请求在处理后会变成`/`。 2.1.3 undertow -------------- 在undertow中,会调用`securityPathMatches.getSecurityInfo(path, exchange.getRequestMethod().toString())`来获取当前请求匹配的安全约束: 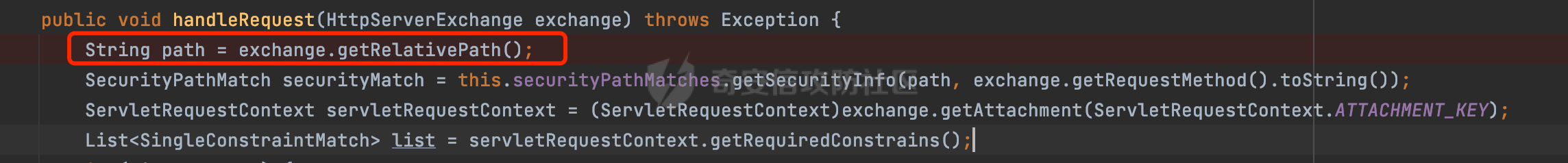 匹配的path是从`HttpServerExchange`的relativePath属性获取的。看看relativePath具体的封装过程,主要是在`io.undertow.server.protocol.http.HttpRequestParser#handlePath`方法进行处理的,主要处理逻辑是会逐个字符进行遍历,根据特定的字符处理相应的逻辑:  这里主要关注对`;`的解析,当解析到`;`时,首先会把`;`前的内容添加到`canonicalPath`,然后调用handlePathParameters方法进行处理:  在handlePathParameters方法中,主要就是对`;`后的值进行处理,当匹配到`/`时,此时解析结束,更新pos的值返回: 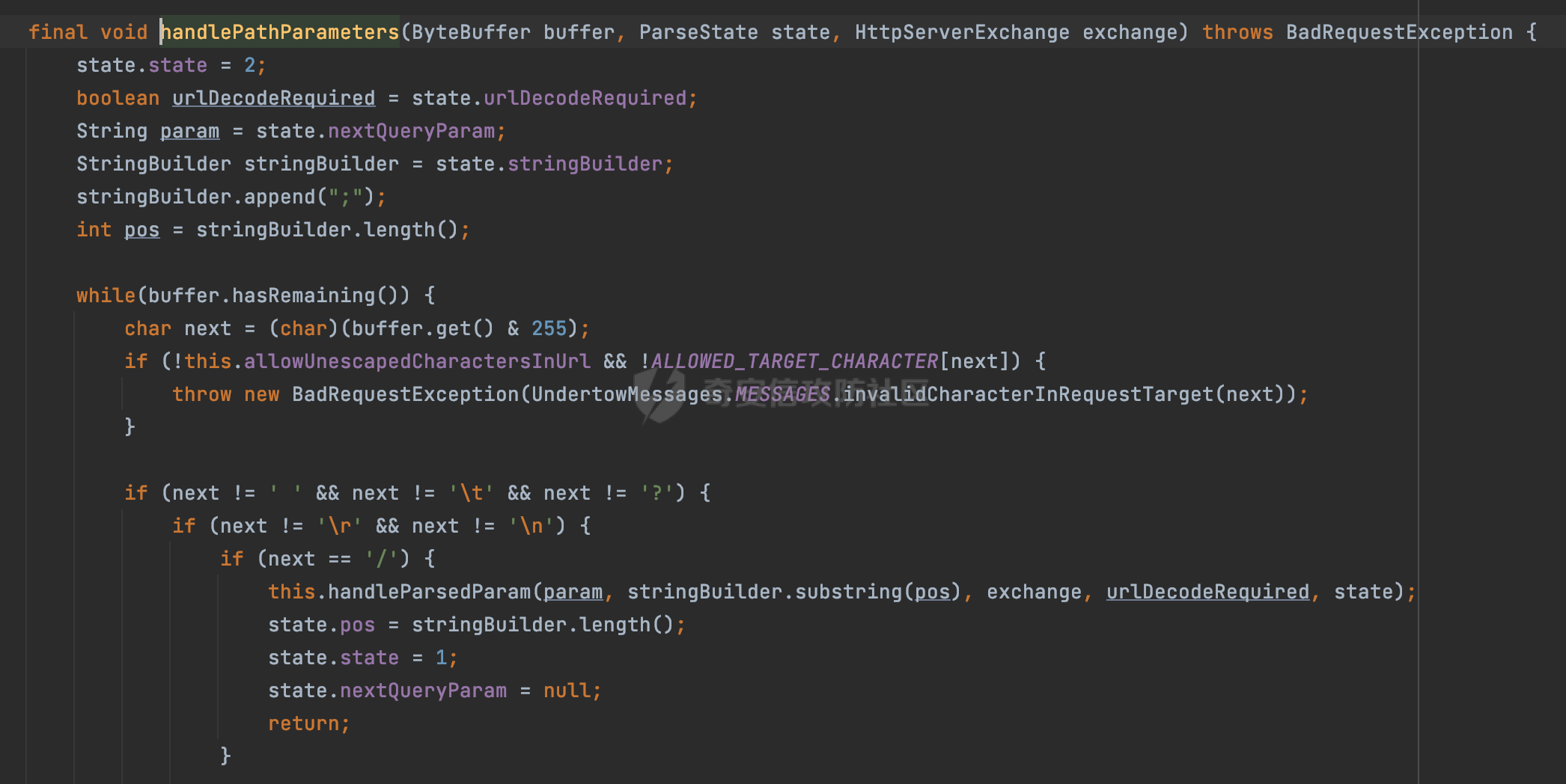 解析完`;`后,会从下一个`/`开始继续遍历,当整个请求path遍历完后,如果`state.canonicalPath.length()`,会进行url解码操作,并调用setRelativePath方法设置对应的值: 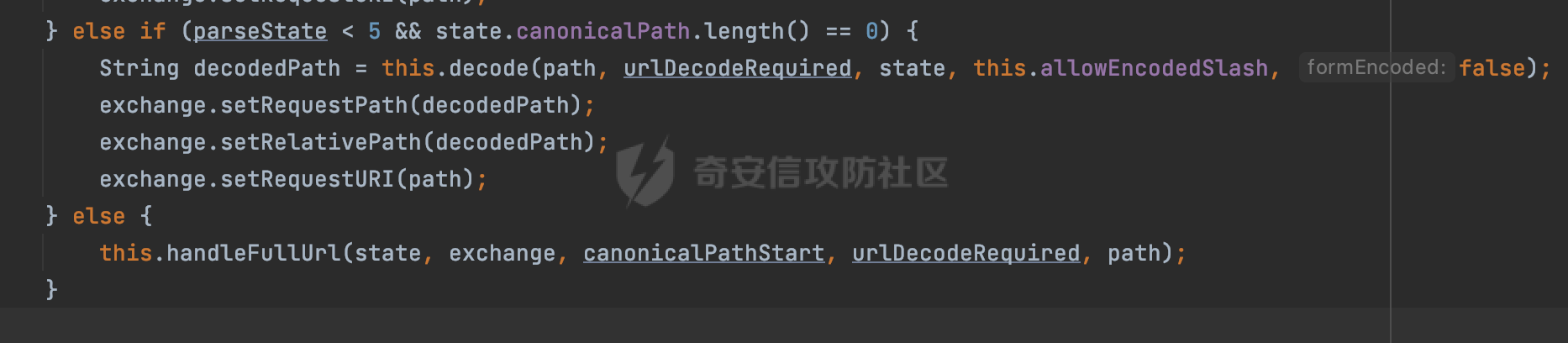 否则会调用`handleFullUrl`方法,从前面设置的`canonicalPath`拿到`;`前的内容,剔除掉`;`部分后再进行url解码并设置relativePath: 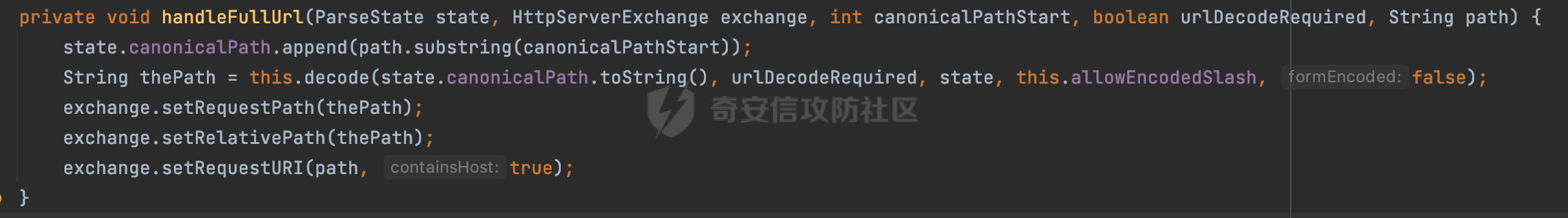 可以看到**相比Tomcat跟Jetty,undertow少了对类似`../`这类穿越符的处理**。 2.2 绕过SecurityConstraint ======================== 根据上面的分析大致可以具体SecurityConstraint具体的解析流程,对比Spring对Path的处理(具体可以参考[Spring Web路由解析过程](https://forum.butian.net/share/2214) ),各个中间件间是存在一定的解析差异的,在某种情况下可能绕过配置的SecurityConstraint安全约束。 以Jetty为例,根据前面的分析,Jetty在解析过程中会调用prepareConstraintInfo方法,根据传入的路径和请求信息,获取当前路径的访问限制信息,即 `RoleInfo`,这个RoleInfo在后面整个权限控制过程中扮演很重要的角色,其会通过\_constraintMap的match() 方法,根据当前请求的路径,在 \_constraintMap 中匹配到对应的数据(存储了在 SecurityHandler 中配置的所有路径和对应的访问权限控制信)进行获取,可以看到如果mappings为null,RoleInfo也为null,此时在某些情况下那么就可以绕过配置的SecurityConstraint安全约束了: 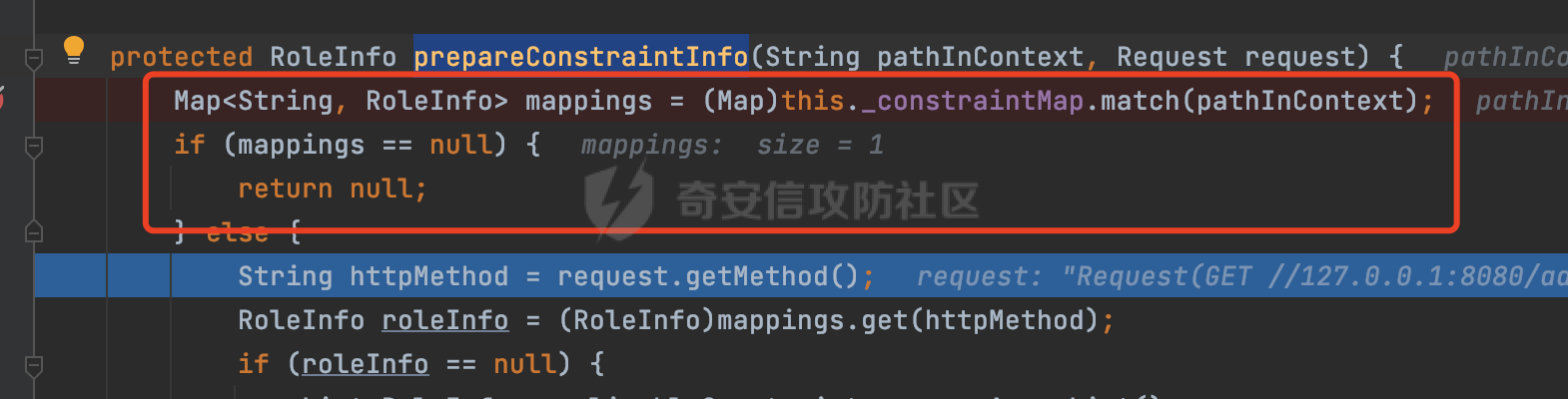 以下列举几个常见的场景: 2.2.1 以`/`结尾的Bypass ------------------- 以undertow为例,假设`/admin/detail.do`需要admin角色才能访问: ```Java @Bean public UndertowServletWebServerFactory undertowServletWebServerFactory() { UndertowServletWebServerFactory factory = new UndertowServletWebServerFactory(); factory.addDeploymentInfoCustomizers(deploymentInfo -> { deploymentInfo.addSecurityConstraint( new SecurityConstraint() .addWebResourceCollection( new WebResourceCollection() .addUrlPattern("/admin/detail") ) .setEmptyRoleSemantic(SecurityInfo.EmptyRoleSemantic.DENY) .addRoleAllowed("admin")); }); return factory; } ``` 正常情况下访问`/admin/detail`,缺少对应角色的话会返回403: 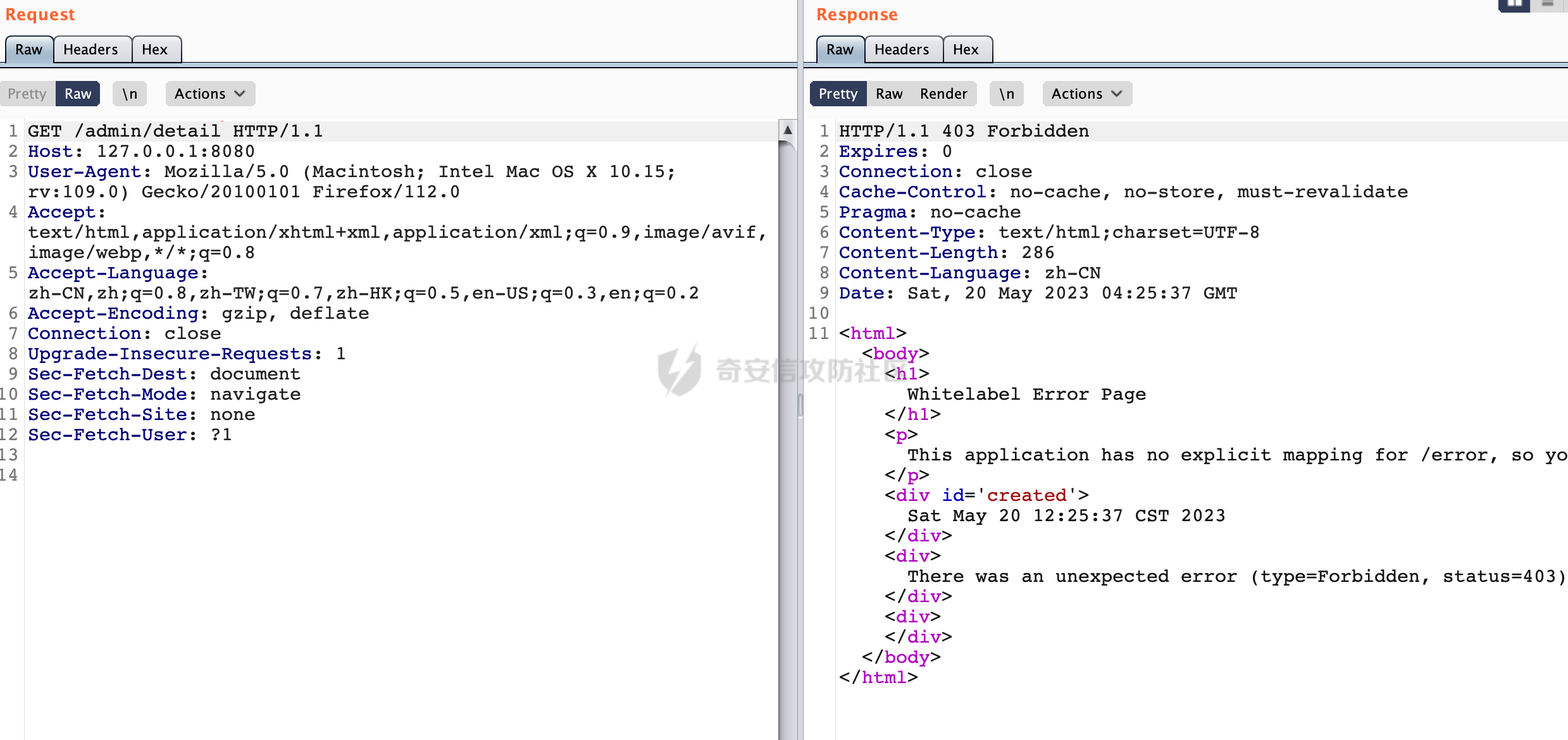 结合Spring两种解析模式AntPathMatcher和PathPattern可以知道默认情况下是都支持尾部`/`的匹配的。 对于AntPathMatcher,当**TrailingSlashMatch**为true时,会应用尾部的`/`匹配:  对于PathPattern,在相应Element解析器解析的最后,会根据matchOptionalTrailingSeparator(此参数为true时,默认为true)进行一定的处理,如果Pattern尾部没有斜杠,请求路径有尾部斜杠也会成功匹配(类似TrailingSlashMatch的作用): 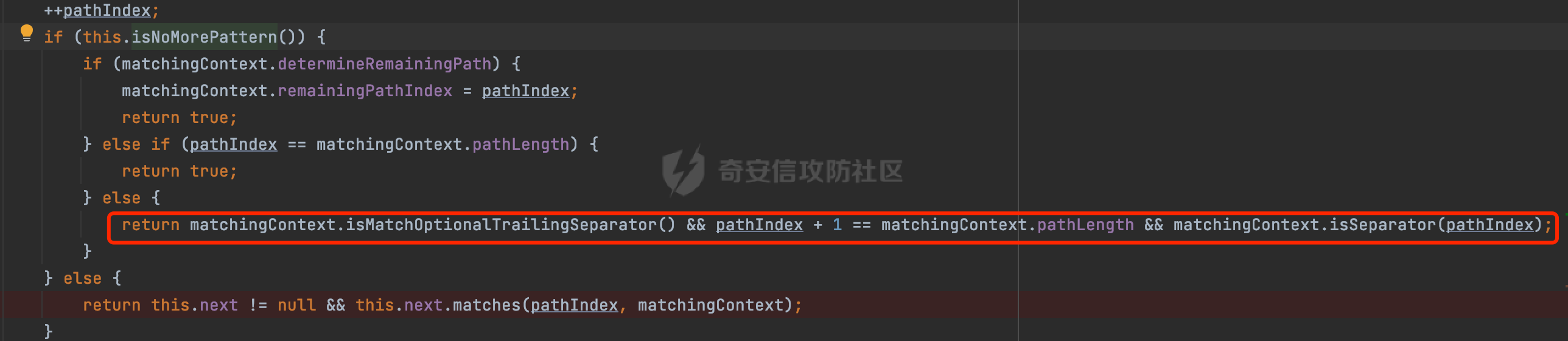 也就是说上述安全约束可以通过在结尾增加`/`进行绕过: 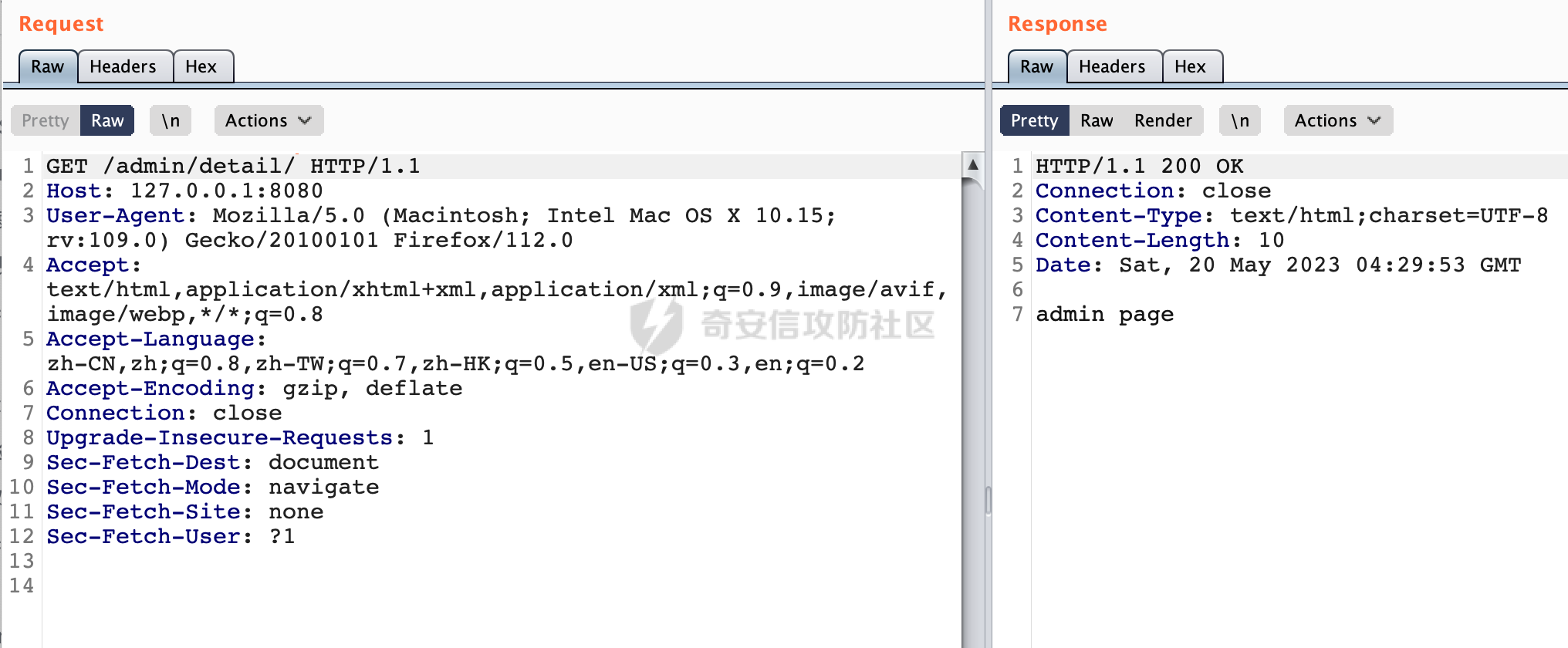 2.2.2 结合目录穿越符的绕过 ---------------- 在Spring中,相比AntPathMatcher,PathPattern获取请求path的逻辑会更简单,当使用PathPattern进行解析时,this.usesPathPatterns()为true: 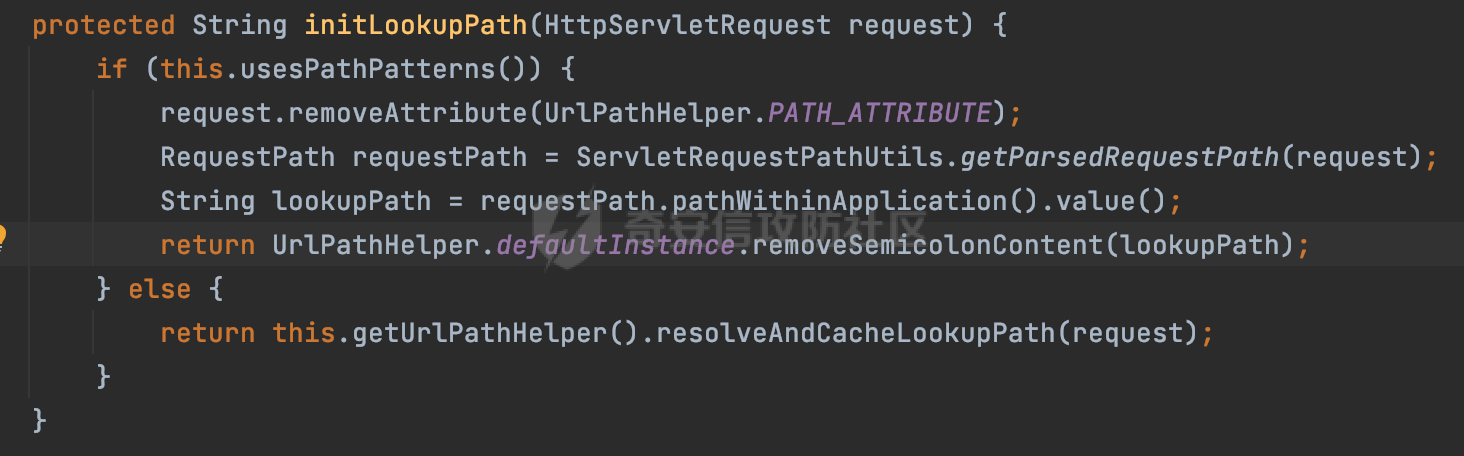 此时会从request域中获取PATH\_ATTRIBUTE属性的内容,然后使用defaultInstance对象进行处理,这里实际上是根据removeSemicolonContent的值(默认为true)确定是移除请求URI中的所有分号内容还是只移除jsessionid部分,类似`//`以及目录穿越符并不会进行处理:  根据前面的分析,tomcat跟jetty在获取当前请求匹配的安全约束时,对应的path是会对目录穿越符进行处理的,那么在某些场景下可能因为解析差异存在绕过的风险。 以tomcat为例,假设`/admin/`目录下的路径都需要以admin角色才能访问: ```Java public TomcatServletWebServerFactory servletContainer() { TomcatServletWebServerFactory tomcatServletContainerFactory = new TomcatServletWebServerFactory(); tomcatServletContainerFactory.addContextCustomizers(new TomcatContextCustomizer() { @Override public void customize(Context context) { SecurityConstraint securityConstraint = new SecurityConstraint(); SecurityCollection collection = new SecurityCollection(); collection.addPattern("/admin/*"); securityConstraint.addCollection(collection); securityConstraint.addAuthRole("admin"); context.addConstraint(securityConstraint); } }); return tomcatServletContainerFactory; } ``` 假设当前Controller的路由配置如下: ```Java @GetMapping("/admin/*") public void Manage(HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException { /*return "Manage page";*/ } ``` 可以看到正常情况下,缺少对应的角色会被拦截: 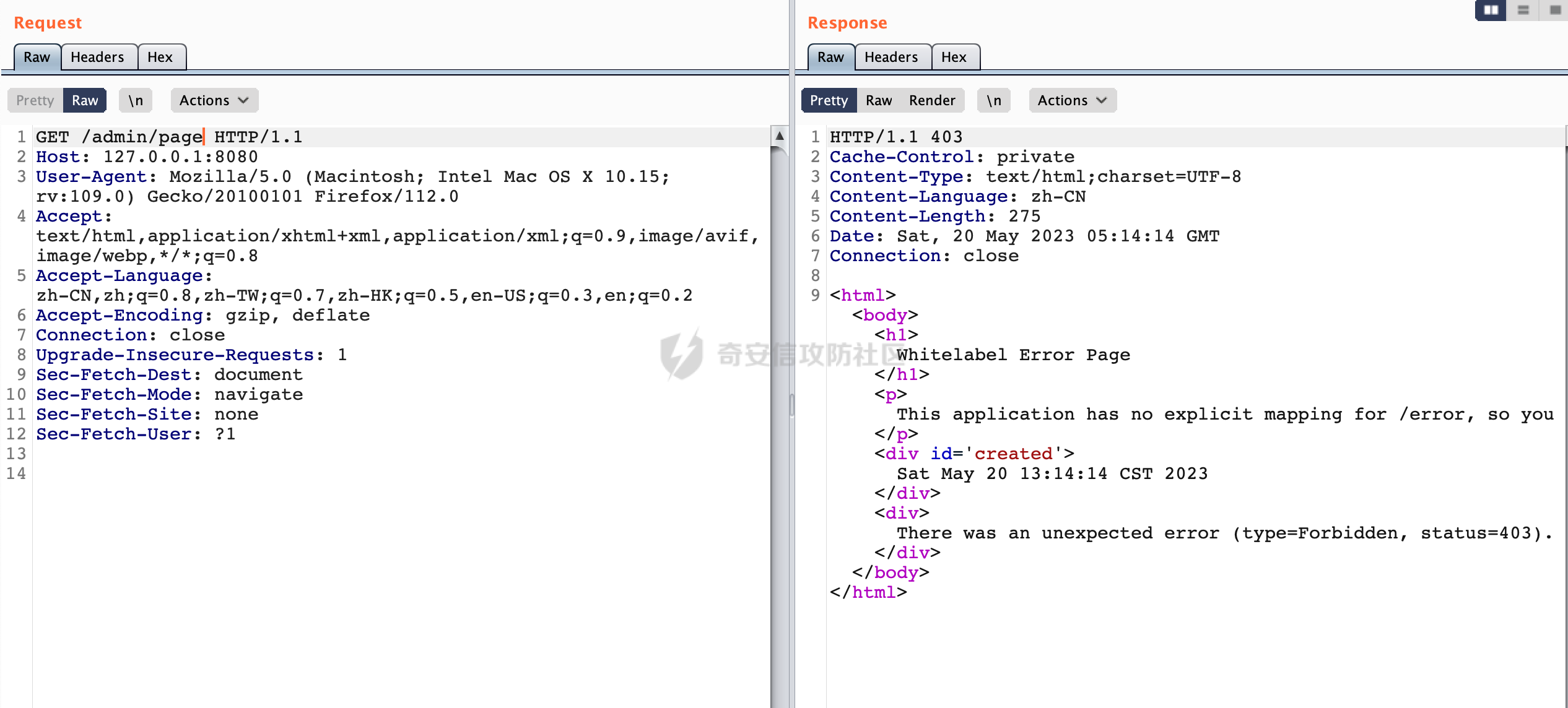 但是因为PathPattern模式下不解析目录穿越符,而在tomcat、jetty中会根据`../`进行回溯,最终导致找不到当前请求匹配的安全约束导致绕过: 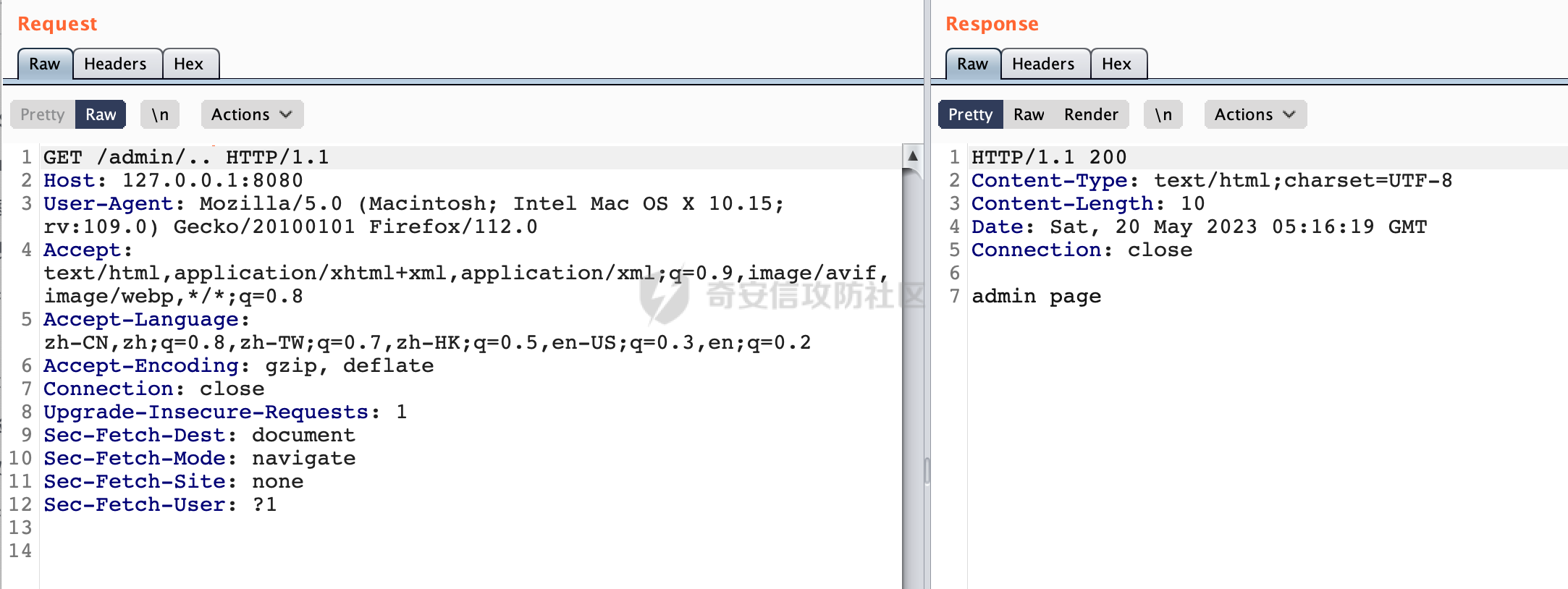 同理`/admin/{param}`以及`/admin/{*path}`也是可以通过`..`进行绕过的。 但是相对于undertow来说,在获取当前请求匹配的安全约束时,会从relativePath进行请求路径的获取,这里同样是不会处理`..`的,那么类似`/admin/..`的请求,在undertow调用`getSecurityInfo`处理时,因为此时处理的path为`/admin/..`,会逐个字符串匹配,然后命中安全约束,如果缺少角色的话会返回403状态码: 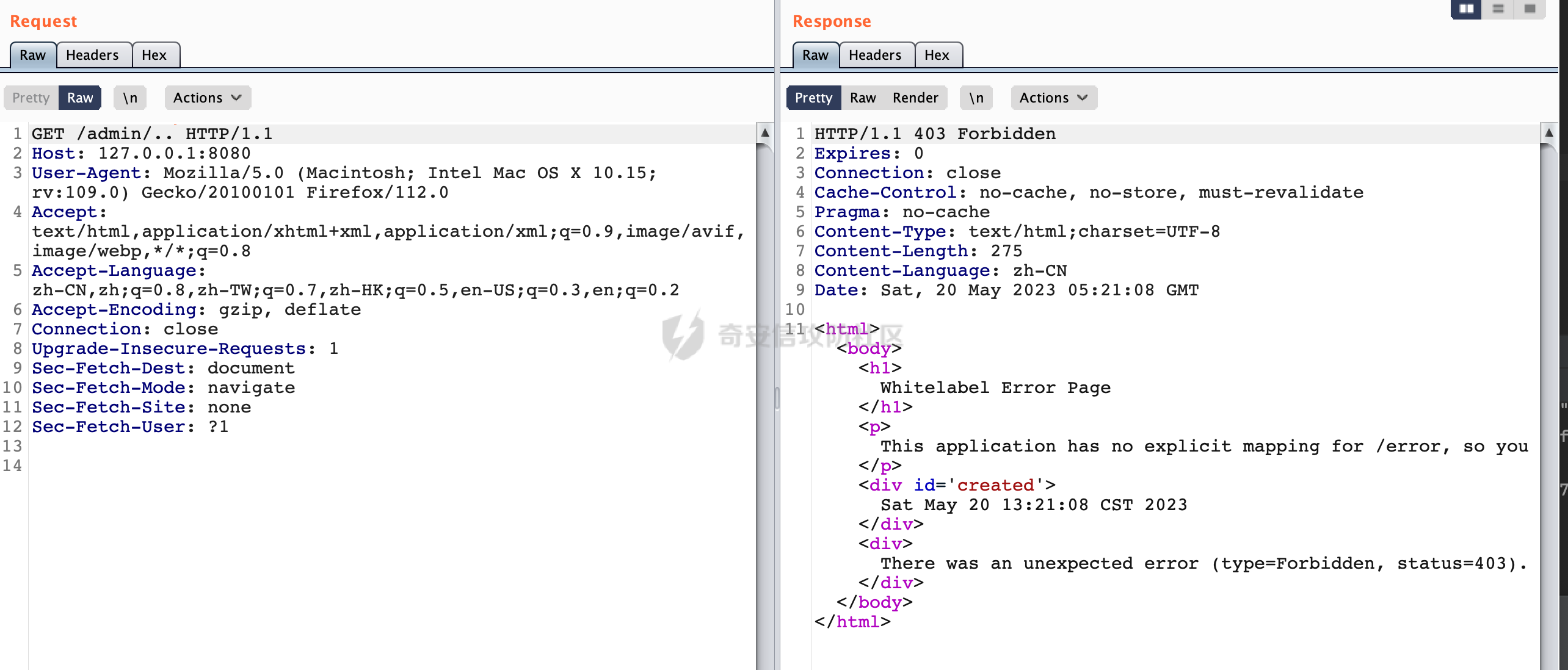 以上是一些绕过安全约束的场景。 0x03 其他 ======= 以上代码片段只是在特定上下文中的一部分,并不能完整地展示出整个处理过程。具体的上下文配置、路径匹配规则和方法定义可能会因应用程序的版本而有所不同。但是整体思路还是基于解析差异来分析的。相比于安全约束,使用类似SpringSecurity等鉴权框架会更为的成熟。
发表于 2023-05-26 09:00:00
阅读 ( 11073 )
分类:
代码审计
1 推荐
收藏
0 条评论
请先
登录
后评论
tkswifty
66 篇文章
×
发送私信
请先
登录
后发送私信
×
举报此文章
垃圾广告信息:
广告、推广、测试等内容
违规内容:
色情、暴力、血腥、敏感信息等内容
不友善内容:
人身攻击、挑衅辱骂、恶意行为
其他原因:
请补充说明
举报原因:
×
如果觉得我的文章对您有用,请随意打赏。你的支持将鼓励我继续创作!