问答
发起
提问
文章
攻防
AI
活动
Toggle navigation
首页
(current)
问答
商城
实战攻防技术
AI安全
NEW
活动
摸鱼办
搜索
登录
注册
浅谈Spring与Filter&Interceptor解析过程
渗透测试
过滤器Filter&拦截器Interceptor是开发中常用到的重要组件,浅谈Spring与Filter&Interceptor解析过程。
0x00 前言 ======= 过滤器(Filter),是JavaEE的标准,依赖于Servlet容器,使用的时候是配置在SpringMVC框架中是配置在web.xml文件中的,可以配置多个,执行的顺序是根据配置顺序从上到下。在SpringBoot项目中也可以采用注解的形式实现。其是基于函数回调实现的。类似常见的权限控制框架Shiro也是基于Filter进行拓展的。 拦截器(Interceptor)不依赖Servlet容器,依赖Spring等 Web 框架,在SpringMVC框架中是配置在SpringMVC的配置文件中,在SpringBoot项目中也可以采用注解的形式实现。拦截器是AOP的一种应用,底层采用Java的反射机制来实现的。 除此之外,两者还有以下区别: - 拦截器中可以注入 Spring 的 Bean,能够获取到各种需要的 Service 来处理业务逻辑,而过滤器则不行。 - 过滤器会拦截所有请求,而拦截器仅会拦截Controller的请求和static资源目录下的请求,对于直接访问静态资源的请求无法处理。 - Spring Controller收到的请求,都是经过 Tomcat 容器解析后交给 Servlet,再由 Servlet 转交给 Controller 的(在DispatcherServlet进行分发处理)。本身并不进行 Web 的处理。所以**Filter总是优先于Interceptor执行**。 0x01 过滤器Filter ============== 1.1 Spring中Filter的使用 -------------------- 通过过滤器Filter,可以实现各种功能和任务。例如用来记录请求和响应的信息,如请求参数、响应状态码等,以便进行调试、监控和分析。也用于实现用户身份验证和授权,以确保只有授权用户可以访问特定的资源。下面看看在Spring中如何创建Filter。 ### 1.1.1 在web.xml配置 对于Spring MVC项目,可以在web.xml进行Filter的配置,例如下面的例子,定义了一个字符编码的过滤器,对项目下的所有路由均生效:  ### 1.1.2 通过@WebFilter 注解配置 Servlet3.0提供@WebFilter注解将一个实现了javax.servlet.Filter接口的类定义为过滤器,这样我们在web应用中使用过滤器时,也不再需要在web.xml文件中配置过滤器的相关描述信息了。 举例说明: 首先通过实现Filter接口创建过滤器,在doFilter方法里实现对应的逻辑对请求和响应进行处理,然后添加`@WebFilter`注解,并通过urlPatterns属性指定URL 匹配模式: ```Java @WebFilter(urlPatterns = "/*") public class InvalidRequestFilter implements Filter { @Override public void doFilter(ServletRequest ServletRequest, ServletResponse ServletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException { // 这里编写Filter的逻辑代码,对请求和响应进行处理 //...... } } ``` 最后在启动类上增加`@ServletComponentScan()`注解,参数就是Filter所在的包路径: ```Java @SpringBootApplication @ServletComponentScan("Filter对应的包路径") public class Application { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args); } } ``` ### 1.1.3 通过@Bean来配置 举例说明: 首先通过实现Filter接口创建过滤器,在doFilter方法里实现对应的逻辑对请求和响应进行处理: ```Java @Component public class InvalidRequestFilter implements Filter { @Override public void doFilter(ServletRequest ServletRequest, ServletResponse ServletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException { // 这里编写Filter的逻辑代码,对请求和响应进行处理 //...... } } ``` 在配置类添加@Configuration注解,通过FilterRegistrationBean实例进行注册,将自定义的 Filter 声明成 Bean 交给 Spring 管理,设置匹配的 URL 、指定 Filter 的先后顺序: ```Java @Configuration public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer { @Bean public FilterRegistrationBean FilterConfig() { FilterRegistrationBean registrationBean = new FilterRegistrationBean<>(); registrationBean.setFilter(new InvalidRequestFilter()); registrationBean.addUrlPatterns("/*"); return registrationBean; } } ``` 1.2 Filter过滤器调用过程分析 ------------------- 过滤器是Servlet的实现规范,仅在tomcat等Web容器中调用。Spring Boot默认内嵌Tomcat作为Web服务器。以tomcat-embed-core-9.0.64为例,查看Filter的具体调用过程。 Filter调用时会在org.apache.catalina.cor.StandardWrapperValve#invoke()方法中被创建执行。主要是通过ApplicationFilterFactory.createFilterChain创建FilterChain: 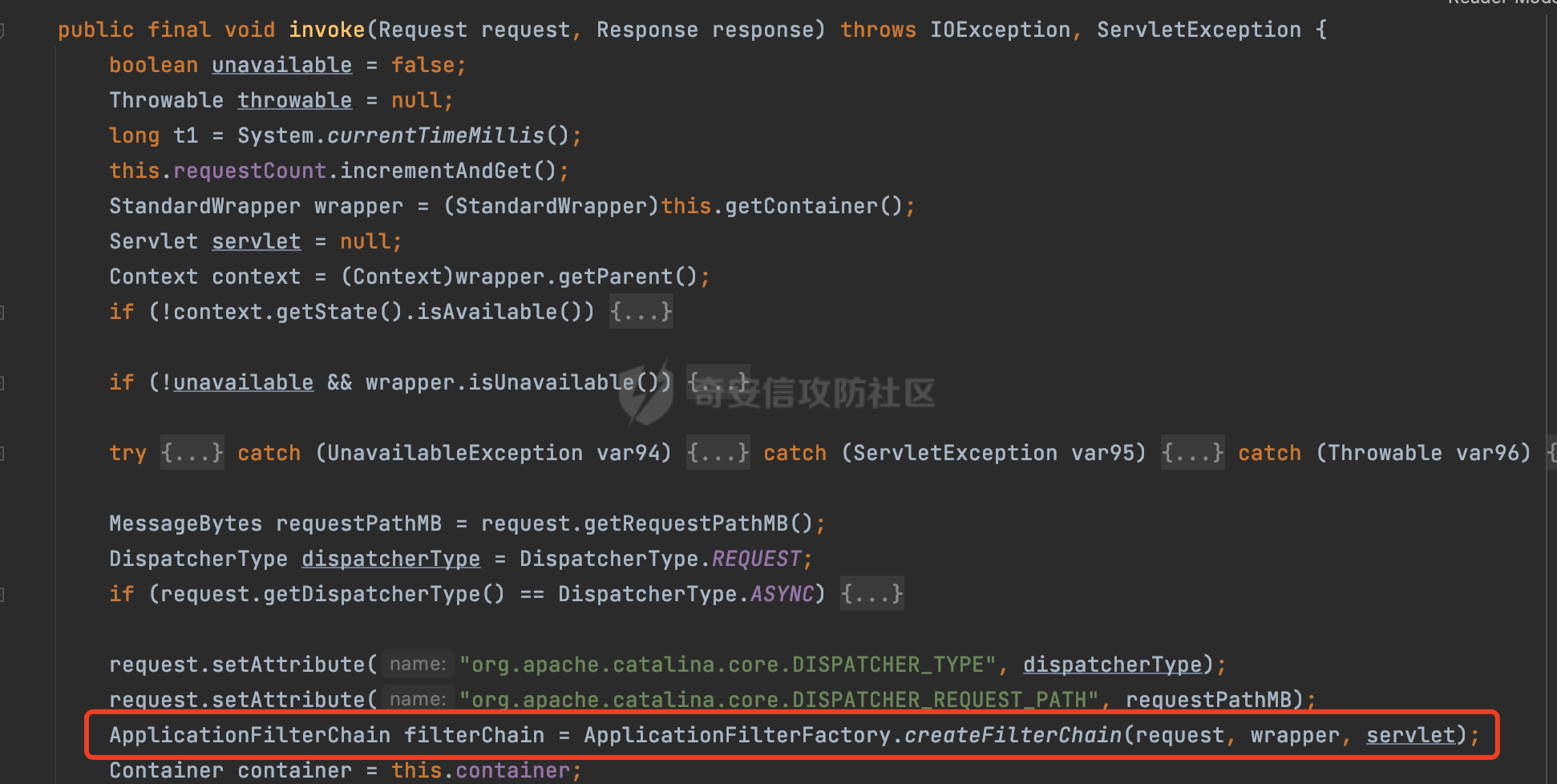 查看createFilterChain方法的具体实现: 首先会检查 `servlet` 是否为 `null`,如果是 `null`,表示没有指定Servlet,就没有需要创建的过滤器链。否则根据不同的情况创建一个 `ApplicationFilterChain` 对象或获取已存在的过滤器链对象。过滤器链对象负责管理一系列的过滤器: 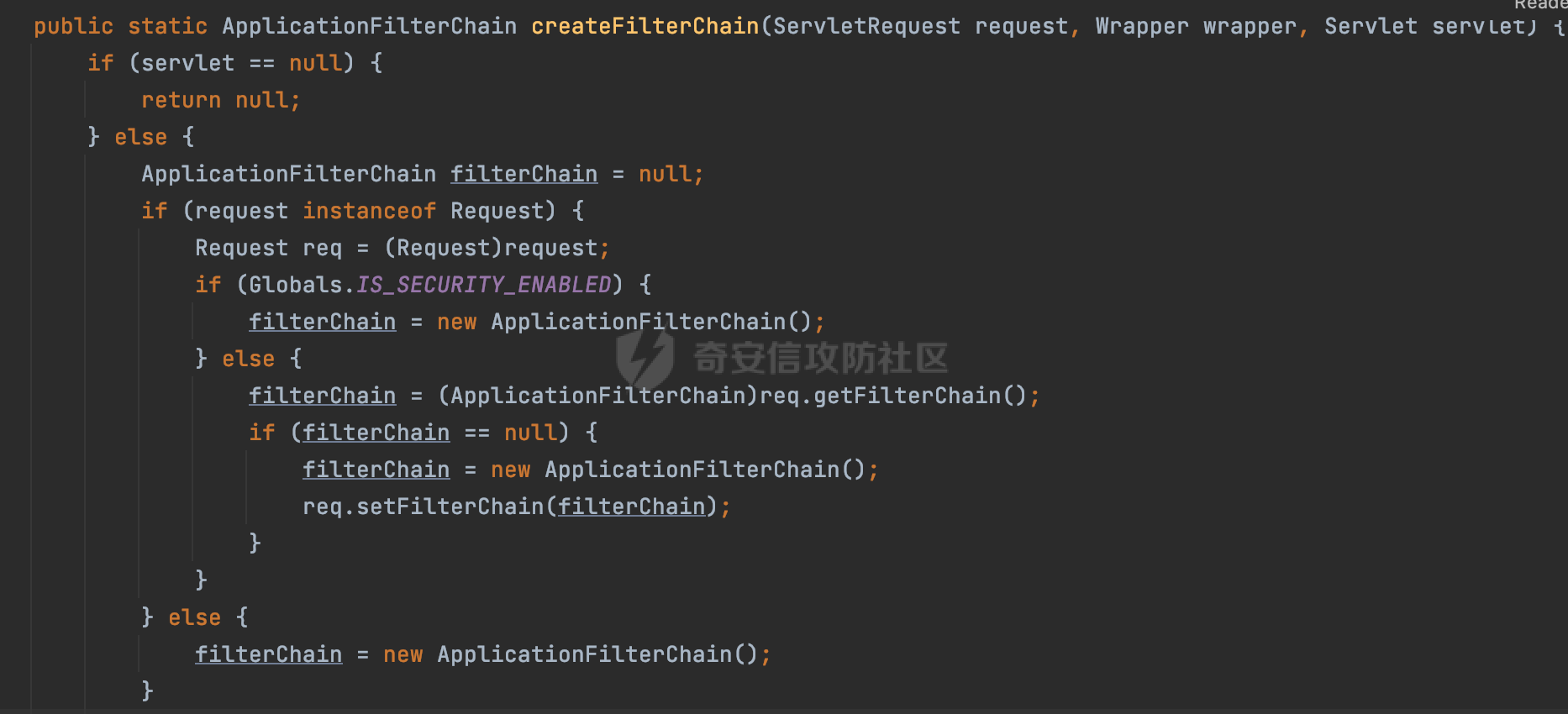 然后获取所有的filter的映射对象,在filterMaps中保存的是各个filter的元数据信息,若filterMaps不为null且length不为0,会对前面创建的filterChain进一步的封装,首先会获取与当前请求相关的标识信息,例如请求的调度类型(dispatcher)和请求的路径(requestPath): 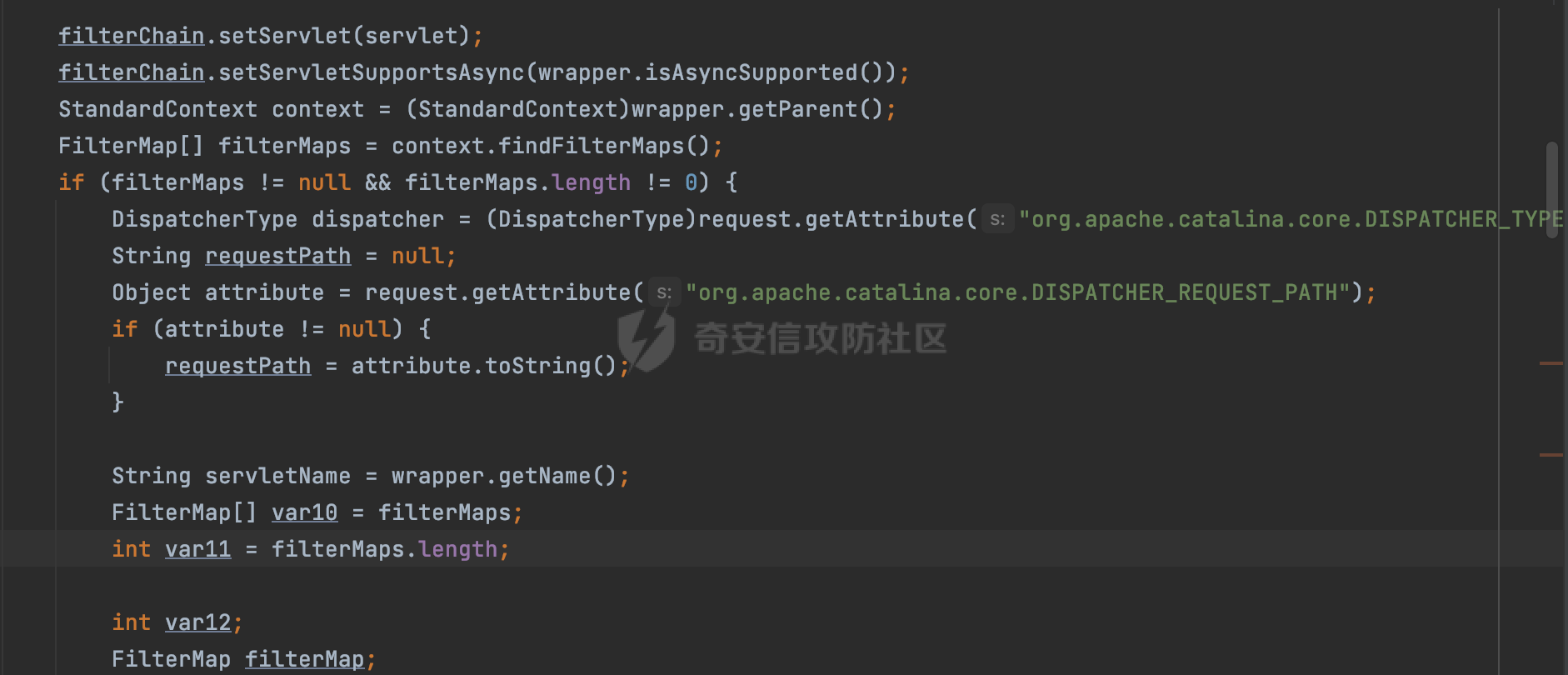 然后遍历所有过滤器映射,根据一定的条件判断将匹配的过滤器添加到过滤器链中。条件包括与调度类型的匹配和与请求路径或Servlet名称的匹配: 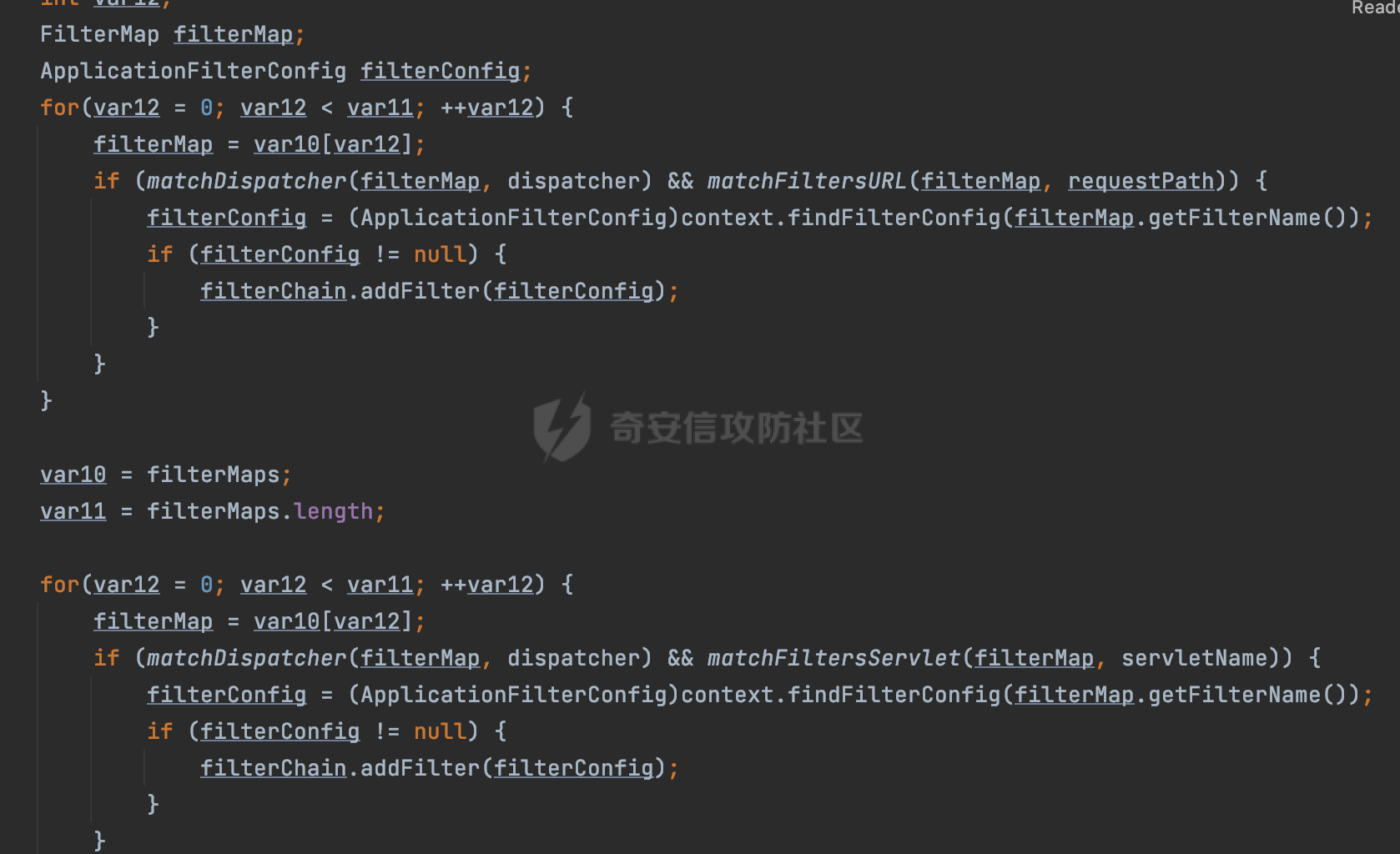 最后,返回创建的过滤器链,该过滤器链包含了所有匹配的过滤器。如果没有找到匹配的过滤器,则返回一个空的过滤器链。创建了filterChain之后,就开始执行ApplicationFilterChain的doFilter进行请求的链式处理: 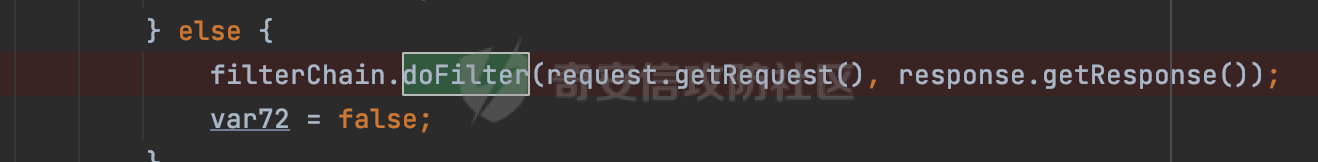 具体的逻辑在org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain#internalDoFilter方法,首先通过pos索引判断是否执行完了所有的filter,如果没有,取出当前待执行的索引filter,调用其doFilter方法: 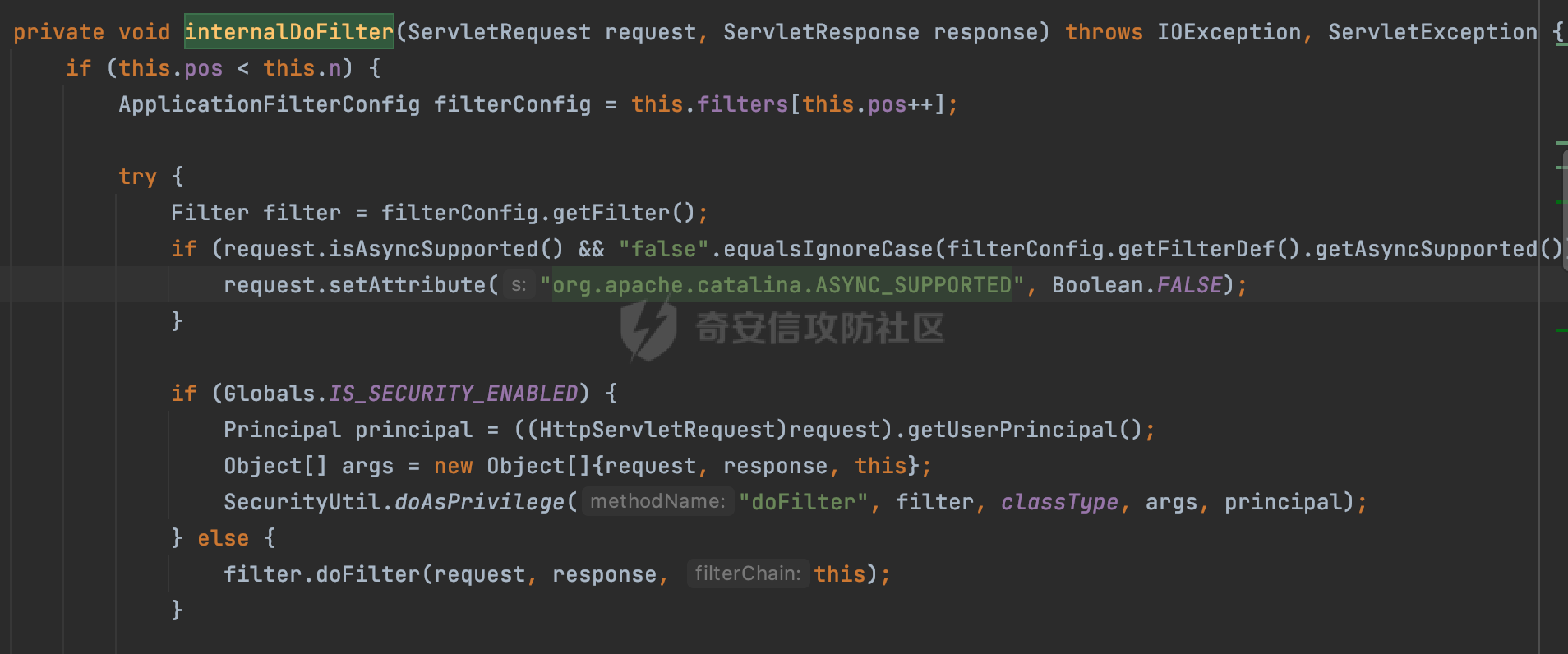 当所有的filter执行完后,会释放掉过滤器链及其相关资源。开始执行servlet业务模块`servlet.service(request, response);` 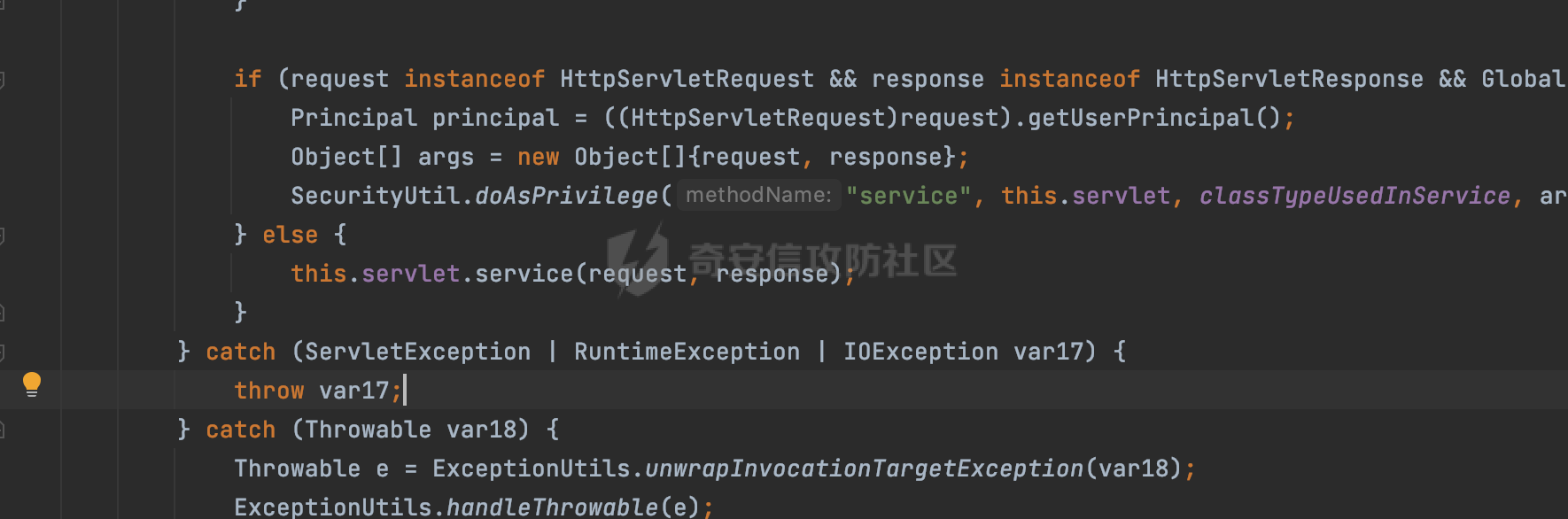 以上是tomcat中整个Filter的调用过程。 ### 1.2.1 Filter的匹配逻辑 在开始匹配前,首先会获取与当前请求相关的标识信息,请求的调度类型(dispatcher)和请求的路径(requestPath)还有servletName,看看具体的值是怎么生成的: 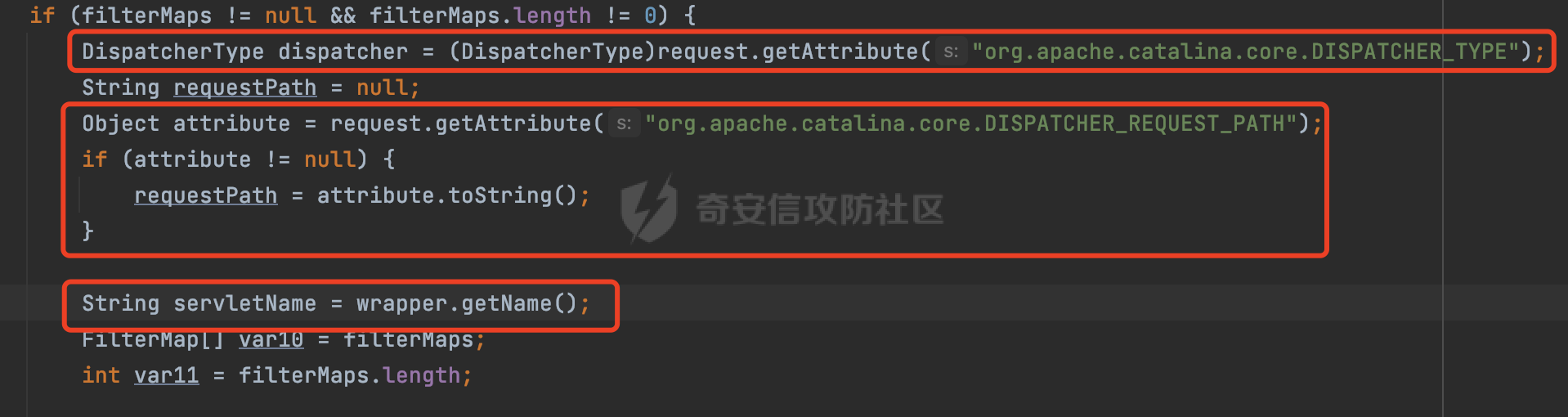 首先是dispatcher,通常情况下是REQUEST,表示对该请求的处理将立即开始,并将一直持续到该请求被完全处理为止。这是默认的调度类型: 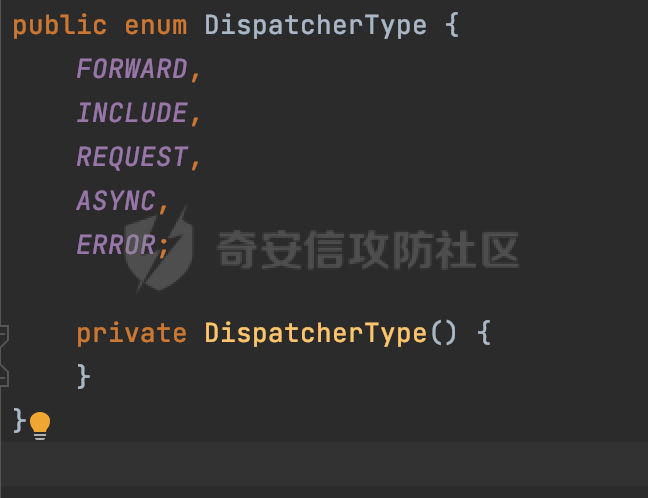 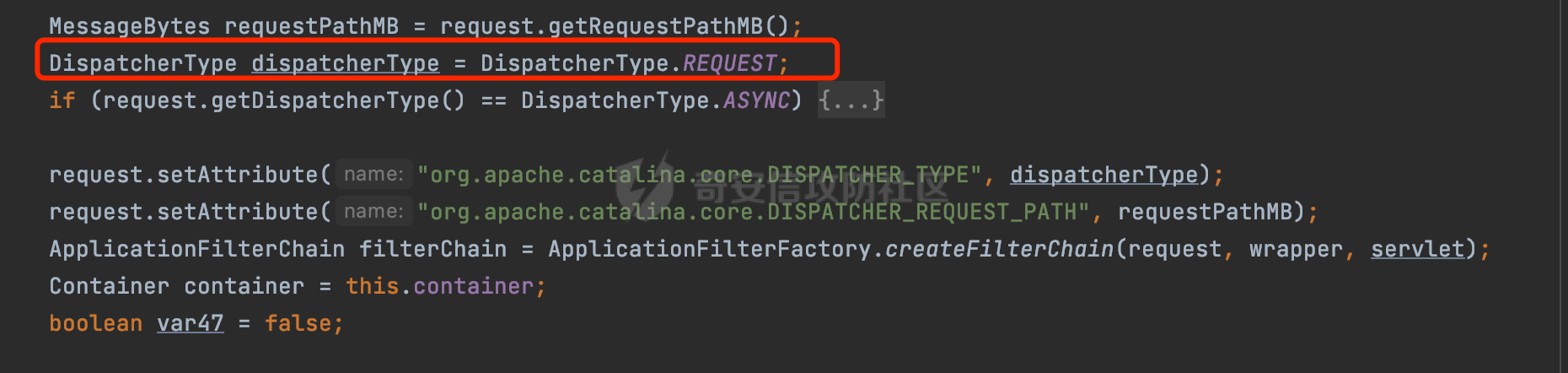 然后是requestPath,其是从request的`org.apache.catalina.core.DISPATCHER_REQUEST_PATH`属性中获取的。 在调用ApplicationFilterFactory.createFilterChain方法创建过滤器链前,将requestPathMB的值赋予给了request的`org.apache.catalina.core.DISPATCHER_REQUEST_PATH`属性: 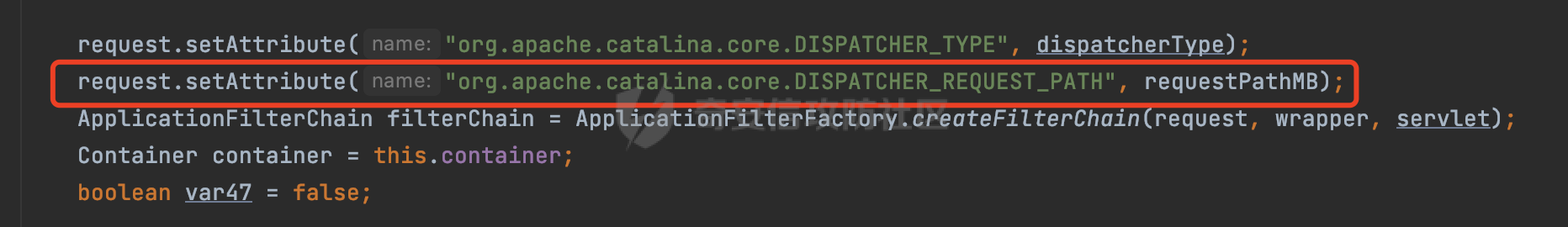 这里实际是从mappingData的requestPath属性获取的: 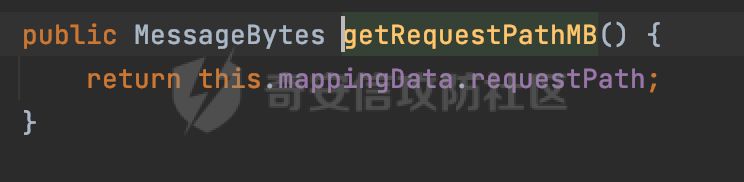 `org.apache.catalina.mapper.MappingData`的封装是在`CoyoteAdapter`中进行的。在`CoyoteAdapter`的`service`方法中,会通过prepareRequest方法设置Request对象的相关属性,包括uri、queryString、mappingData等。 在prepareRequest方法中,会调用MappingData类的recycle方法对mappingData对象进行重置,然后调用Mapper类的map方法对请求进行映射,最后将解析后的结果封装到MappingData对象中: 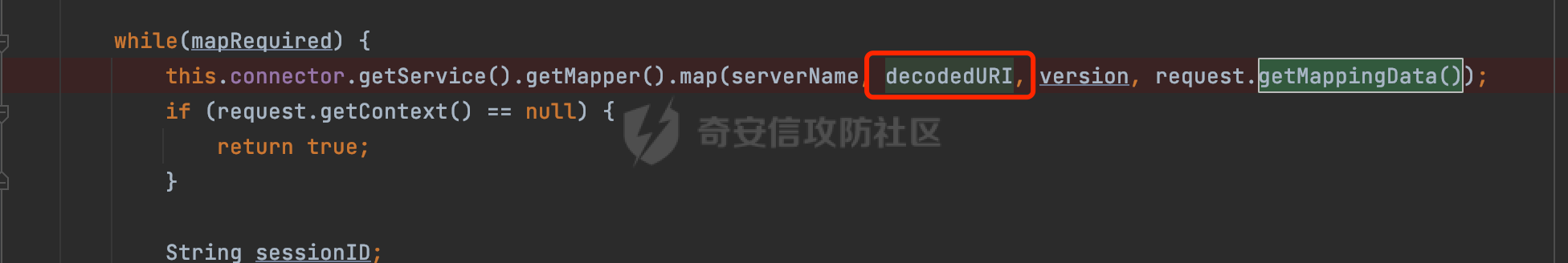 查看具体的逻辑可以看到这里会设置mappingData的requestPath属性: 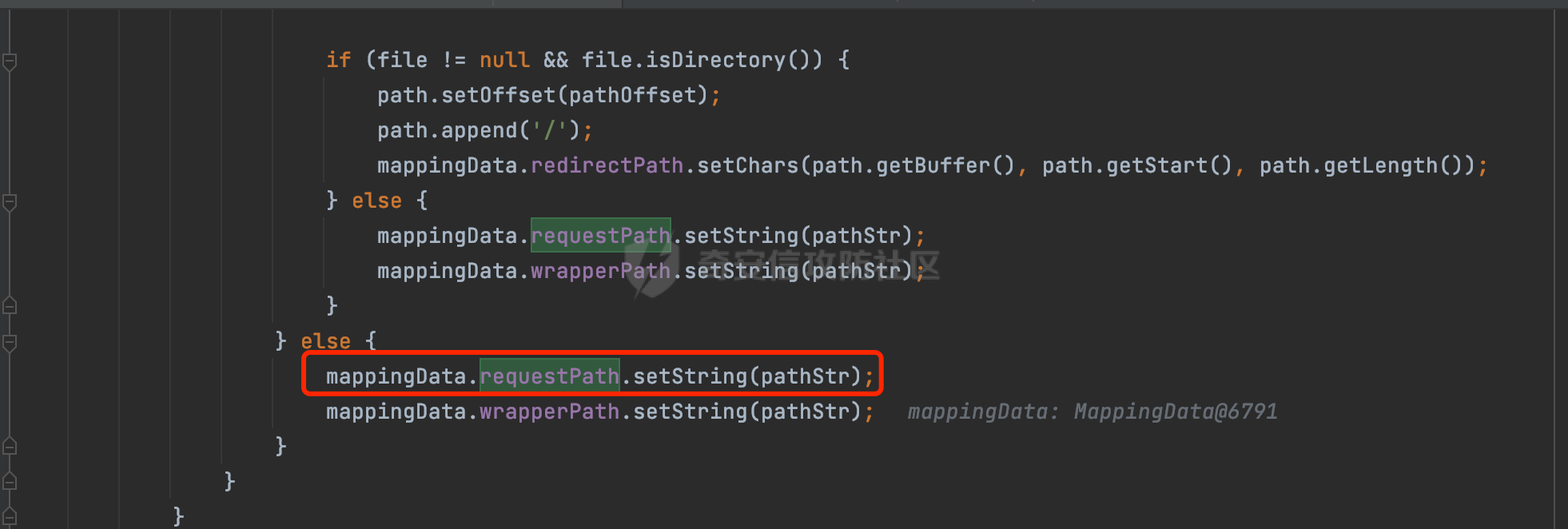 在Tomcat中,主要是在CoyoteAdapter.service()函数上对请求URL进行解析处理的,其会调用postParseRequest()函数来解析URL请求内容,主要处理逻辑如下,会调用parsePathParameters()和normalize()函数对请求内容进行解析处理: 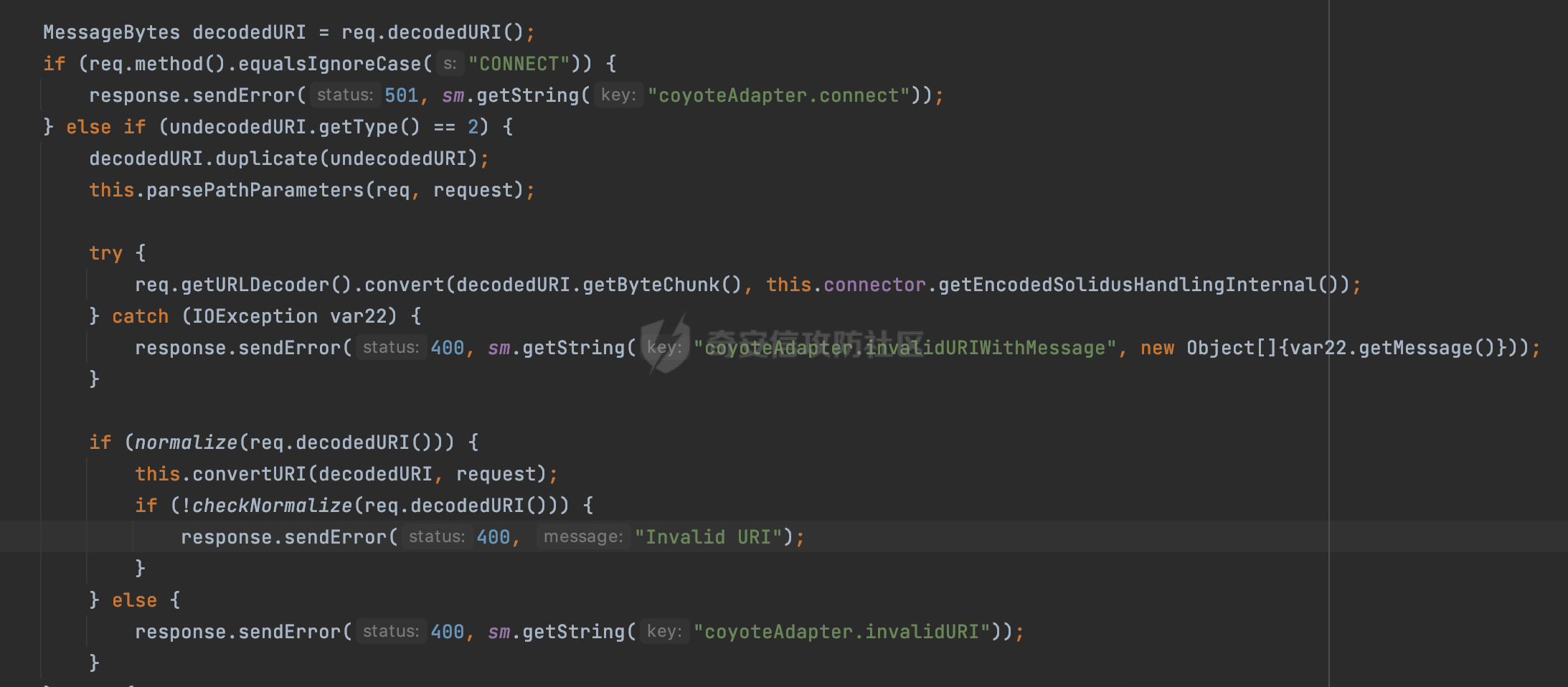 在parsePathParameters()中,先是寻找URL中是否存在`;`号,存在的话会将`;xxx/`中的分号与斜杠之间的字符串以及分号本身剔除: 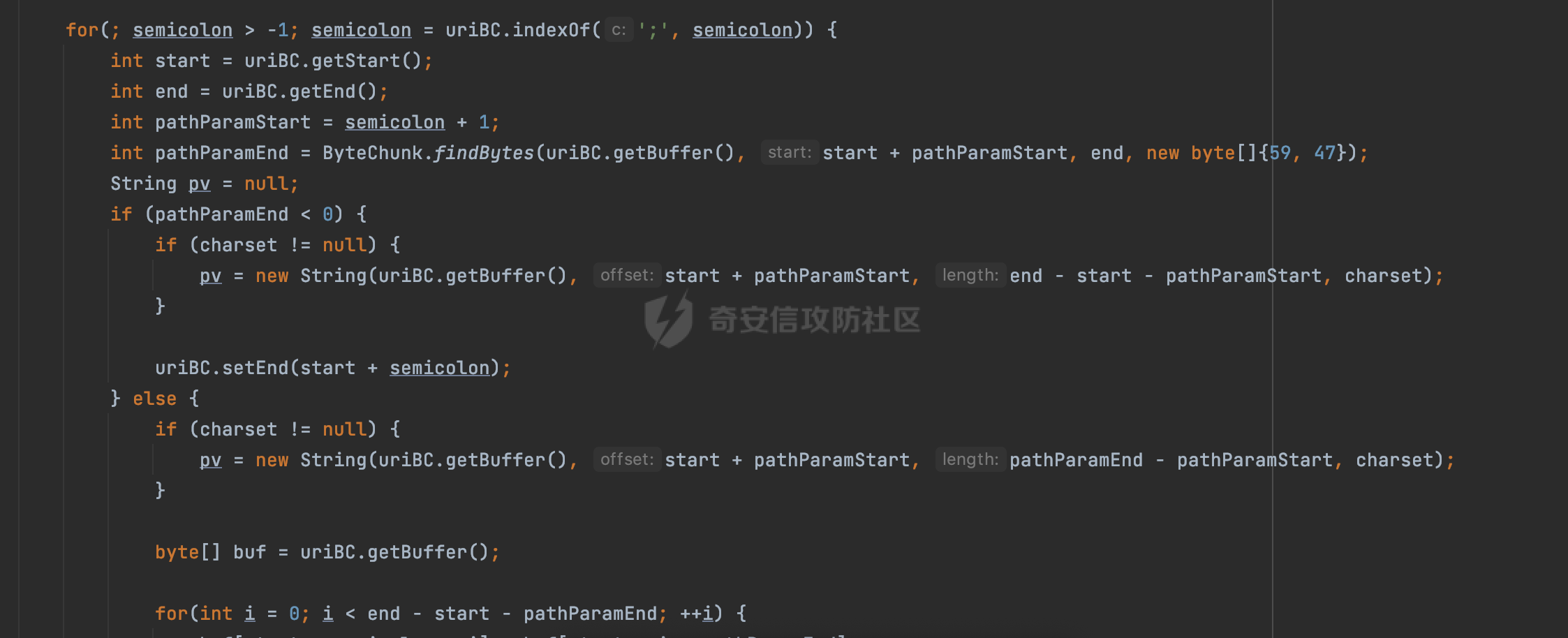 normalize()主要是对请求URL进行标准化处理,例如循环删除掉多余的`/`,处理目录穿越符号`/../`进行路径的回溯等: 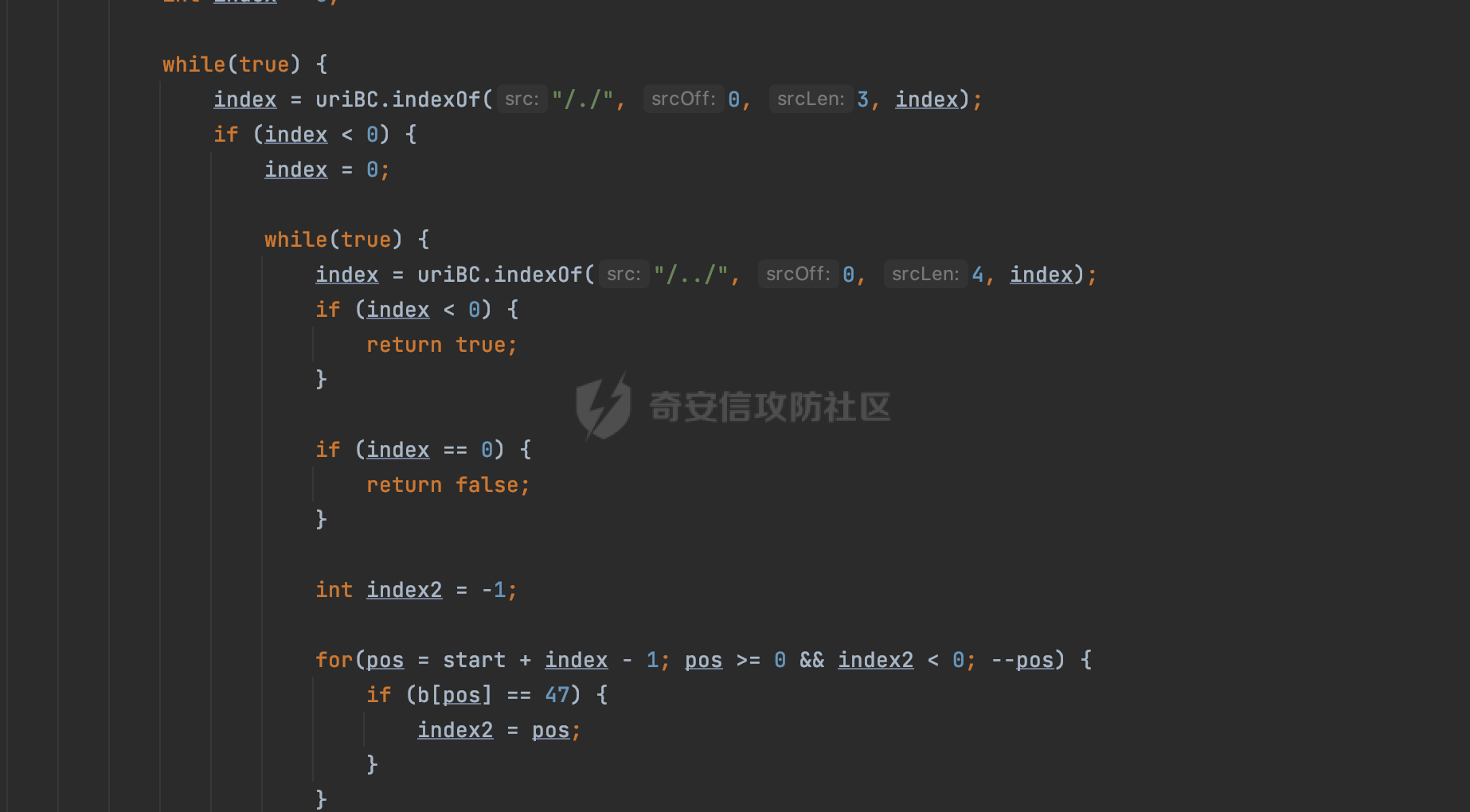 也就是说,**requestPathMB是对请求的URI进行一定规范化处理后的值**。 后续匹配Filter时,有一种情况是匹配类型和servlet名称都匹配,而servletName是从wrapper的name属性获取的,在Spring中DispatcherServlet会把请求分发给各个处理器进行处理,例如在Spring中常见的dispatcherServlet: 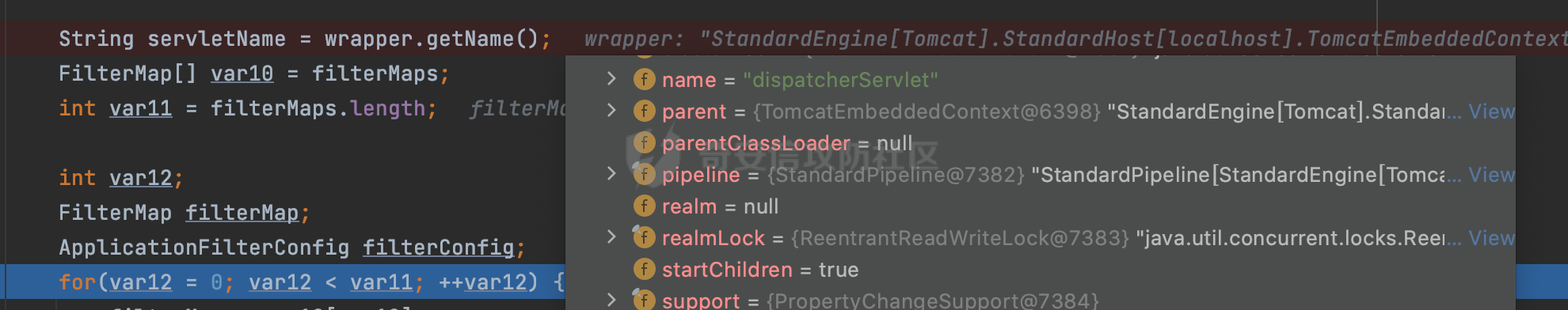 获取完与当前请求相关的标识信息后,会进入对应的匹配逻辑。主要是以下两种情况: - **类型和路径都匹配** 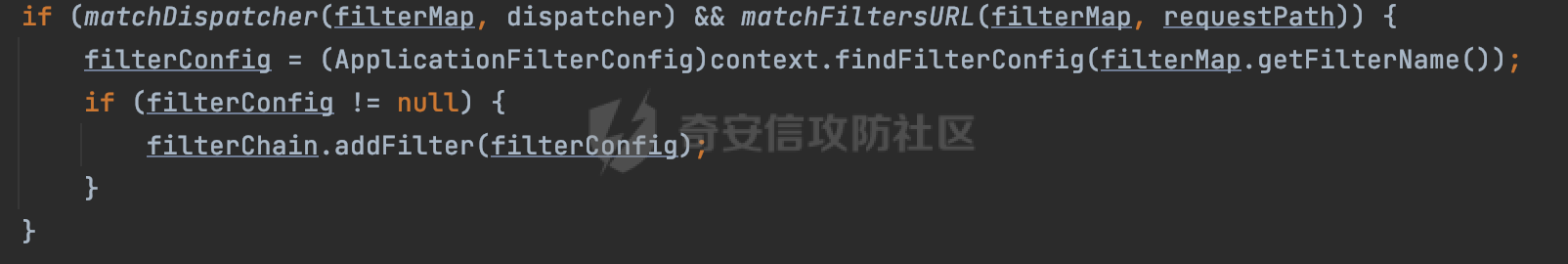 - **类型和servlet名称都匹配** 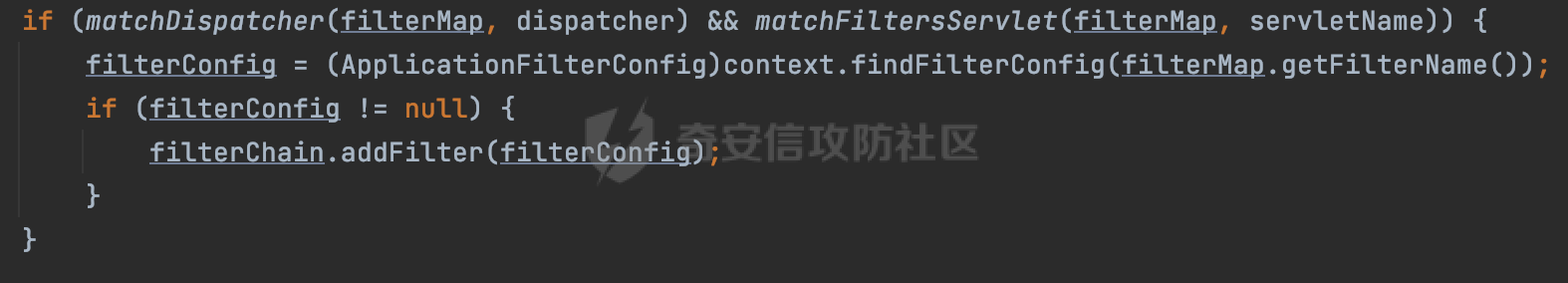 主要的匹配逻辑主要是跟如下三个函数有关: - matchDispatcher(filterMap, dispatcher) - matchFiltersURL(filterMap, requestPath) - matchFiltersServlet(filterMap, servletName) 两个匹配逻辑都会调用matchDispatcher方法判断给定的 `FilterMap` 是否与指定的调度类型 (`DispatcherType`) 匹配,Filter默认为`DispatcherType.REQUEST`: 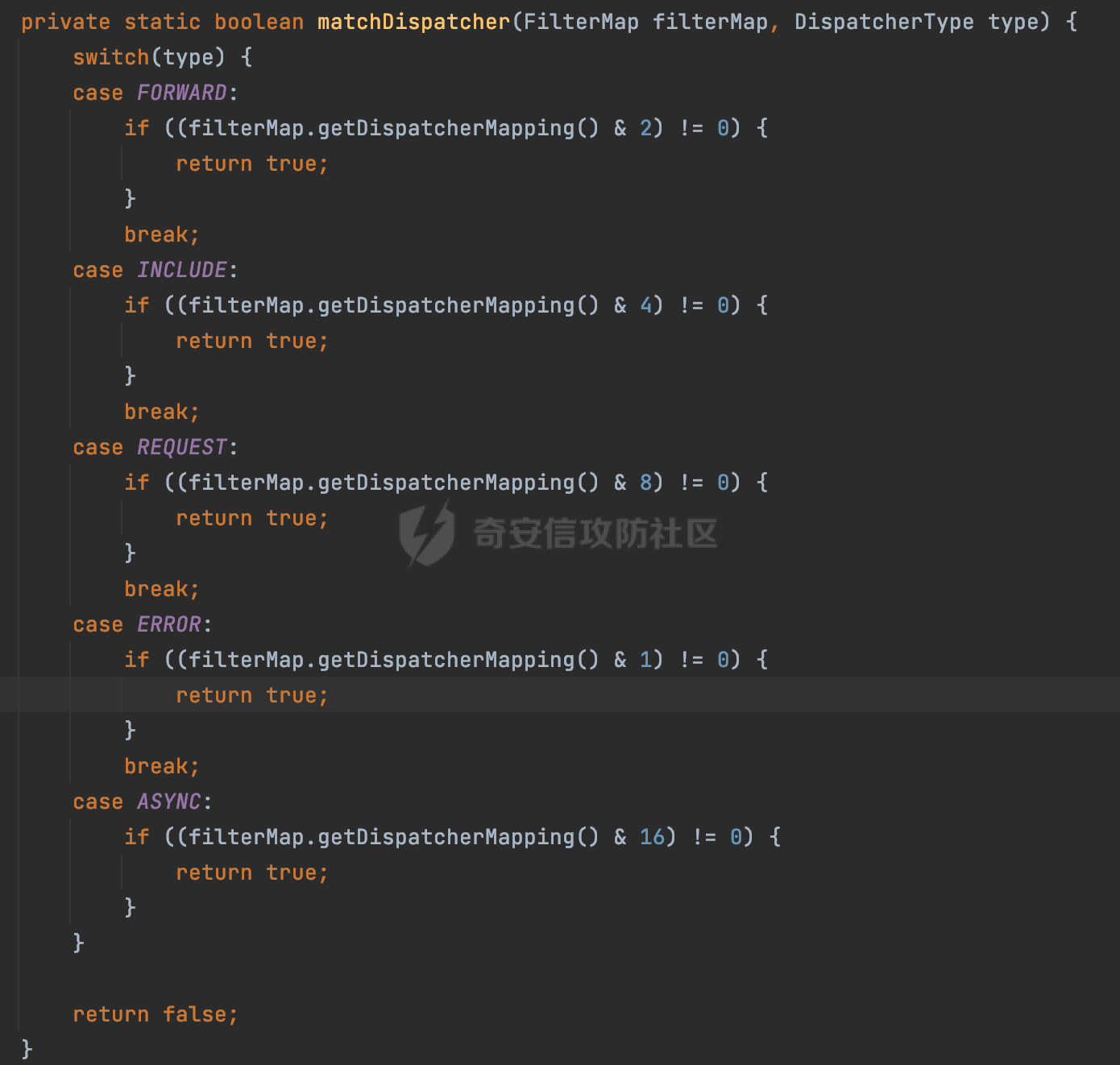 路径匹配关键函数`matchFiltersURL`主要用于判断给定的请求路径 (requestPath) 是否与 FilterMap 中配置的URL模式匹配。首先检查 `FilterMap` 是否配置为匹配所有URL模式,是则返回 `true`,表示该过滤器适用于所有请求路径。否则会遍历 `FilterMap` 中的URL模式,调用 `matchFiltersURL` 方法来判断请求路径是否与当前URL模式匹配。如果找到匹配的URL模式,就返回 `true`,表示该过滤器适用于当前请求路径: 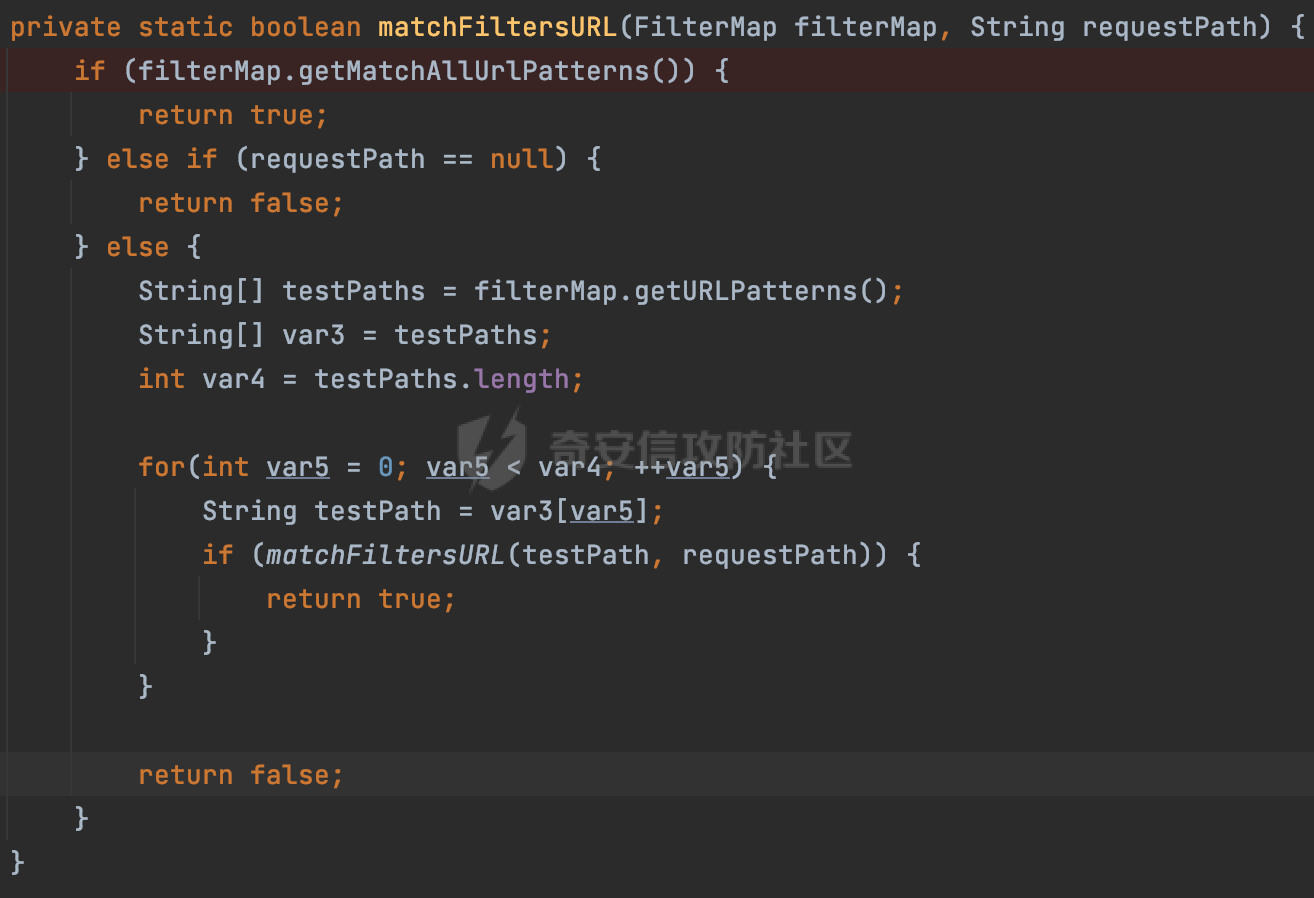 查看 `matchFiltersURL` 方法的具体实现,主要是检查以下几点: - `testPath` 是否不为 `null`以及 `testPath` 是否与 `requestPath` 完全相等 - `testPath` 是 `/*`则返回 `true`,表示匹配所有请求路径 - `testPath` 以 `/*` 结尾,会检查是否以 `testPath` 开头前缀部分与 `requestPath` 匹配。如果匹配成功,就返回 `true` - 如果 `testPath` 以 `*.` 开头,代码会检查是否以 `testPath` 中指定的文件扩展名结尾的 `requestPath` 是否匹配。如果匹配成功,就返回 `true` - 如果以上所有条件都不满足,最终返回 `false`,表示两个路径不匹配 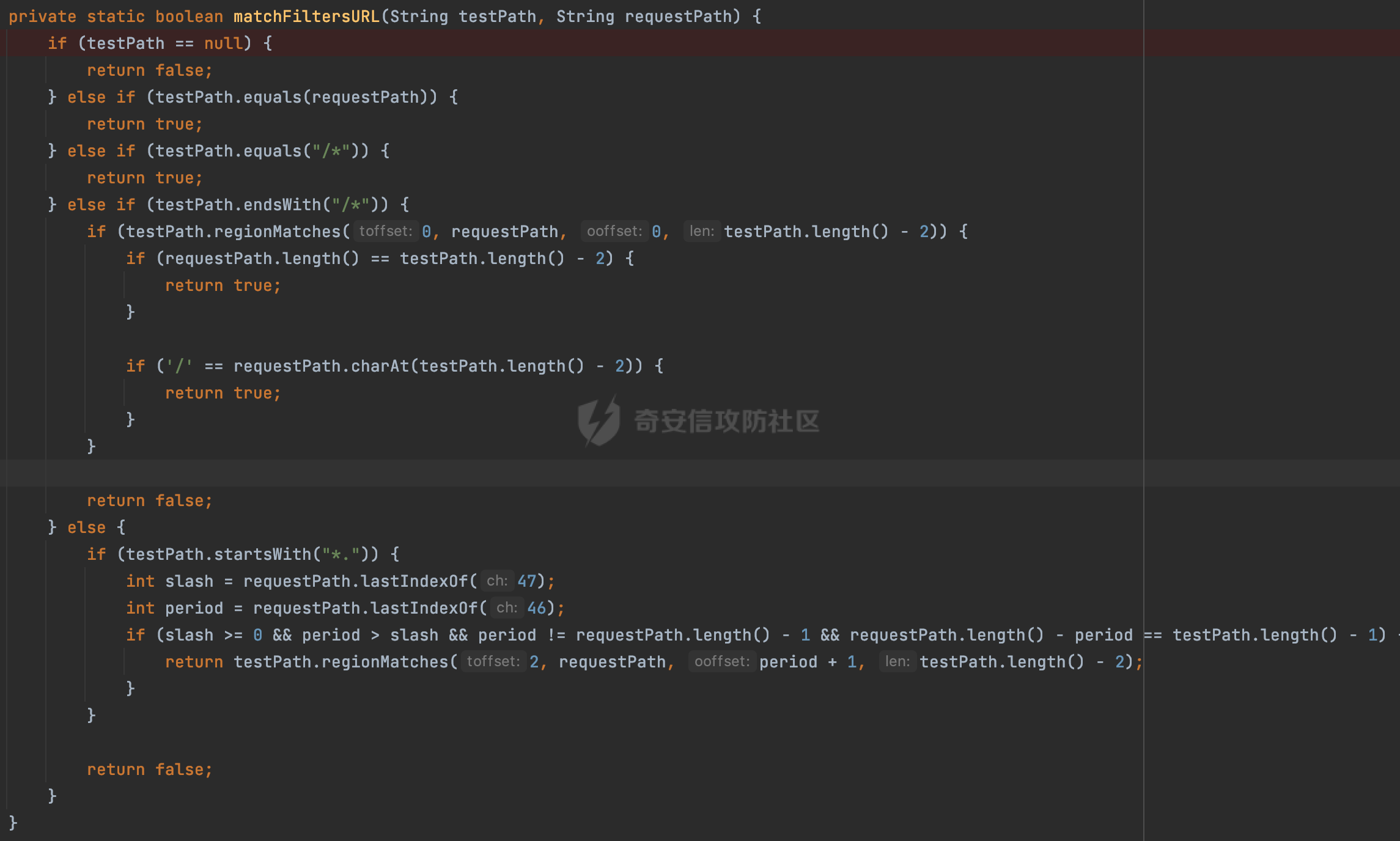 servlet名称匹配关键函数`matchFiltersURL`用于判断给定的Servlet名称(`servletName`)是否与 `FilterMap` 中配置的Servlet名称匹配,主要是通过遍历 `FilterMap` 中的Servlet名称数组,比较它与给定的 `servletName` 是否相等。如果找到相等的Servlet名称,就返回 `true`,表示该过滤器适用于当前Servlet: 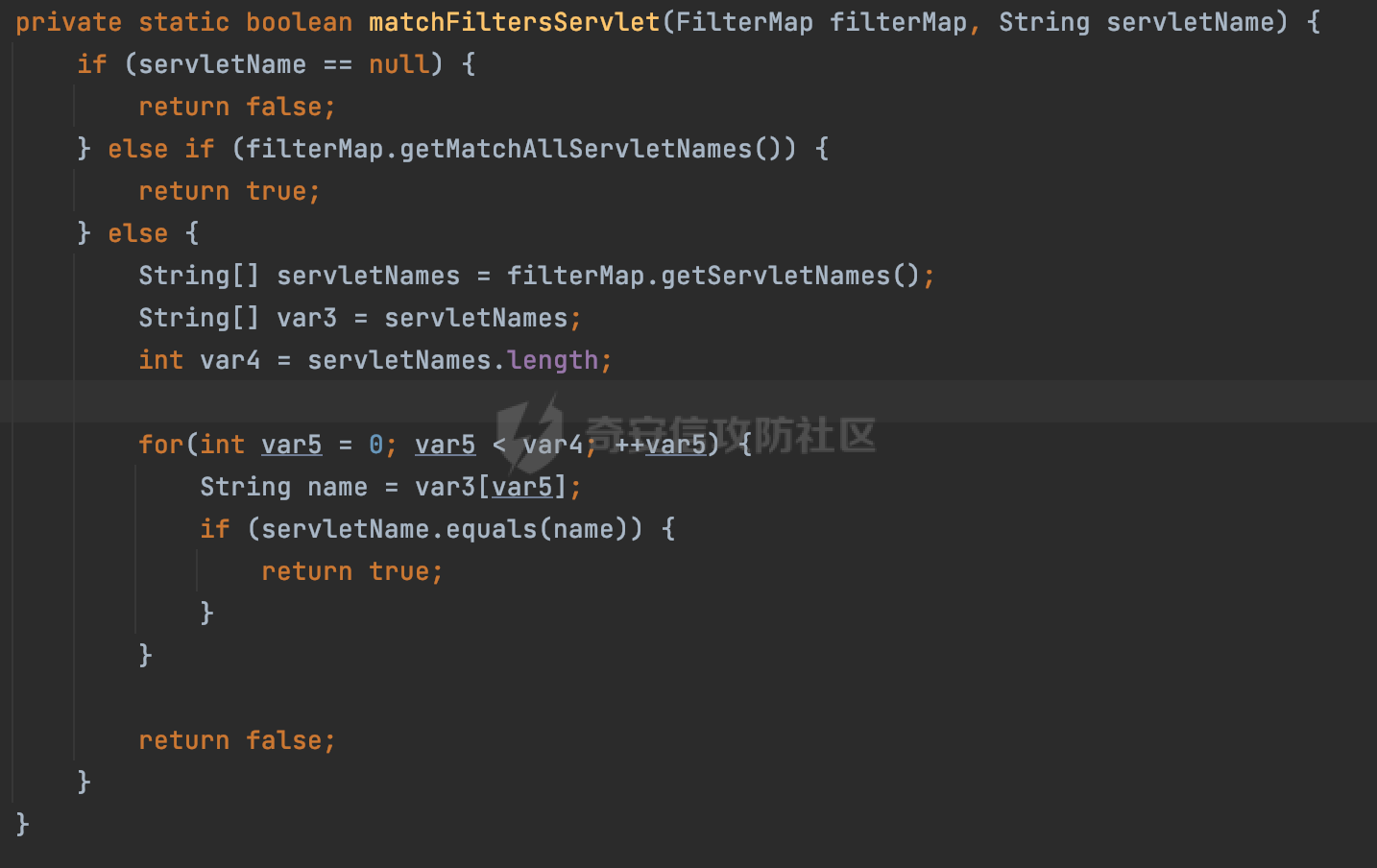 至此整个匹配过程结束。 0x02 拦截器Interceptor =================== 在Spring框架中,拦截器(Interceptor)是一种强大的工具,是AOP的一种应用,底层采用Java的反射机制来实现的。其允许您在请求到达控制器之前和离开控制器之后执行一些自定义的逻辑。拦截器通常用于处理诸如身份验证、日志记录、性能监控、国际化等非业务逻辑的需求。下面看看在Spring中如何创建Interceptor。 2.1 Spring中Interceptor的使用 ------------------------- Spring MVC提供了HandlerInterceptor接口来实现拦截器功能,可以通过实现这个接口注册拦截器,以添加常见的预处理行为。例如下面的例子: 首先通过实现HandlerInterceptor 接口自定义拦截器AuthInterceptor: ```Java public class AuthInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor { //前置处理 @Override public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { // 可以通过handler获取执行方法的相关信息, 方法名,注解等 } } ``` 在配置类添加@Configuration注解,通过重写addInterceptors方法,添加拦截器,并配置匹配路径: ```Java @Configuration public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer { @Override public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) { // 注册拦截器 registry.addInterceptor(new AuthInterceptor()).addPathPatterns("/**").excludePathPatterns("/test/**"); } } ``` 2.2 Interceptor拦截器调用过程分析 ------------------------ 以spring-webmvc-5.3.21为例,查看具体的解析过程。 当Spring MVC接收到请求时,Servlet容器会调用DispatcherServlet的service方法。这里会调用doDispatch方法进行进一步的处理。来获取对应的mappedHandler: 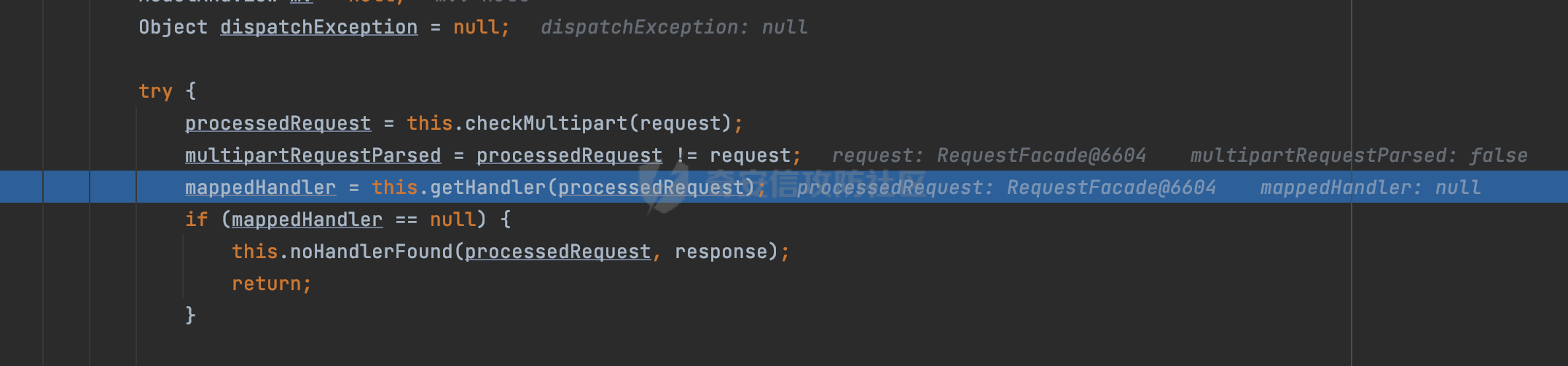 在getHandler方法中,会顺序循环调用HandlerMapping的getHandler方法: 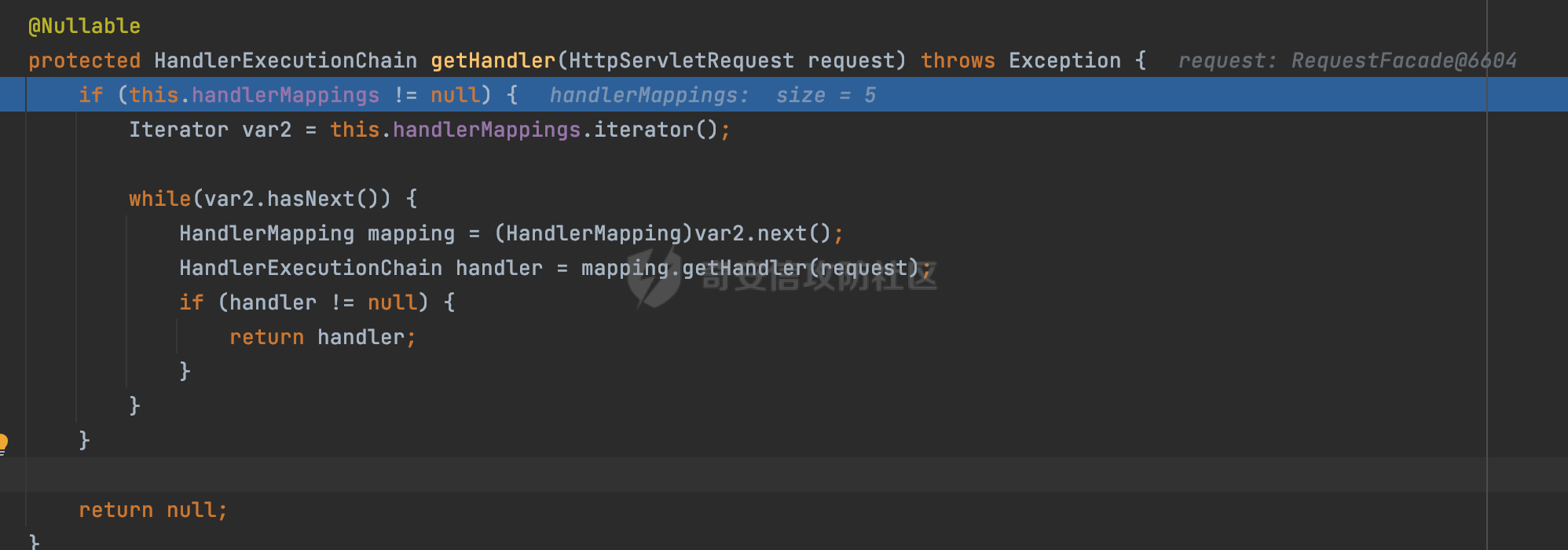 首先会通过RequestMappingHandlerMapping处理,在其getHandler方法中通过getHandlerInternal获取handler构建HandlerExecutionChain并返回,这里会添加该请求相关的所有Interceptor: 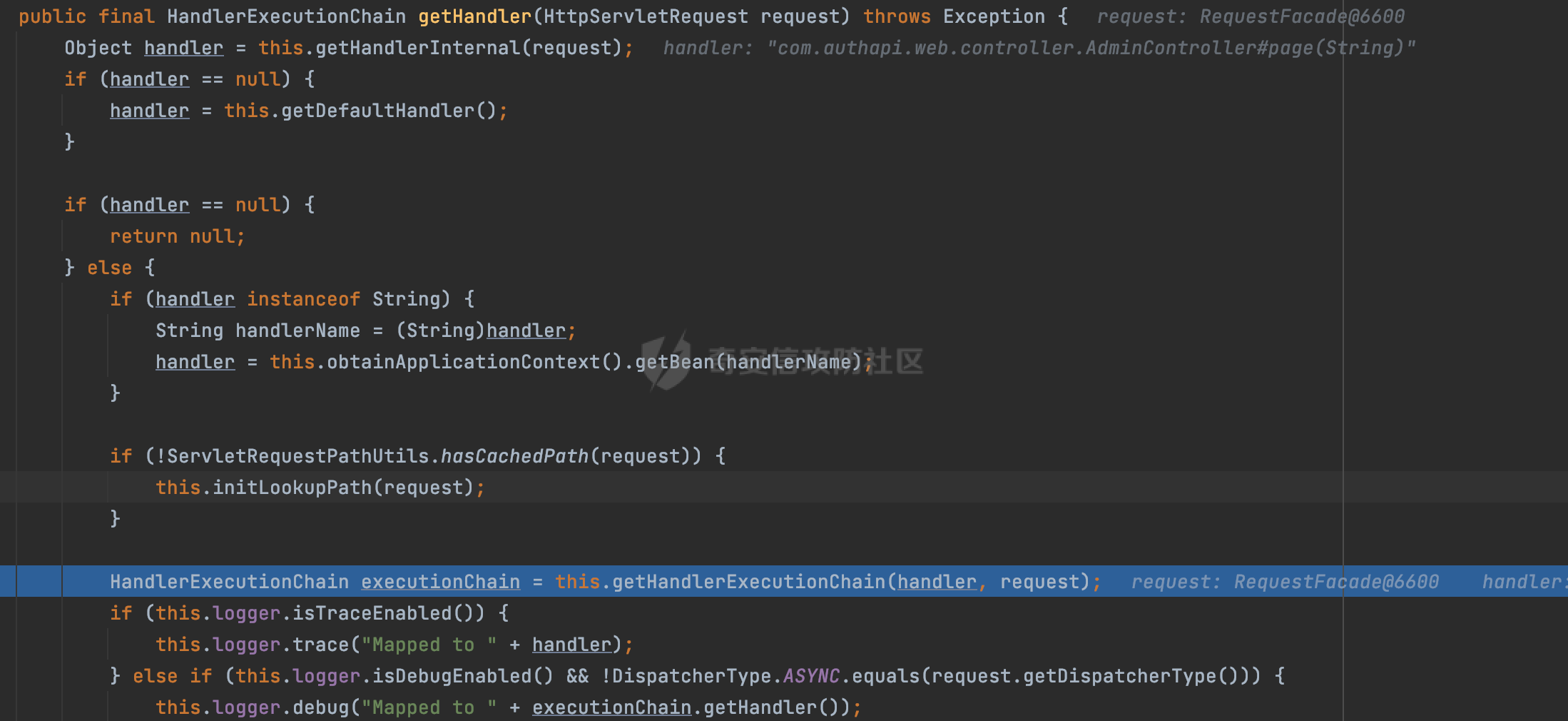 在getHandlerExecutionChain方法中,首先会创建一个`HandlerExecutionChain`对象,用于存储处理器和拦截器。这里会遍历 `adaptedInterceptors` 的拦截器集合,如果拦截器是 `MappedInterceptor` 的实例,并且它的 `matches(request)` 方法返回 `true`(表示请求的URL路径匹配该拦截器),则将该拦截器中的实际拦截器添加到 `chain` 中。否则直接将它添加到 `chain` 中,无需进行路径匹配: 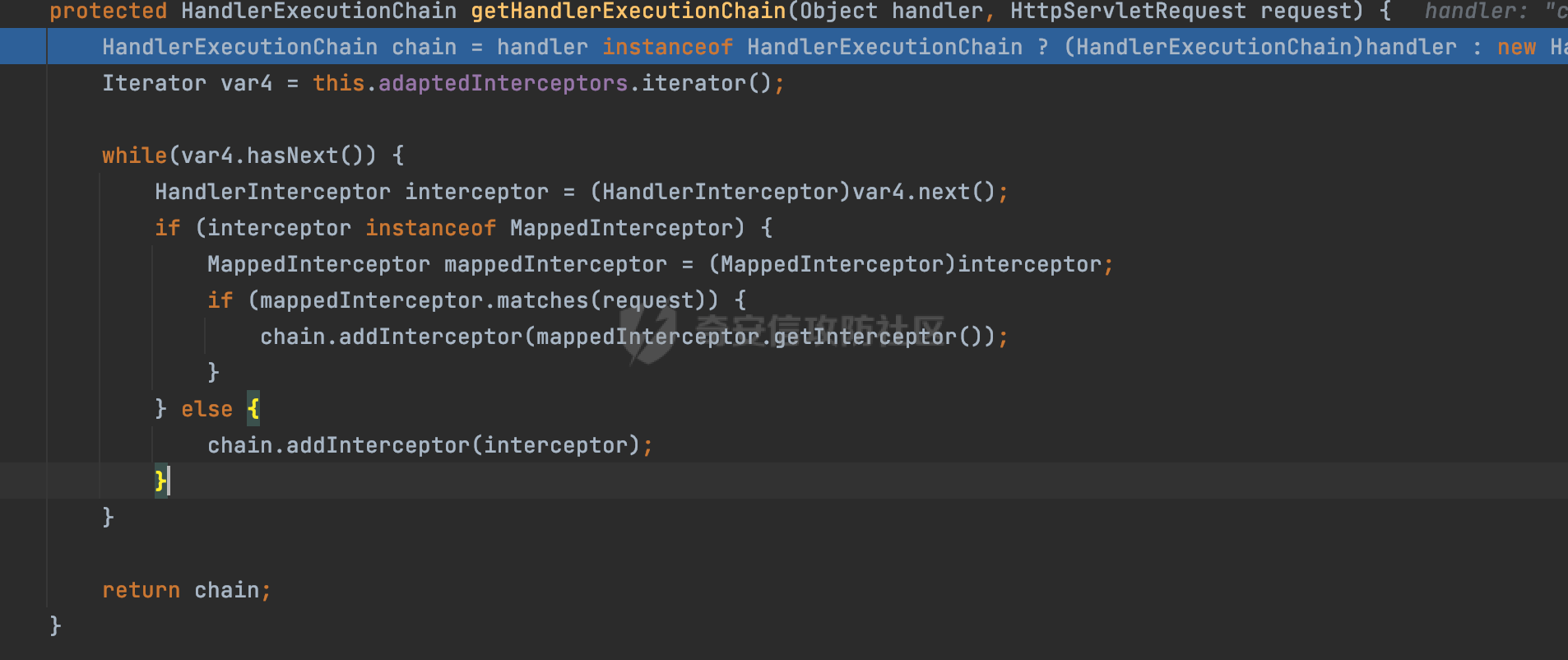 最后会返回构建好的 `HandlerExecutionChain` 对象 `chain`,其中包含了处理程序和相应的拦截器,以便在处理HTTP请求时按照一定的顺序执行这些拦截器操作。处理完后会获取处理器适配器,然后调用applyPreHandle方法进行处理:  这里实际就是执行拦截器前置处理preHandle方法: 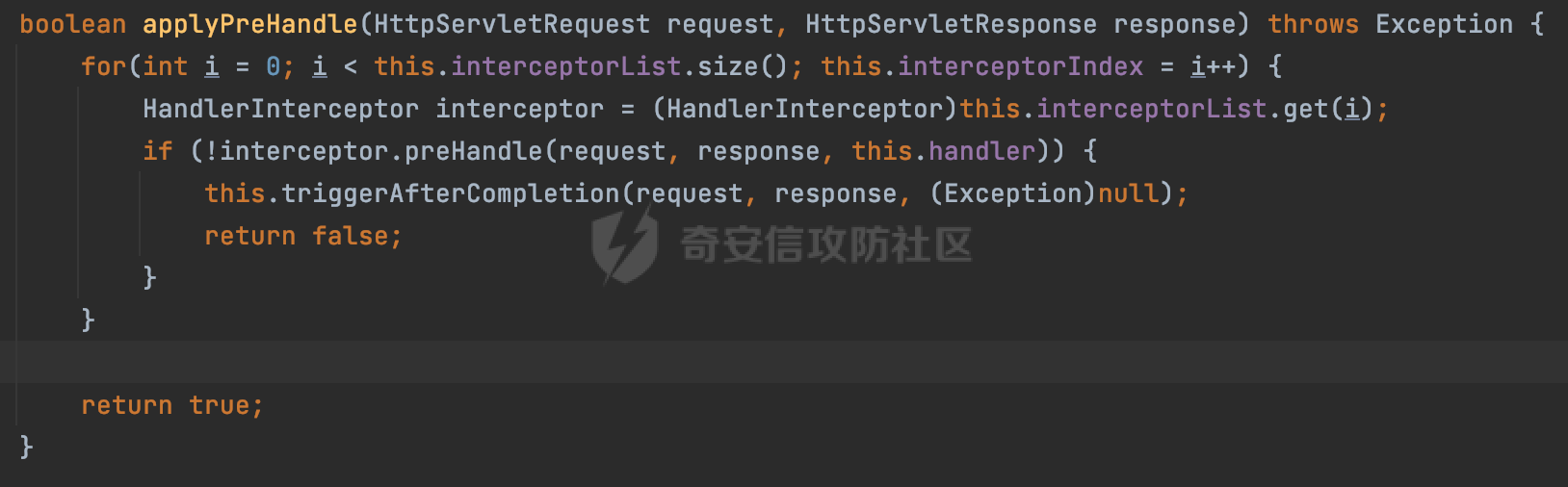 后续会执行具体Controller下的服务,以及执行HandlerInterceptor的PostHandle和AfterCompletion方法: 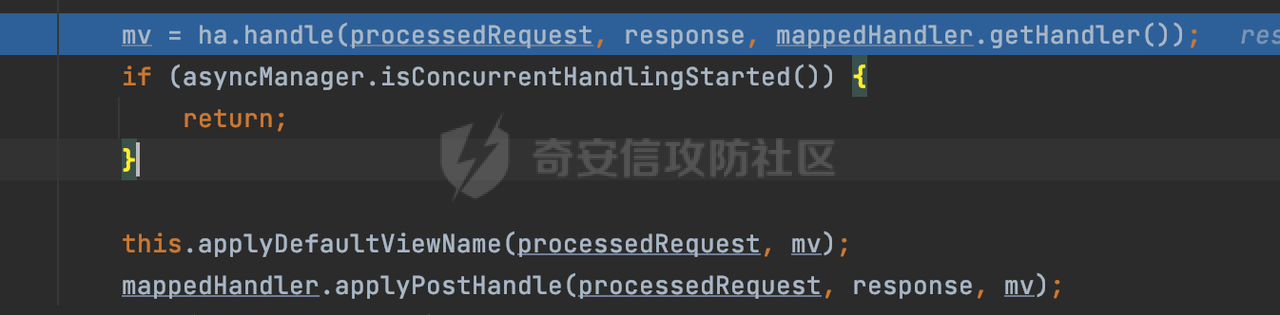 以上是拦截器Interceptor的大致执行流程。 ### 2.2.1 Interceptor的匹配逻辑 查看请求的URL路径与拦截器的具体匹配逻辑,主要是在org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.MappedInterceptor#matches方法进行处理: 首先会通过ServletRequestPathUtils.getCachedPath方法获取请求路径,如果当前的pathMatcher(一般情况下是AntPathMatcher)与默认的不相等,则将path转换成String类型: 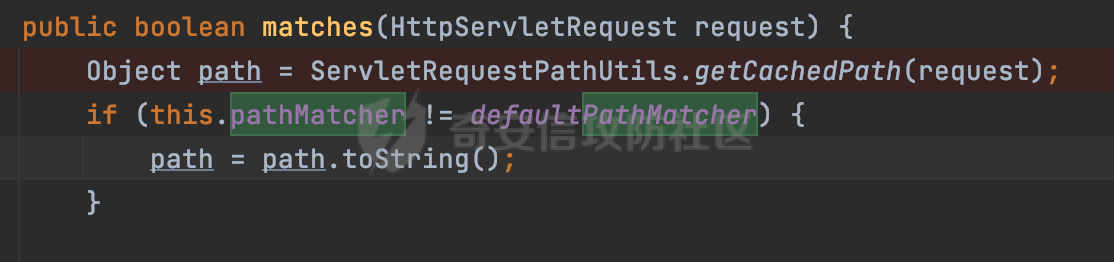 默认的匹配模式是AntPathMatcher:  然后会判断当前path的类型(高版本String的话默认使用PathPatternParser模式进行路由解析,isPathContainer为true):  然后就是对拦截器的excludePatterns和includePatterns调用PatternAdapter.match方法进行匹配,如果isPathContainer为true的话(说明当前Spring使用PathPatternParser模式进行路由解析),若this.pathPattern不为null(一般是AntPathMatcher),会调用PathPatternParser进行匹配,否则调用removeSemicolonContent方法对当前path进行规范化处理,然后调用AntPathMatcher进行匹配: 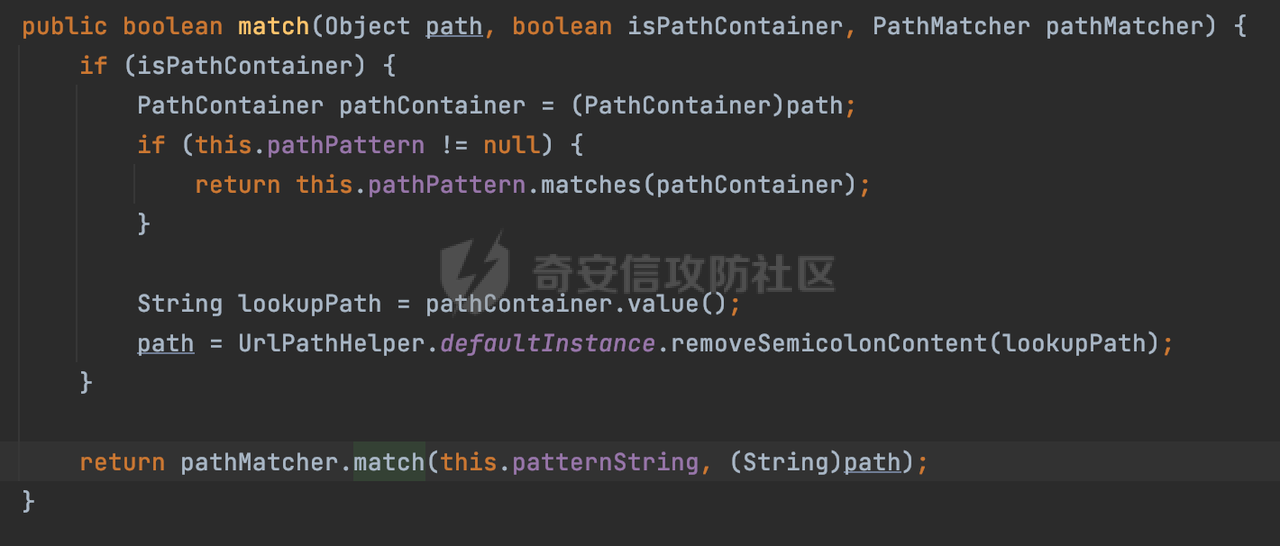 综上,Interceptor的匹配逻辑主要是根据情况,使用Spring内置的AntPathMatcher或PathPatternParser模式进行匹配。 0x03 潜在的安全问题 ============ 3.1 解析差异导致的Filter失效 ------------------- Springboot默认集成了tomcat进行解析,因为Filter是基于Servlet的,而不是Spring内部的解析逻辑。因为高版本Spring使用的是PathPattern进行路径匹配的,跟Filter的匹配逻辑有差异,在某些情况下可能会存在Filter失效的问题。 结合具体案例说明: 首先创建了一个InvalidRequestFilter,用于过滤用户请求路径上的特殊字符,若包含类似`../`、`;`等字符的话会返回400 Status: ```Java public class InvalidRequestFilter implements Filter { private static final List SEMICOLON = Collections.unmodifiableList(Arrays.asList(";", "%3b", "%3B")); private static final List BACKSLASH = Collections.unmodifiableList(Arrays.asList("\\", "%5c", "%5C")); private static final List FORWARDSLASH = Collections.unmodifiableList(Arrays.asList("%2f", "%2F")); private static final List PERIOD = Collections.unmodifiableList(Arrays.asList("%2e", "%2E")); @Override public void doFilter(ServletRequest ServletRequest, ServletResponse ServletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException { HttpServletRequest request = toHttp(ServletRequest); HttpServletResponse response = toHttp(ServletResponse); if (!(isValid(request.getRequestURI()) // user request string (not decoded) && isValid(request.getServletPath()) // decoded servlet part && isValid(request.getPathInfo()))){ response.sendError(400, "Invalid request"); } // 继续请求链 filterChain.doFilter(request,response); } private boolean isValid(String uri) { return !StringUtils.hasText(uri) || !this.containsSemicolon(uri) && !this.containsBackslash(uri) && !this.containsTraversal(uri); } private boolean containsTraversal(String uri) { return !(isNormalized(uri) && PERIOD.stream().noneMatch(uri::contains) && FORWARDSLASH.stream().noneMatch(uri::contains)); } private boolean containsSemicolon(String uri) { return SEMICOLON.stream().anyMatch(uri::contains); } private boolean containsBackslash(String uri) { return BACKSLASH.stream().anyMatch(uri::contains); } private boolean isNormalized(String path) { if (path == null) { return true; } for (int i = path.length(); i > 0;) { int slashIndex = path.lastIndexOf('/', i - 1); int gap = i - slashIndex; if (gap == 2 && path.charAt(slashIndex + 1) == '.') { return false; // ".", "/./" or "/." } if (gap == 3 && path.charAt(slashIndex + 1) == '.' && path.charAt(slashIndex + 2) == '.') { return false; } i = slashIndex; } return true; } public HttpServletRequest toHttp(ServletRequest request) { return (HttpServletRequest) request; } public HttpServletResponse toHttp(ServletResponse response) { return (HttpServletResponse) response; } } ``` 然后通过注入Bean的方式来注入Filter,该Filter对于/admin下的所有路径均会进行检查: ```Java @Configuration public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer { @Bean public FilterRegistrationBean FilterConfig() { FilterRegistrationBean registrationBean = new FilterRegistrationBean<>(); registrationBean.setFilter(new InvalidRequestFilter()); registrationBean.addUrlPatterns("/admin/*"); return registrationBean; } } ``` 假设Controller如下: ```Java @RestController @RequestMapping("/admin") public class AdminController { @RequestMapping(value = "/**", method = {RequestMethod.GET}) public String page() { return "admin page"; } } ``` 正常情况下,访问`/admin/info/page;`因为请求内容中包含`;`,会返回400 Status,说明该路径经过了Filter进行处理: 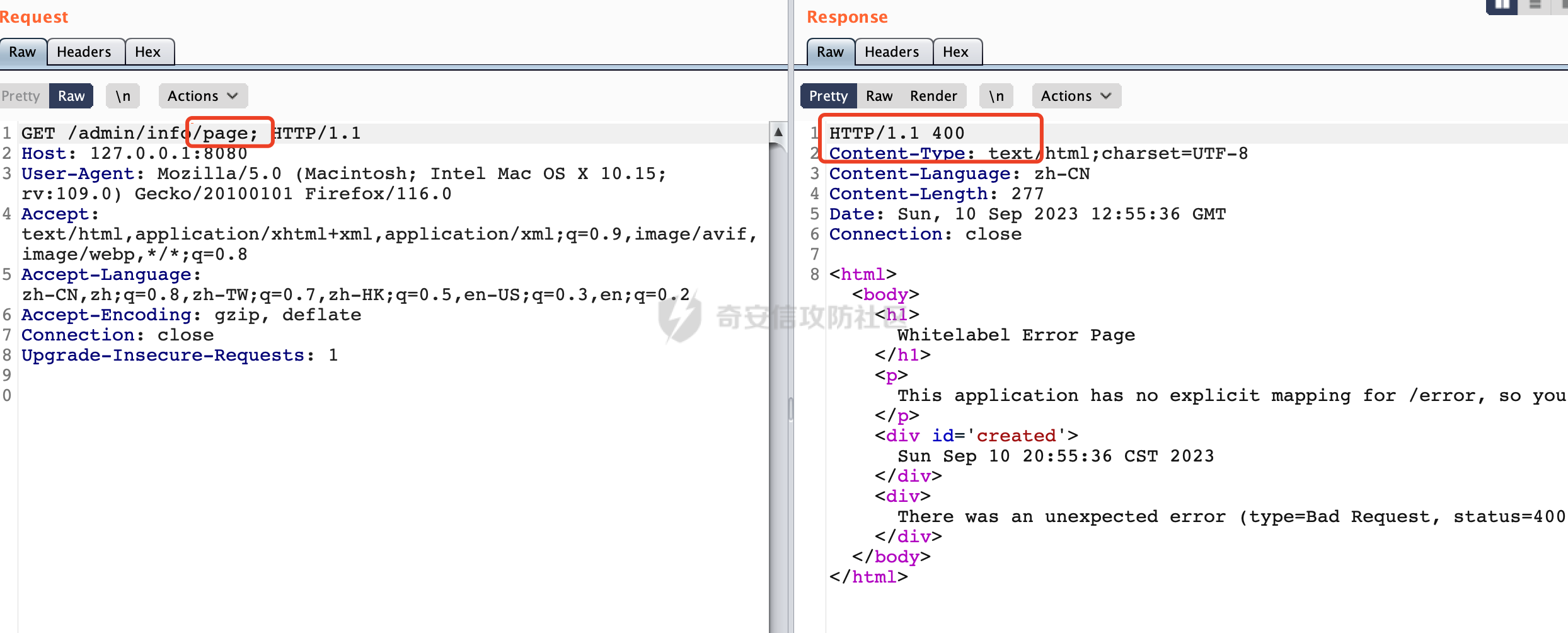 根据前面的分析,因为tomcat中,Filter在进行匹配时会对请求路径进行规划化处理,而PathPattern不会,利用解析差异即可达到绕过的效果,请求`/admin/../page;`可以发现不再返回400 status: 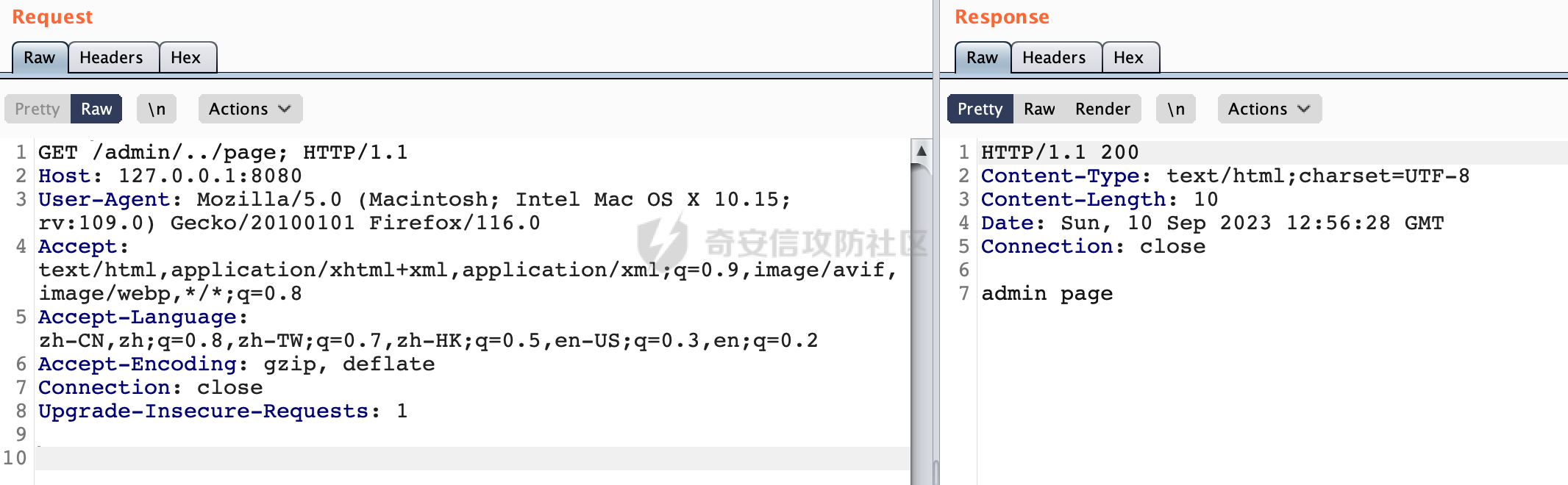 同样的,类似/admin/{param}等path在某种情况下可能也存在类似的问题: ```Java @RequestMapping("/{path:.*}") public String page(@PathVariable("path") String path) { return path; } ``` 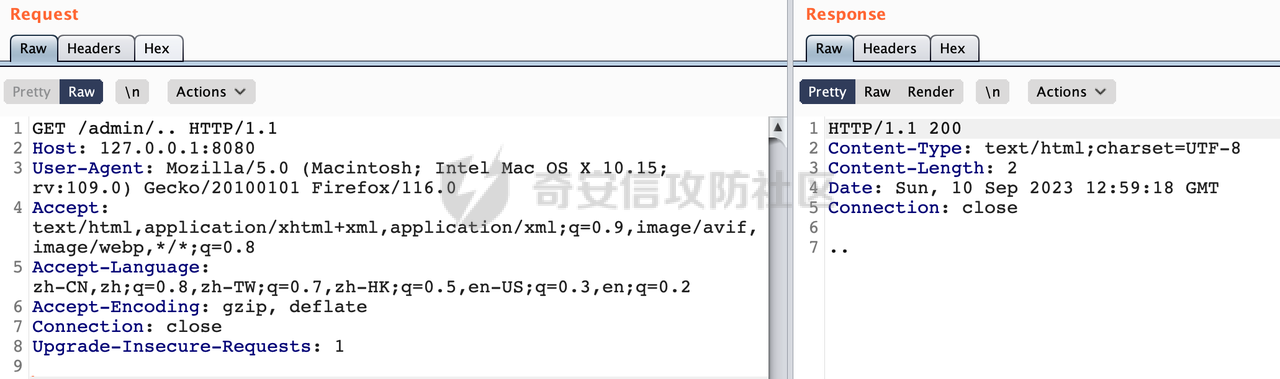 而对于Interceptor,其实之前也出现过类似的问题https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/reference/web/webmvc/mvc-config/interceptors.html : 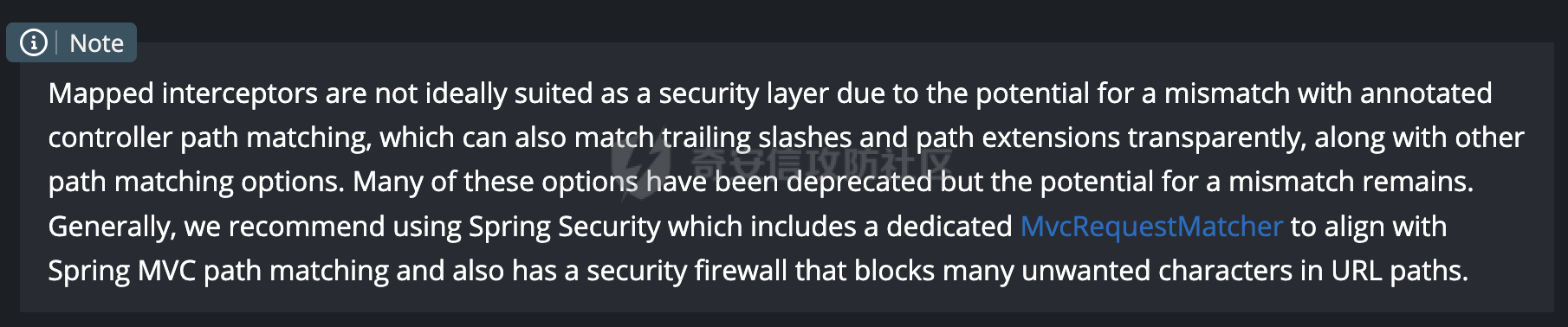 0x04 其他 ======= 实际上从PathPattern的解析模式就可以看到,一般情况下,`..`对Controller映射没有影响,而且Spring MVC对其的态度是中立的。并不会对它们采取任何特殊操作,它们与其他路径段一样,要么匹配要么不匹配,但不会改变请求的路径结构。同时,将Spring MVC匹配与Servlet映射进行对齐也是一件很困难的事,相比Servlet,Spring MVC具有更灵活的匹配行为。 考虑到上述的风险,Spring Security提供了一个 HTTP Firewall Filter,用于拒绝存在风险的的字符(因为配置的生效范围为`/*`。避免了上述问题)。所以,当希望通过filter实现访问控制/鉴权等安全需求时,现有的成熟框架无疑是更好的选择。
发表于 2023-09-25 09:00:00
阅读 ( 9539 )
分类:
代码审计
1 推荐
收藏
0 条评论
请先
登录
后评论
tkswifty
66 篇文章
×
发送私信
请先
登录
后发送私信
×
举报此文章
垃圾广告信息:
广告、推广、测试等内容
违规内容:
色情、暴力、血腥、敏感信息等内容
不友善内容:
人身攻击、挑衅辱骂、恶意行为
其他原因:
请补充说明
举报原因:
×
如果觉得我的文章对您有用,请随意打赏。你的支持将鼓励我继续创作!