问答
发起
提问
文章
攻防
活动
Toggle navigation
首页
(current)
问答
商城
实战攻防技术
活动
摸鱼办
搜索
登录
注册
浅谈Spring Security授权规则配置错误漏洞(CVE-2023-34035)
渗透测试
Spring官方发布了CVE-2023-34035,当应用程序使用了 requestMatchers(String) 和多个 Servlet(其中一个是 Spring MVC 的 DispatcherServlet)的情况下,Spring Security漏洞版本存在可能受到授权规则配置错误的影响。
0x01 漏洞描述 ========= Spring官方发布了CVE-2023-34035,当应用程序使用了 `requestMatchers(String)` 和多个 Servlet(其中一个是 Spring MVC 的 DispatcherServlet)的情况下,Spring Security漏洞版本存在可能受到授权规则配置错误的影响。  1.1 影响版本 -------- - Spring Security 5.8.0 to 5.8.4 - Spring Security 6.0.0 to 6.0.4 - Spring Security 6.1.0 to 6.1.1 1.2 利用条件 -------- - SpringMVC依赖存在于classpath - Spring Security在单个应用程序中对多个Servlet进行安全保护(其中一个是Spring MVC的DispatcherServlet) - 使用 requestMatchers(String) 来保护非Spring MVC端点 0x02 原理分析 ========= 以SpringSecurity 5.8.4为例,查看具体的原理。查看requestMatchers的具体实现: 首先根据是否存在SpringMVC,来选择不同的方式创建RequestMatcher。如果存在 SpringMVC的话,则创建MvcRequestMatcher,否则创建AntPathRequestMatcher:  根据漏洞利用条件,可以知道这里创建的是MvcRequestMatcher。 在SpringSecurity中,会通过org.springframework.security.web.access.intercept.RequestMatcherDelegatingAuthorizationManager#check 方法通过遍历请求匹配器列表,根据请求的 URL 和 HTTP 方法来决定哪个授权管理器应该处理该请求,并最终决定是否授予或拒绝对该请求的访问权限: 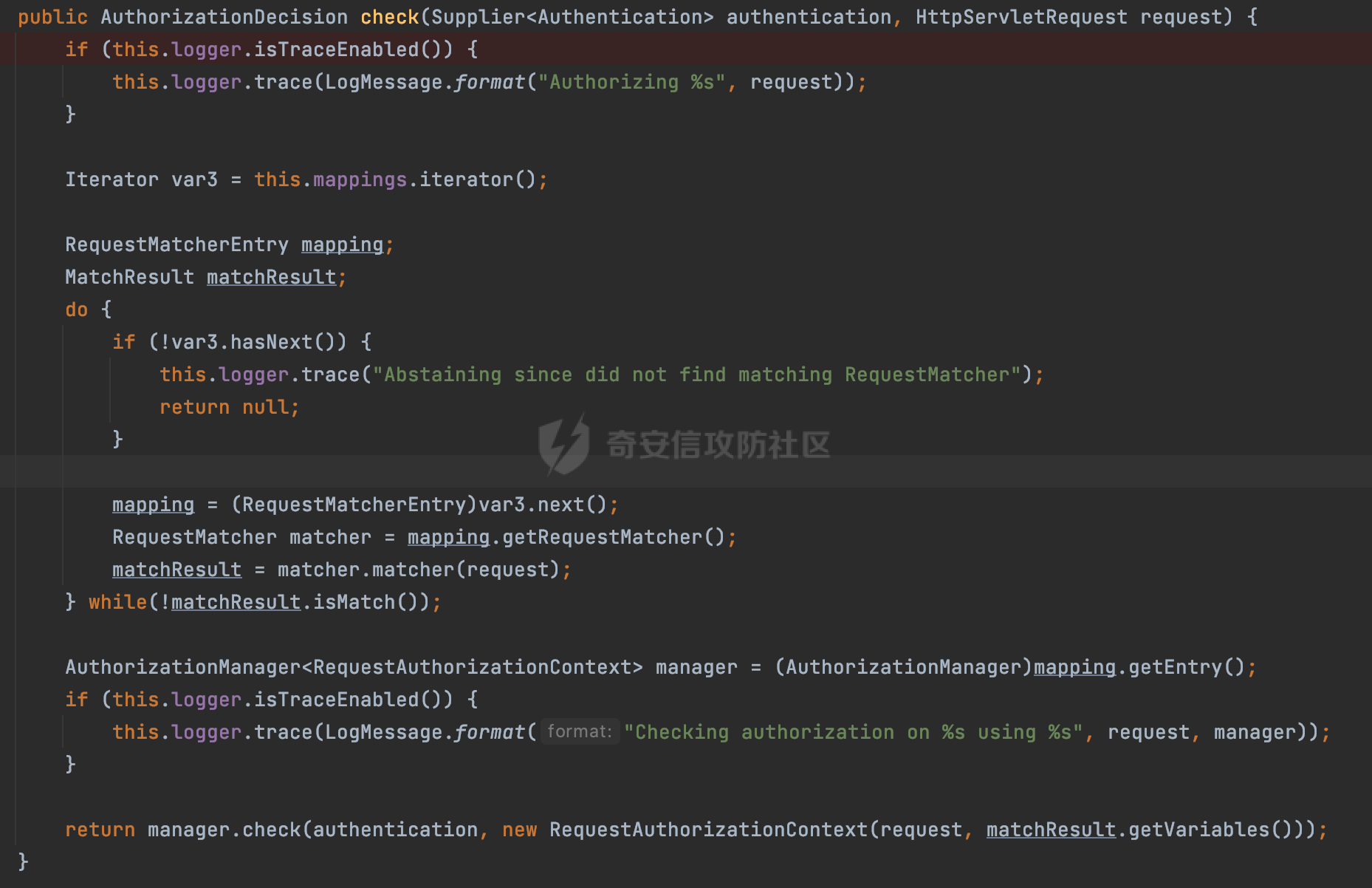 因为这里创建的是MvcRequestMatcher,所以直接查看org.springframework.security.web.servlet.util.matcher.MvcRequestMatcher#matcher的具体实现。 首先接收request对象,然后调用 this.notMatchMethodOrServletPath(request) 方法来检查当前请求的 HTTP 方法和 Servlet 路径是否与预定义的条件匹配。如果不匹配,将返回 MatchResult.notMatch() 表示不匹配:  否则调用`this.getMapping(request)` 方法获取请求的处理器映射对象(`MatchableHandlerMapping`)。如果不存在与当前请求相匹配的处理器映射,则调用 `this.defaultMatcher.matcher(request)` 方法,使用默认的请求匹配器来进行匹配,否则使用请求匹配器和预定义的 URL 模式来进行匹配,即调用 mapping.match(request, this.pattern) 方法: 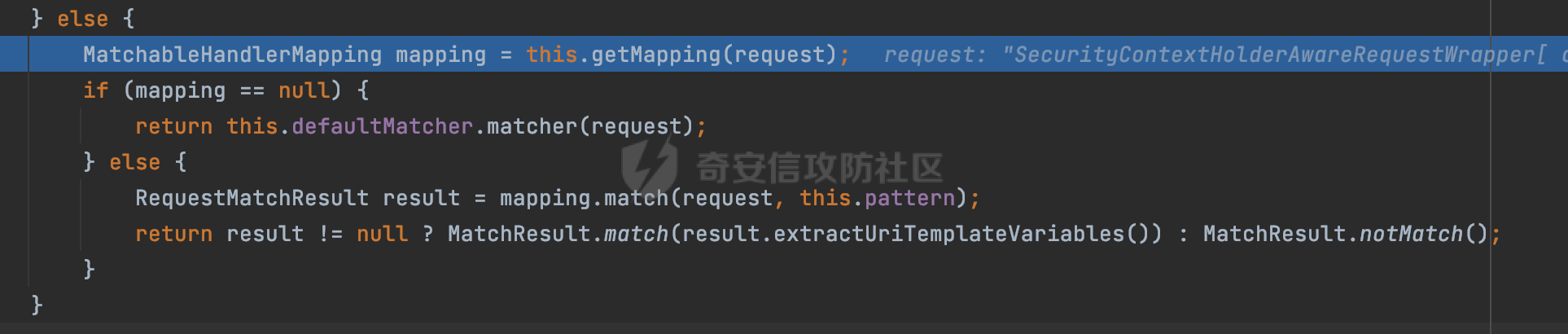 最后,根据匹配结果来返回相应的 MatchResult 对象。如果请求匹配成功,则返回 MatchResult.match(result.extractUriTemplateVariables()),其中 result.extractUriTemplateVariables() 用于提取匹配的路径变量。否则,返回 MatchResult.notMatch() 表示不匹配。 继续查看mapping.match(request, this.pattern) 的解析过程,这里会使用请求匹配器来进行请求匹配,得到匹配结果 `RequestMatchResult`:  在match方法中,首先获取当前请求的路径,并将其表示为 `PathContainer` 对象,然后通过PathPattern的方式来匹配当前请求的路径: 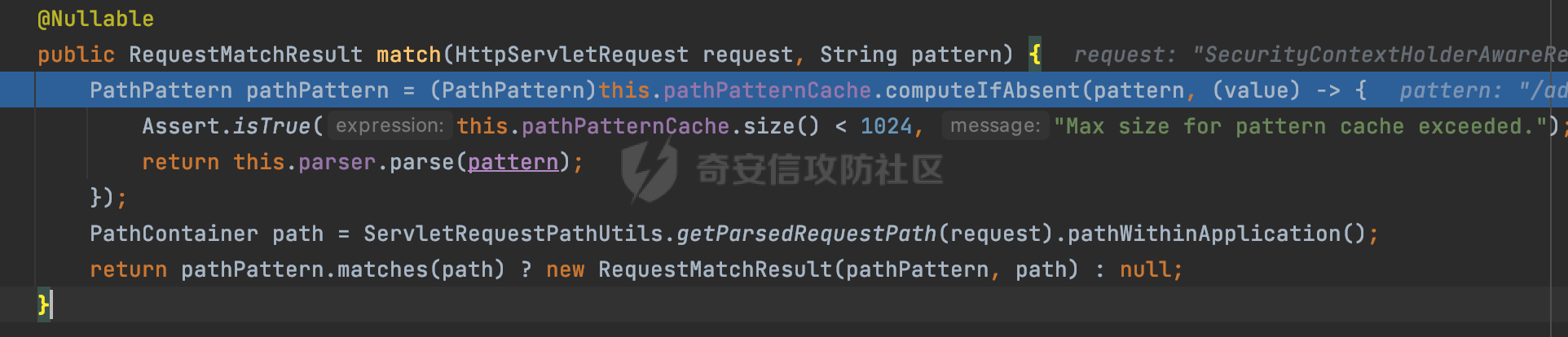 这里path的获取主要是从pathWithinApplication属性获取,主要是fullPath和contextPath属性决定的: 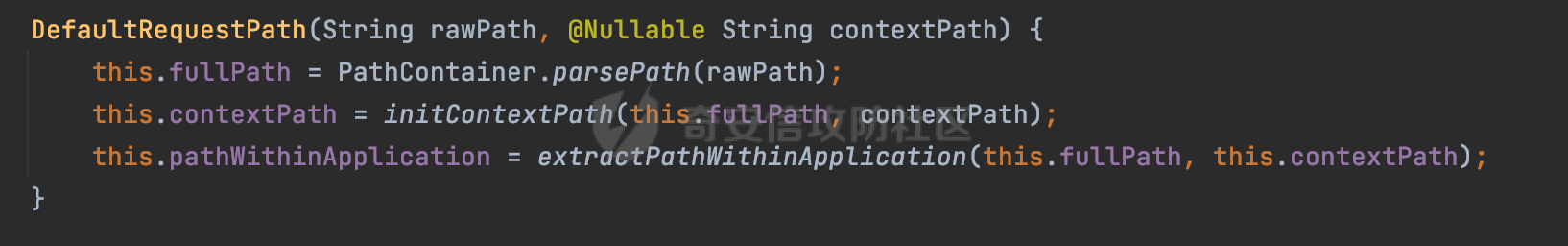  在处理contextPath属性时,servlet跟SpringMVC endpoint直接会有差异。主要在ServletRequestPathUtils.ServletRequestPath.parse中: 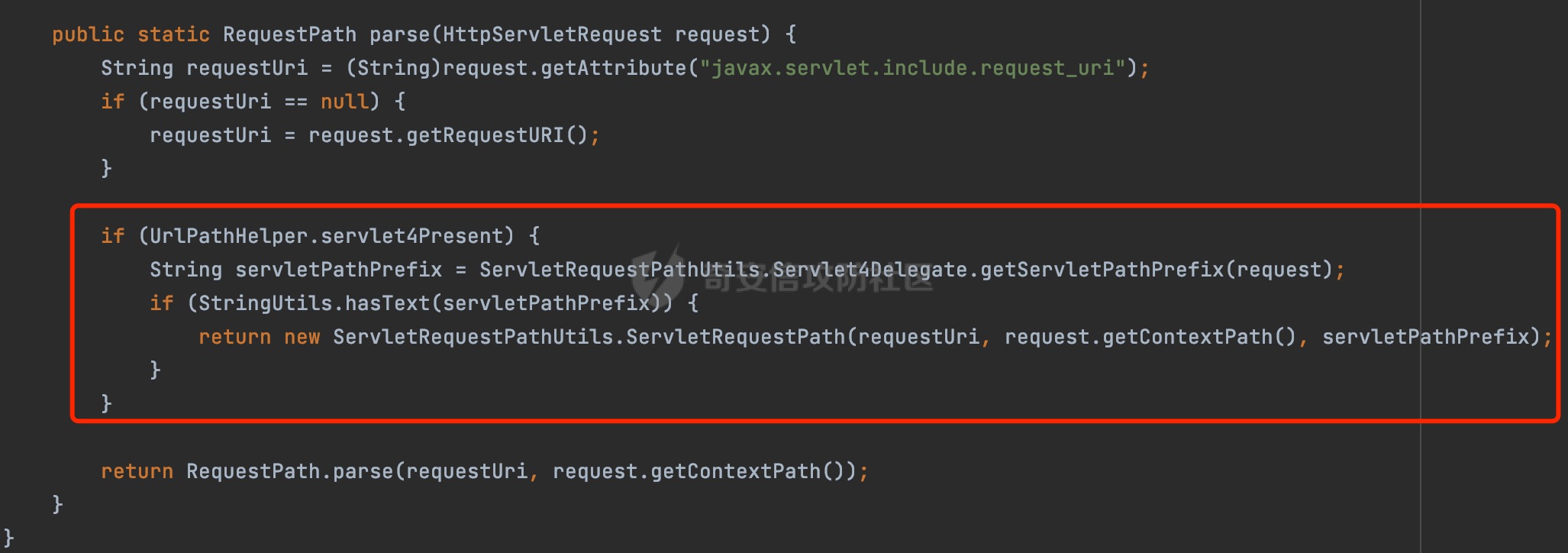 整个解析的过程比较复杂,通过一个实际的例子来说明: ```Java @Controller @RequestMapping("/admin/") public class AdminController { @GetMapping("/*") public String Manage(){ /*return "Manage page";*/ return "manage"; } } ``` 默认情况下,当通过请求/admin/page解析上述Controller时,在调用getServletPathPrefix方法时返回为null,此时contextPath属性为"":  返回的当前请求的路径为/admin/page。 而对于自定义Servlet来说: ```Java @WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/admin/*") public class UserServlet extends HttpServlet{ private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; @Override public void init() throws ServletException { } @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { System.out.println(req.getContextPath()); resp.getWriter().write("user page"); return ; } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { this.doGet(req, resp); } @Override public void destroy() { } } ``` 当通过请求/admin/page解析时,在调用getServletPathPrefix方法时返回为admin,此时contextPath属性为admin: 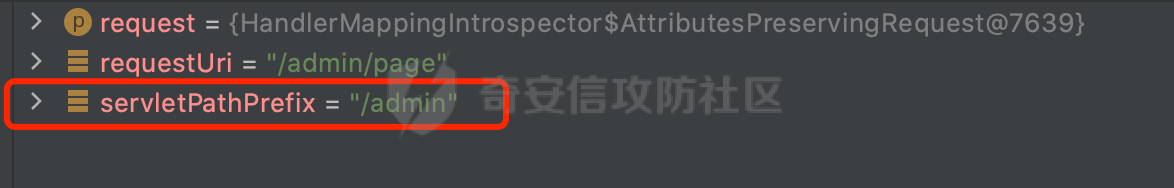 此时返回的当前请求的路径为/page:  但是对于SpringSecurity来说,理论上requestMatchers("/admin/\*\*").hasRole("ADMIN")都应该能覆盖上述两个资源。根据前面的分析,在match方法中,在获取当前请求的路径后,通过PathPattern的方式来匹配当前请求的路径时servlet明显会获取不到,这里存在解析差异导致意料之外的结果。 0x03 漏洞复现 ========= 根据前面的分析,主要是MvcRequestMatcher对于自定义Servlet端点的解析存在差异,导致Authorization规则可能与预期不一致的问题。以SpringSecurity 5.8.4为例,下面看一个具体的例子: 假设当前配置类的安全规则如下,对于admin路径下的资源要求用户具有"ADMIN"权限,对于manage路径下的资源要求用户具有"MANAGE"权限,而对于其他任意请求路径,则直接放行: ```Java @Configuration @EnableWebSecurity public class SpringSecurityConfig { @Bean public SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { http.authorizeHttpRequests().requestMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("ADMIN").requestMatchers("/manage/**").hasRole("MANAGE").anyRequest().permitAll(); return http.build(); } } ``` 其中应用注册的资源如下,首先是SpringMVC的endpoint: ```Java @Controller public class ManageController { @GetMapping("/manage/page") public String Manage(){ /*return "Manage page";*/ return "manage"; } } ``` 然后是通过@WebServlet注解自定义的UserServlet,这里urlPatterns定义成了`/admin/*`,代表以 "/admin/" 开头的所有 URL 请求都会由这个 Servlet 来处理: ```Java @WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/admin/*") public class UserServlet extends HttpServlet{ private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; @Override public void init() throws ServletException { } @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { resp.getWriter().write("user page"); return ; } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { this.doGet(req, resp); } @Override public void destroy() { } } ``` 按照前面SpringSecurity的配置,正常情况下这两个资源在未授权的情况下访问,预期应该都会返回403 status。 - SpringMVC endpoint(符合预期) 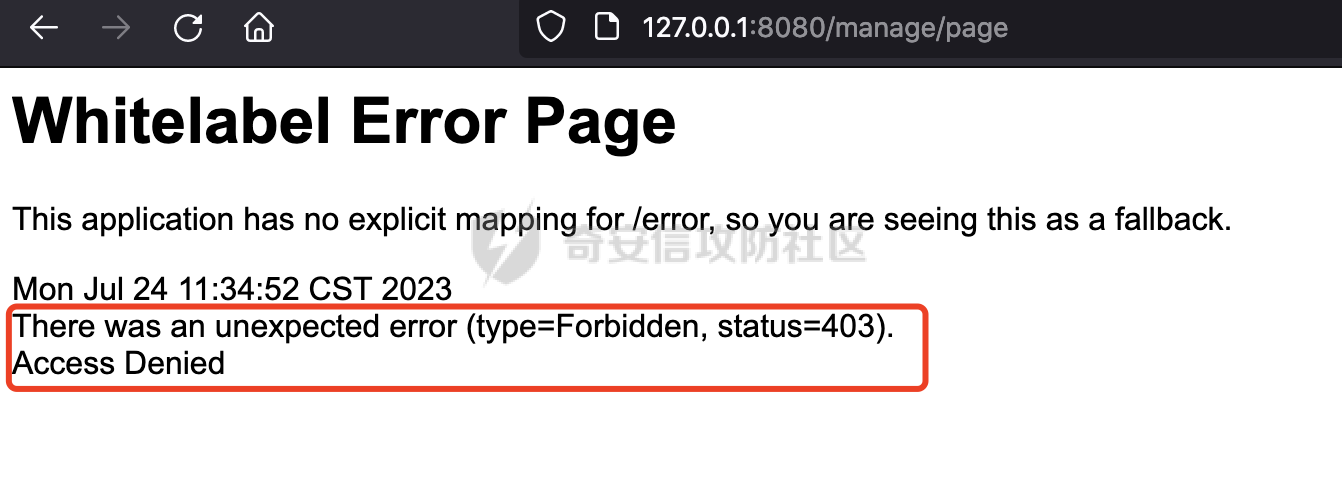 - 自定义Servlet(不符合预期) 可以看到这里对于`/admin/**`的防护,并没有生效: 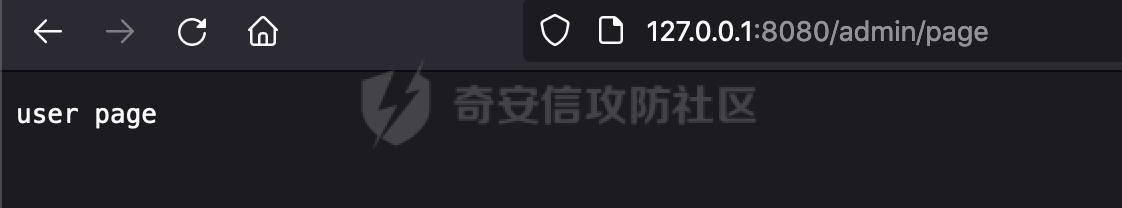 0x04 修复方式 ========= 通过对比SpringSecurity 5.8.4与5.8.5,可以发现关键的修复代码主要在`org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.AbstractRequestMatcherRegistry#requestMatchers`,该方法主要用于匹配对应的RequestMatcher。 - spring-security-config-5.8.4 这里主要是根据是否存在SpringMVC,来选择不同的方式创建RequestMatcher。如果存在 SpringMVC的话,则创建MvcRequestMatcher,否则创建AntPathRequestMatcher: 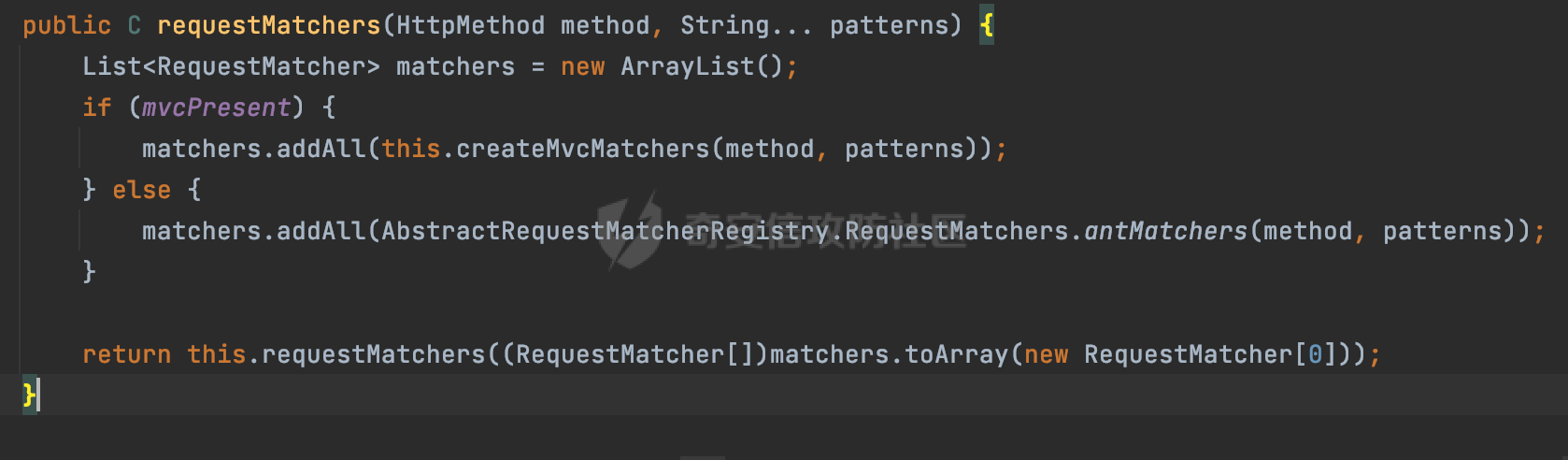 - spring-security-config-5.8.5 可以看到在5.8.5版本,对应的方法做了比较大的改动。首先检查是否存在SpringMVCmvcPresent 是否为 true以及应用程序是否使用了 WebApplicationContext,如果不满足条件会创建AntPathRequestMatcher。 如果存在SpringMVC并且使用了WebApplicationContext,则获取WebApplicationContext对象,并从中获取 ServletContext。如果 ServletContext 为null同样会创建AntPathRequestMatcher。 如果存在 ServletContext,则检查其中注册的 Servlet。如果不存在任何 Servlet 或没有 Spring MVC 的 DispatcherServlet,同样会创建AntPathRequestMatcher。 如果只有一个注册的 Servlet,并且是 Spring MVC 的 DispatcherServlet,那么将调用 this.createMvcMatchers(method, patterns) 方法创建 MVC 请求匹配器,也就是创建MvcRequestMatcher。如果包含多个Servlet的情况(registrations的size大于1),会抛出异常并打印相应的错误信息,对于非Spring MVC endpoint,请使用AntPathRequestMatcher进行对应的配置: ```Java This method cannot decide whether these patterns are Spring MVC patterns or not. If this endpoint is a Spring MVC endpoint, please use `requestMatchers(MvcRequestMatcher)`; otherwise, please use `requestMatchers(AntPathRequestMatcher)`. ```  查看具体的效果,同样是上面的例子,此时registrations的size大于1,会抛出对应的异常:   同样是上面的案例,当使用AntPathRequestMatcher处理/admin/\*\*请求后,自定义的Servlet安全防护符合预期: ```Java @Configuration @EnableWebSecurity public class SpringSecurityConfig { @Bean public SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { http.authorizeHttpRequests().requestMatchers(new AntPathRequestMatcher("/admin/**")).hasRole("ADMIN").requestMatchers("/manage/**").hasRole("MANAGE").anyRequest().permitAll(); return http.build(); } } ``` 
发表于 2023-08-11 09:00:01
阅读 ( 11298 )
分类:
漏洞分析
1 推荐
收藏
0 条评论
请先
登录
后评论
tkswifty
66 篇文章
×
发送私信
请先
登录
后发送私信
×
举报此文章
垃圾广告信息:
广告、推广、测试等内容
违规内容:
色情、暴力、血腥、敏感信息等内容
不友善内容:
人身攻击、挑衅辱骂、恶意行为
其他原因:
请补充说明
举报原因:
×
如果觉得我的文章对您有用,请随意打赏。你的支持将鼓励我继续创作!